django restframework框架二 认证
@(python之路)[django restframework框架二 认证]
django restframework框架二 认证
需求分析
为用户访问时,显示用户未登录
原始方法
urls.py
from django.conf.urls import url,include
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^api/(?P<version>\w+)', include("app01.urls")),
]
app01.urls.py
from django.conf.urls import url
from app01 import views
urlpatterns = [
url(r'user/$', views.UserView.as_view()),
# url(r'^auth/$', views.UserView.as_view()),
]
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.versioning import URLPathVersioning,QueryParameterVersioning
class UserView(APIView):
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
token = request.query_params.get("token")
if not token:
return HttpResponse("未认证")
print(request.version)
return HttpResponse("get")
def post(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
return HttpResponse("post")
def put(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
return HttpResponse("put")
def delete(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
return HttpResponse("delete")
利用rest framework方法去做
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.versioning import URLPathVersioning,QueryParameterVersioning
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication
from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed
class MyAuthtication(BaseAuthentication):
def authenticate(self, request):
token = request.query_params.get("token")
if not token:
raise AuthenticationFailed("认证失败")
return ("小公子","www.xxxx.com")
class UserView(APIView):
authentication_classes = [MyAuthtication,]
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
return HttpResponse("get")
def post(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
return HttpResponse("post")
def put(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
return HttpResponse("put")
def delete(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
return HttpResponse("delete")
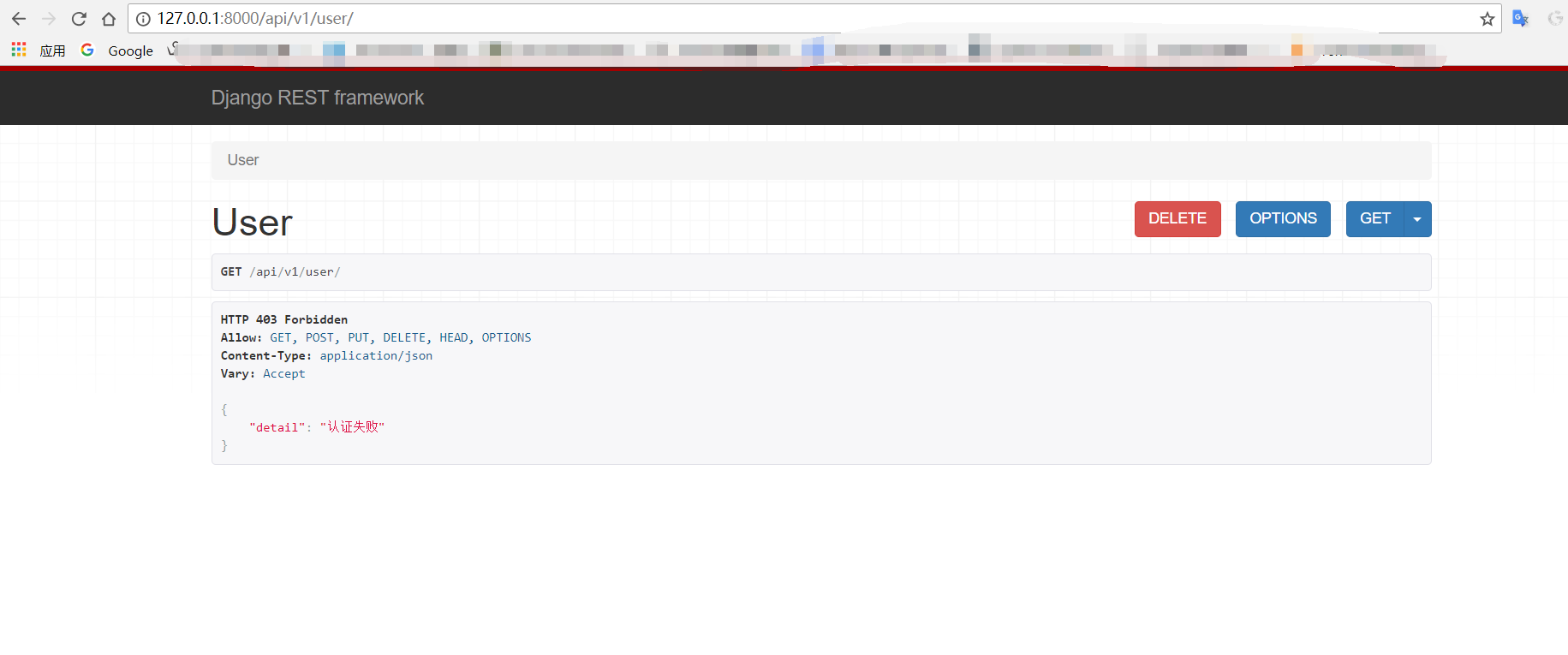

源码分析
我们已经知道,认证是封装在了新的reqeust里边了。忘记点我
def initialize_request(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
parser_context = self.get_parser_context(request)
return Request(
request,
parsers=self.get_parsers(),
authenticators=self.get_authenticators(), [MyAuthtication,]对象
negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(),
parser_context=parser_context
)
我们可以看看认证具体做了什么authenticators
1
def get_authenticators(self):
return [auth() for auth in self.authentication_classes]
2
self.authentication_classes实例化所有的认证
class APIView(View):
……
authentication_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES
……
我们主要关注的是这里。当我们在自己的views.py中定义好了,他就会优先查找views.py中的了。
3
我们关注一下这个认证传递到了哪里了
def initialize_request(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
parser_context = self.get_parser_context(request)
return Request(
request,
parsers=self.get_parsers(),
authenticators=self.get_authenticators(),
negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(),
parser_context=parser_context
)
从上边我们知道,他首先封装到了request里边了,传入的地方在这里
class Request(object):
def __init__(self, request, parsers=None, authenticators=None,
negotiator=None, parser_context=None):
assert isinstance(request, HttpRequest), (
'The `request` argument must be an instance of '
'`django.http.HttpRequest`, not `{}.{}`.'
.format(request.__class__.__module__, request.__class__.__name__)
)
self._request = request
self.parsers = parsers or ()
self.authenticators = authenticators or () ####### 就是这里[MyAuthentcators]
self.negotiator = negotiator or self._default_negotiator()
self.parser_context = parser_context
self._data = Empty
self._files = Empty
self._full_data = Empty
self._content_type = Empty
self._stream = Empty
上述只是认证的封装真正的处理在这里dispatch
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
self.args = args
self.kwargs = kwargs
request = self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs)
self.request = request
self.headers = self.default_response_headers # deprecate?
try:
self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs)
if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names:
handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(),
self.http_method_not_allowed)
else:
handler = self.http_method_not_allowed
response = handler(request, *args, **kwargs)
except Exception as exc:
response = self.handle_exception(exc)
self.response = self.finalize_response(request, response,
这些处理都在self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs)这里
def initial(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
self.format_kwarg = self.get_format_suffix(**kwargs)
neg = self.perform_content_negotiation(request)
request.accepted_renderer, request.accepted_media_type = neg
version, scheme = self.determine_version(request, *args, **kwargs)
request.version, request.versioning_scheme = version, scheme
# Ensure that the incoming request is permitted
# 处理认证
self.perform_authentication(request)
self.check_permissions(request)
self.check_throttles(request)
self.perform_authentication(request)
def perform_authentication(self, request):
request.user
我们猜测request.user会触发认证对象列表。他们应该回有关系。
仅仅猜测是不好使的我们需要证明
def user(self):
if not hasattr(self, '_user'):
with wrap_attributeerrors():
self._authenticate()
return self._user
因为没有hasattr(self, '_user'):所以他会走
def _authenticate(self):
for authenticator in self.authenticators:
try:
user_auth_tuple = authenticator.authenticate(self)
except exceptions.APIException:
self._not_authenticated()
raise
if user_auth_tuple is not None:
self._authenticator = authenticator
self.user, self.auth = user_auth_tuple
return
self._not_authenticated()
我们需要关注的是self.authenticators
class Request(object):
def __init__(self, request, parsers=None, authenticators=None,
negotiator=None, parser_context=None):
assert isinstance(request, HttpRequest), (
'The `request` argument must be an instance of '
'`django.http.HttpRequest`, not `{}.{}`.'
.format(request.__class__.__module__, request.__class__.__name__)
)
self._request = request
self.parsers = parsers or ()
self.authenticators = authenticators or ()
self.negotiator = negotiator or self._default_negotiator()
self.parser_context = parser_context
self._data = Empty
self._files = Empty
self._full_data = Empty
self._content_type = Empty
self._stream = Empty
if self.parser_context is None:
self.parser_context = {}
self.parser_context['request'] = self
self.parser_context['encoding'] = request.encoding or settings.DEFAULT_CHARSET
force_user = getattr(request, '_force_auth_user', None)
force_token = getattr(request, '_force_auth_token', None)
if force_user is not None or force_token is not None:
forced_auth = ForcedAuthentication(force_user, force_token)
self.authenticators = (forced_auth,)
他就是原来的self.authenticators,也就是说我们自己的[MyAuthtion对象,]
所以他会循环我们的[MyAuthtion对象,],所以 user_auth_tuple = authenticator.authenticate(self)这里就会返回一个元组。下面捕获异常,
为什么元组返回两个元组
def _authenticate(self):
for authenticator in self.authenticators:
try:
user_auth_tuple = authenticator.authenticate(self)
except exceptions.APIException:
self._not_authenticated()
raise
if user_auth_tuple is not None:
self._authenticator = authenticator
self.user, self.auth = user_auth_tuple
return
self._not_authenticated()
返回后一个给self.user,一个给self.auth。
所以,返回有三种情况。
第一种:
raise AuthenticationFailed("认证失败")
抛出异常,认证失败
第二种:
return ("xiaogozi",'123123')
返回元组,认证成功
第三种:
返回None
匿名用户登陆
如果不是not None,self._authenticator = authenticator
def _not_authenticated(self):
self._authenticator = None
# 如果我们配置UNAUTHENTICATED_USER;就会执行
# self.user
if api_settings.UNAUTHENTICATED_USER:
self.user = api_settings.UNAUTHENTICATED_USER()
else:
self.user = None
# 如果我们配置UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN
# 就会执行self.auth
if api_settings.UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN:
self.auth = api_settings.UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN()
else:
self.auth = None
settings.py添加
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_VERSIONING_CLASS":"rest_framework.versioning.URLPathVersioning",
"ALLOWED_VERSIONS":["v1","v2"],
"UNAUTHENTICATED_USER":None, # 允许用户匿名登陆
"UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN":None, #
}
也可以这样写
"UNAUTHENTICATED_USER":lambda:None, # 允许用户匿名登陆
"UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN":lambda:None, #
推荐用第一种方式
当我们自己写的MyAuthtication返回(user,auth)的时候,我们认为认证成功,
并将元组分别赋值给request.user/request.auth;
raise AuthenticationFailed("认证失败") 此时认证失败;
返回None,表示匿名用户。
认证与数据库关联
我们返回的是用户和认证信息,这种信息我们最好写在数据库中;
整理:
urls.py
from django.conf.urls import url
from app01 import views
urlpatterns = [
url(r'user/$', views.UserView.as_view()),
url(r'auth/$', views.Auth.as_view()),
# url(r'^auth/$', views.UserView.as_view()),
]
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
from django.http import JsonResponse
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.versioning import URLPathVersioning,QueryParameterVersioning
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication
from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed
from app01 import models
class MyAuthtication(BaseAuthentication):
def authenticate(self, request):
token = request.query_params.get("token")
if not token:
raise AuthenticationFailed("认证失败")
return ("小公子","www.xxxx.com")
class UserView(APIView):
authentication_classes = [MyAuthtication,]
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
self.dispatch
return HttpResponse("get")
def post(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
return HttpResponse("post")
def put(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
return HttpResponse("put")
def delete(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
return HttpResponse("delete")
class Auth(APIView):
def post(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
response = {"code":1000}
user = request.data.get("username")
pwd = request.data.get("password")
obj = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=user,password=pwd).first()
if not obj:
response["code"] = 1001
response["msg"] = "用户名密码错误"
return JsonResponse(responsejson_dumps_params={"ensure_ascii":False})
import uuid
token = str(uuid.uuid4())
models.UserInfo.objects.update_or_create(user=obj,defaults={"token":token})
response["token"] = token
return JsonResponse(responsejson_dumps_params={"ensure_ascii":False})
models.py
from django.db import models
class UserInfo(models.Model):
username = models.CharField(max_length=32)
password = models.CharField(max_length=64)
class UserToken(models.Model):
user = models.OneToOneField("UserInfo")
token = models.CharField(max_length=64)
或者:
我们把认证这里拿出来,形成 一个单独的文件例如:在app01下新建一个目录utils。
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication
from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed
from app01 import models
class TokenAuthtication(BaseAuthentication):
def authenticate(self, request):
"""
:param request:
:return:
(user,auth) 表示认证成功,并将元组分别复制给request.user/request.auth
raise AuthenticationFailed('认证失败') 表示认证失败
None, 表示匿名用户
"""
token = request.query_params.get('token')
if not token:
raise AuthenticationFailed('用户Token未携带')
token_obj = models.UserToken.objects.filter(token=token).first()
if not token_obj:
raise AuthenticationFailed('token已失效或错误')
return (token_obj.user.username,token_obj)
只需要在settings.py添加一行;
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES':['app01.utils.auth.TokenAuthtication',]
}
这样就将验证添加到全局,访问所有都需要token认证;
如果有的页面不需要我们只需要在那个类下添加:
class AuthView(APIView):
authentication_classes = []
……
这样这个AuthView就不需要验证。
补充
class MyAuthtication(BaseAuthentication):
pass
我们继承的是BaseAuthentication:
class BaseAuthentication(object):
def authenticate(self, request):
raise NotImplementedError(".authenticate() must be overridden.")
# 如果认证失败可以返回响应头;
def authenticate_header(self, request):
pass
其他方式认证
class CSRFCheck(CsrfViewMiddleware)
class BasicAuthentication(BaseAuthentication):
class SessionAuthentication(BaseAuthentication):
class TokenAuthentication(BaseAuthentication)
class RemoteUserAuthentication(BaseAuthentication)



