异常处理之动手动脑
异常处理
1.观察代码,了解异常处理机制
import javax.swing.*; class AboutException { public static void main(String[] a) { int i=1, j=0,k; // k=i/j; try { k = i/j; // Causes division-by-zero exception throw new Exception("Hello.Exception!"); } catch ( ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("被0除. "+ e.getMessage()); } catch (Exception e) { if (e instanceof ArithmeticException) System.out.println("被0除"); else { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } finally//用于善后的代码 { JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(null,"OK"); } } }
输出:被0除. / by zero
从中我们可以看出,在try中一共有两个异常,但最终只执行了ArithmeticException异常,这代表他的机制并不是都要执行,而是谁先出异常,就先去catch捕捉那个异常,而我们对try。。catch进行注释后,发现finally都会执行。

jdk中与异常相关的类:
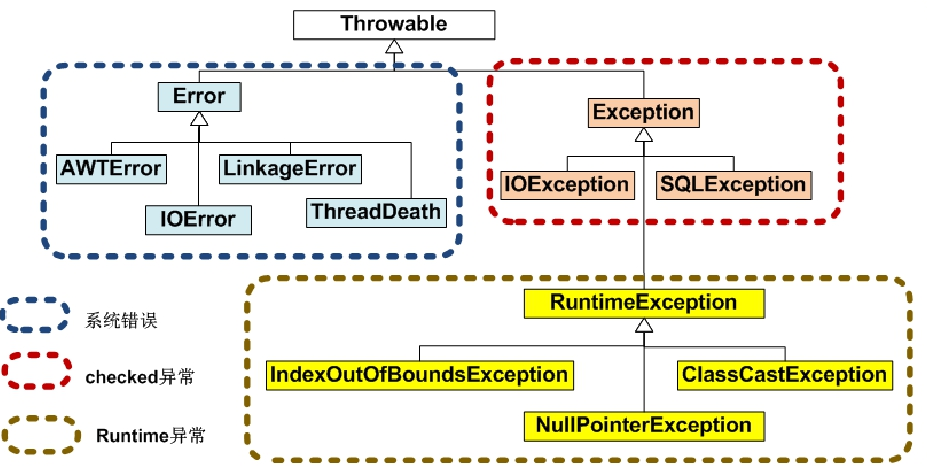
二,浮点数的异常
public class ThrowDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { try { double data = 100 / 0.0; System.out.println("浮点数除以零:" + data); if(String.valueOf(data).equals("Infinity")) { System.out.println("In Here" ); throw new ArithmeticException("除零异常"); } } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println(e); } } }
输出:
浮点数除以零:Infinity
In Here
java.lang.ArithmeticException: 除零异常
为啥会输出Infinity呢?
因为浮点数在除0时,他不是把他当做0而是看做是最小值,因此得出的结果为极大值。
三、异常“多态”的特性

四、多层异常的捕获
public class CatchWho { public static void main(String[] args) { try { try { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); } throw new ArithmeticException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); } } }
输出:
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException/内层try-catch
发生ArithmeticException
当内层的try抛出异常,会被最近的符合要求的catch捕获,之后又抛出一个新的异常,再被离他最近的符合要求的catch捕获,因此输出如上
再看接下来的多层异常捕获
public class CatchWho2 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { try { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); } throw new ArithmeticException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); } } }
输出:
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException/外层try-catch
在最内层的异常抛出后,内层没有可以接受异常的catch,就跑到外层的try结构里,发现也没有,就跳出外层的try,被外层的catch接受,输出上面的内容。
五、多层嵌套导致finaly执行顺序的差异
public class EmbededFinally { public static void main(String args[]) { int result; try { System.out.println("in Level 1"); //result=100/0; //Level 1 try { System.out.println("in Level 2"); //result=100/0; //Level 2 try { System.out.println("in Level 3"); result=100/0; //Level 3 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 3:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 3 finally"); } result=100/0; //Level 2 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 2:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 2 finally"); } result = 100 / 0; //level 1 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 1:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 1 finally"); } } }
输出:
in Level 1
in Level 2
in Level 3
Level 3:class java.lang.ArithmeticException
In Level 3 finally
Level 2:class java.lang.ArithmeticException
In Level 2 finally
Level 1:class java.lang.ArithmeticException
In Level 1 finally
通过不同的异常导致有些try语句块未能执行,其原因在于发生异常的try块外有无final语句,如果有就会执行,那么凡是在发生异常的try语句块里的finaly语句将都不会执行。

话说finaly语句块一定会执行吗?
public class SystemExitAndFinally { public static void main(String[] args) { try{ System.out.println("in main"); throw new Exception("Exception is thrown in main"); //System.exit(0); } catch(Exception e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); System.exit(0); } finally { System.out.println("in finally"); } } }
输出:
in main
Exception is thrown in main
当发生异常后,catch捕获后自动结束程序,那么之后的finaly语句块就不会被执行了。


// UsingExceptions.java // Demonstrating the getMessage and printStackTrace // methods inherited into all exception classes. public class PrintExceptionStack { public static void main( String args[] ) { try { method1(); } catch ( Exception e ) { System.err.println( e.getMessage() + "\n" ); e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void method1() throws Exception { method2(); } public static void method2() throws Exception { method3(); } public static void method3() throws Exception { throw new Exception( "Exception thrown in method3" ); } }
输出:
Exception thrown in method3
java.lang.Exception: Exception thrown in method3
at PrintExceptionStack.method3(PrintExceptionStack.java:28)
at PrintExceptionStack.method2(PrintExceptionStack.java:23)
at PrintExceptionStack.method1(PrintExceptionStack.java:18)
at PrintExceptionStack.main(PrintExceptionStack.java:8)
通过printStackTrace()打印方法调用堆栈,我们可以跟踪到程序的出错来源和传播路径
六、自定义异常
package com.test1; import java.util.Scanner; //自定义的异常 class MyException extends Exception { public MyException(String Message) { super(Message); } public MyException(String message, Throwable cause) { super(message, cause); } public MyException( Throwable cause) { super(cause); } } class Sanj { private double x,y,z; public Sanj(double x, double y, double z) { super(); this.x = x; this.y = y; this.z = z; } //调用异常的方法 public void getArea() throws Exception { int flag=0; if(this.x+this.y<=this.z||Math.abs(this.x-this.y)>=this.z) { flag=1; } if(flag==1) { throw new MyException("NotSanjiaoException"); } else { double sum=(this.x+this.y+this.z)*1.0/2; double ans=Math.sqrt(sum*(sum-this.x)*(sum-this.y)*(sum-this.z)); System.out.println("三角形面积为:"+ans); } } public void showInfo() throws Exception { int flag=0; if(this.x+this.y<=this.z||Math.abs(this.x-this.y)>=this.z) { flag=1; } if(flag==1) { throw new MyException("NotSanjiaoException"); } else { System.out.println("三边长分别是:"+this.x+" "+this.y+" "+this.z); } } } public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub double a,b,c; Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入三角形三个边(整数):"); a=in.nextDouble(); b=in.nextDouble(); c=in.nextDouble(); Sanj s=new Sanj(a,b,c); //try-catch语句块 try { s.getArea(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } try { s.showInfo(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } }
个人总结:
遇到异常最多的就是在写文件的时候会自动抛出许多受控异常,这也提醒这我们要多考虑一些方面,用户并不会按照你给的方向去测试,我们应该改做更多的异常处理,尽可能的完善程序,是自己的程序更加的健壮。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号