序列化和反序列化实现
1. 什么是序列化?
程序员在编写应用程序的时候往往需要将程序的某些数据存储在内存中,然后将其写入文件或是将其传输到网络中的另一台计算机上以实现通讯。这个将程序数据转换成能被存储并传输的格式的过程被称为序列化(serialization),而它的逆过程被称为反序列化(deserialization)。
简单来说,序列化就是将对象实例的状态转换为可保持或传输的格式的过程。与序列化相对的是反序列化,它根据流重构对象。这两个过程结合起来,可以轻松地存储和传输数据。
序列化:将对象变成字节流的形式传出去。
反序列化:从字节流恢复成原来的对象。
2. 序列化实现
可以通过将对象转换成json、xml和二进制流的方式实现序列化,鉴于json和xml在不同编程语言中其组包、解包的API接口实现方法的不同,我决定采用通用的二进制流的方式实现序列化。
2.1 类图设计

3. 各个组件代码实现
3.1 元组实现
该元组可以接纳我们自定义的任意类型
数据类型定义:
enum class Type { Invalid, Boolean, Character, Int8, Int16, Int32, Int64, Float, Double, String };
联合体InnerValue定义:联合体的优点在于所有的值共享一篇存储空间,因此不会引起额外的空间存储消耗
union InnerValue { bool booleanValue; char characterValue; int8_t int8Value; int16_t int16Value; int32_t int32Value; int64_t int64Value; float floatValue; double doubleValue; };
Values类实现:
#include <vector> class Values : public std::vector<Value> { public: Values() = default; Values(std::initializer_list<Value> list) : std::vector<Value>(list) { } Value& operator[](size_t index) { return std::vector<Value>::operator[](index); } const Value& operator[](size_t index) const { return std::vector<Value>::operator[](index); } };
异常类TypeMismatchException实现:
#ifdef WIN32 #define NOEXCEPT #else #define NOEXCEPT noexcept #endif class TypeMismatchException : public std::exception { public: TypeMismatchException(const std::string& message) : _message(message){} const char* what() const NOEXCEPT override { return _message.c_str(); } private: std::string _message; };
元组类的使用:
Values list = {5, "hello"};
for (Value value : list)
{
std::cout << value << " ";
}
3.2 ByteArray类实现
该类主要扩展字节的基本操作
class ByteArray : public std::vector<char> { public: ByteArray() = default; ByteArray(int32_t size) : std::vector<char>(size) { } ByteArray(const char *buffer, int32_t size) : std::vector<char>(buffer, buffer + size) { } ByteArray(const std::string &str) : std::vector<char>(str.size()) { memcpy(data(), str.c_str(), str.size()); } std::string ToStdString() const { std::string result(this->cbegin(), this->cend()); return result; } ByteArray &Concat(const ByteArray &buffer2) { size_t oldSize = size(); size_t newSize = oldSize + buffer2.size(); resize(newSize); memcpy(this->data() + oldSize, buffer2.data(), buffer2.size()); return *this; } ByteArray operator+(const ByteArray &buffer2) const { ByteArray buffer1(this->size() + buffer2.size()); memcpy(buffer1.data(), this->data(), this->size()); memcpy(buffer1.data() + this->size(), buffer2.data(), buffer2.size()); return buffer1; } };
3.3 ByteArrayReader和ByteArrayWriter类实现
ByteArrayReader:实现二进制流到指定类型T的转换,即将ByteArrray写入到类型Tbuff中
ByteArrayWriter:将T类型的Buff写到ByteArray中
具体代码实现如下:

#pragma once #include "ByteArray.h" #include <stdint.h> class IODevice { public: enum class SeekMode { Set, Forward, Backward }; }; class ByteArrayWriter : public IODevice { public: ByteArrayWriter() { } template <class T> int32_t Write(const T* buffer, int32_t size) { int32_t nWriteSize = sizeof(T) * size; ByteArray buffer2((const char *)buffer, nWriteSize); _bytes.Concat(buffer2); return nWriteSize; } template <class T> int32_t Write(const T& value) { return Write((T *)&value, 1); } int32_t Write(const ByteArray& byteArray) { _bytes.Concat(byteArray); return byteArray.size(); } ByteArray ToByteArray() const{ return _bytes; } int32_t Tell() const{ return _bytes.size(); } private: ByteArray _bytes; }; class ByteArrayReader : public IODevice { public: ByteArrayReader(const ByteArray& byteArray): _bytes(byteArray), _pos(0) { } template <class T> int32_t Read(T *buff, int32_t count) { int nSizeToRead = sizeof(T) * count; if(_pos >= _bytes.size()) { return 0; } else if (_bytes.size() - _pos < nSizeToRead) { nSizeToRead = _bytes.size() - _pos; } memcpy(buff, _bytes.data() + _pos, nSizeToRead); _pos += nSizeToRead; return nSizeToRead; } template <class T> T Read() { T t; int32_t nSize = Read(&t, 1); return t; } ByteArray Read(int32_t size) { int nSizeToRead = size; if(_pos >= _bytes.size()) { return 0; } else if (_bytes.size() - _pos < nSizeToRead) { nSizeToRead = _bytes.size() - _pos; } ByteArray byteArray(_bytes.data() + _pos, nSizeToRead); _pos += nSizeToRead; return byteArray; } int32_t Tell() const { return _pos; } void Seek(SeekMode mode, int32_t size) { if(mode == SeekMode::Set) { _pos = size; } else if(mode == SeekMode::Forward) { _pos += size; } else if(mode == SeekMode::Backward) { _pos -= size; } } private: ByteArray _bytes; int32_t _pos; };
3.4 各数据类型读写控制类实现
在进行数据序列化和反序列化的过程中都必须根据数据类型进行指定数据类型的读写操作,我们用两个map其类型和Writeable类的映射关系:
std::map<Value::Type, int32_t> CodeToTypeMap; std::map<int32_t, std::shared_ptr<IWriteble>> WriterMap; CodeToTypeMap.insert({ Value::Type::Int32, 5 }); CodeToTypeMap.insert({ Value::Type::String, 9 }); WriterMap.insert({ 5, std::shared_ptr<IWriteble>(new Int32Writeable) }); WriterMap.insert({ 9, std::shared_ptr<IWriteble>(new StringWriteable) });
代码实现:

class IWriteble { public: virtual int32_t Write(ByteArrayWriter& Writer, const Value& value) = 0; virtual int32_t Read(ByteArrayReader& Reader, Value& value) = 0; }; class Int32Writeable : public IWriteble { public: Int32Writeable(){} int32_t Write(ByteArrayWriter& Writer, const Value& value) override { int32_t nValue = value.GetInt32Value(); return Writer.Write<int32_t>(nValue); } int32_t Read(ByteArrayReader& Reader, Value& value) override { int32_t nValue = Reader.Read<int32_t>(); value.SetInt32Value(nValue); return sizeof(int32_t); } }; class StringWriteable : public IWriteble { public: StringWriteable(){} int32_t Write(ByteArrayWriter& Writer, const Value& value) override { std::string stringValue = value.GetStringValue(); Writer.Write(stringValue.size()); Writer.Write(stringValue.c_str(), stringValue.size()); return sizeof(int32_t) + stringValue.size(); } int32_t Read(ByteArrayReader& Reader, Value& value) override { // 对于string类型,前4个字节为字符串的长度,后面为字符串的内容 int32_t nSize = Reader.Read<int32_t>(); ByteArray byteArray = Reader.Read(nSize); value.SetStringValue(byteArray.ToStdString()); return sizeof(int32_t) + byteArray.size(); // 注意这个位置不应该直接写nSize } };
3.5 序列化和反序列化函数实现
class DataPachage { public: DataPachage() { CodeToTypeMap.insert({ Value::Type::Int32, 5 }); CodeToTypeMap.insert({ Value::Type::String, 9 }); WriterMap.insert({ 5, std::shared_ptr<IWriteble>(new Int32Writeable) }); WriterMap.insert({ 9, std::shared_ptr<IWriteble>(new StringWriteable) }); } ByteArray Serialize(const Values& values) { ByteArrayWriter Writer; for (Value value : values) { Value::Type type = value.GetValueType(); int32_t code = CodeToTypeMap[type]; std::shared_ptr<IWriteble> pInt32Writer = std::shared_ptr<IWriteble>(new Int32Writeable()); pInt32Writer->Write(Writer, code); std::shared_ptr<IWriteble> Writeable = WriterMap[code]; Writeable->Write(Writer, value); } return Writer.ToByteArray(); } Values DeSerialize(const ByteArray& byteArray) { Values values; int32_t i = 0; ByteArrayReader Reader(byteArray); int32_t pos = 0; while (( pos = Reader.Tell()) < byteArray.size()) { std::shared_ptr<IWriteble> pInt32Writer = std::shared_ptr<IWriteble>(new Int32Writeable()); Value value; pInt32Writer->Read(Reader, value); std::shared_ptr<IWriteble> Writeable = WriterMap[value.GetInt32Value()]; Writeable->Read(Reader, value); values.push_back(value); } return values; } private: std::map<Value::Type, int32_t> CodeToTypeMap; std::map<int32_t, std::shared_ptr<IWriteble>> WriterMap; };
3.6 测试
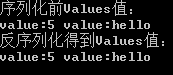
#include "stdio.h" #include "Serialize.h" int main() { Values list = {5, "hello"}; std::cout << "序列化前Values值:" << std::endl; for (Value value : list) { std::cout << value << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; DataPachage data; ByteArray bytes = data.Serialize(list); Values list1 = data.DeSerialize(bytes); std::cout << "反序列化得到Values值:" << std::endl; for (Value value : list1) { std::cout << value << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; return 0; }
附:

#pragma once #include <vector> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <stdint.h> class ByteArray : public std::vector<char> { public: ByteArray() = default; ByteArray(int32_t size) : std::vector<char>(size) { } ByteArray(const char *buffer, int32_t size) : std::vector<char>(buffer, buffer + size) { } ByteArray(const std::string &str) : std::vector<char>(str.size()) { memcpy(data(), str.c_str(), str.size()); } std::string ToStdString() const { std::string result(this->cbegin(), this->cend()); return result; } ByteArray &Concat(const ByteArray &buffer2) { size_t oldSize = size(); size_t newSize = oldSize + buffer2.size(); resize(newSize); memcpy(this->data() + oldSize, buffer2.data(), buffer2.size()); return *this; } ByteArray operator+(const ByteArray &buffer2) const { ByteArray buffer1(this->size() + buffer2.size()); memcpy(buffer1.data(), this->data(), this->size()); memcpy(buffer1.data() + this->size(), buffer2.data(), buffer2.size()); return buffer1; } };

#pragma once #include "ByteArray.h" #include <stdint.h> class IODevice { public: enum class SeekMode { Set, Forward, Backward }; }; class ByteArrayWriter : public IODevice { public: ByteArrayWriter() { } template <class T> int32_t Write(const T* buffer, int32_t size) { int32_t nWriteSize = sizeof(T) * size; ByteArray buffer2((const char *)buffer, nWriteSize); _bytes.Concat(buffer2); return nWriteSize; } template <class T> int32_t Write(const T& value) { return Write((T *)&value, 1); } int32_t Write(const ByteArray& byteArray) { _bytes.Concat(byteArray); return byteArray.size(); } ByteArray ToByteArray() const{ return _bytes; } int32_t Tell() const{ return _bytes.size(); } private: ByteArray _bytes; }; class ByteArrayReader : public IODevice { public: ByteArrayReader(const ByteArray& byteArray): _bytes(byteArray), _pos(0) { } template <class T> int32_t Read(T *buff, int32_t count) { int nSizeToRead = sizeof(T) * count; if(_pos >= _bytes.size()) { return 0; } else if (_bytes.size() - _pos < nSizeToRead) { nSizeToRead = _bytes.size() - _pos; } memcpy(buff, _bytes.data() + _pos, nSizeToRead); _pos += nSizeToRead; return nSizeToRead; } template <class T> T Read() { T t; int32_t nSize = Read(&t, 1); return t; } ByteArray Read(int32_t size) { int nSizeToRead = size; if(_pos >= _bytes.size()) { return 0; } else if (_bytes.size() - _pos < nSizeToRead) { nSizeToRead = _bytes.size() - _pos; } ByteArray byteArray(_bytes.data() + _pos, nSizeToRead); _pos += nSizeToRead; return byteArray; } int32_t Tell() const { return _pos; } void Seek(SeekMode mode, int32_t size) { if(mode == SeekMode::Set) { _pos = size; } else if(mode == SeekMode::Forward) { _pos += size; } else if(mode == SeekMode::Backward) { _pos -= size; } } private: ByteArray _bytes; int32_t _pos; };

#pragma once #include <stdint.h> #include <exception> #include <string> #include <iostream> #ifdef WIN32 #define NOEXCEPT #else #define NOEXCEPT noexcept #endif class TypeMismatchException : public std::exception { public: TypeMismatchException(const std::string& message) : _message(message){} const char* what() const NOEXCEPT override { return _message.c_str(); } private: std::string _message; }; class Value { public: enum class Type { Invalid, Boolean, Character, Int8, Int16, Int32, Int64, Float, Double, String }; union InnerValue { bool booleanValue; char characterValue; int8_t int8Value; int16_t int16Value; int32_t int32Value; int64_t int64Value; float floatValue; double doubleValue; }; Value() : _type(Type::Invalid) { } Value(bool value) : _type(Type::Boolean) { _value.booleanValue = value; } Value(char value) : _type(Type::Character) { _value.characterValue = value; } Value(int8_t value) : _type(Type::Int8) { _value.int8Value = value; } Value(int16_t value) : _type(Type::Int16) { _value.int16Value = value; } Value(int32_t value) : _type(Type::Int32) { _value.int32Value = value; } Value(int64_t value) : _type(Type::Int64) { _value.int64Value = value; } Value(float value) : _type(Type::Float) { _value.floatValue = value; } Value(double value) : _type(Type::Double) { _value.doubleValue = value; } Value(const std::string& value) : _type(Type::String) { _stringValue = value; } Value(const char* value) : Value(std::string(value)) { } bool ToBoolean() const { if ( _type != Type::Boolean ) { throw TypeMismatchException("The type of value is not boolean"); } } int8_t ToInt8() const { if ( _type != Type::Int8 ) { throw TypeMismatchException("The type of value is not int8"); } return _value.int8Value; } int16_t ToInt16() const { if ( _type != Type::Int16 ) { throw TypeMismatchException("The type of value is not int16"); } return _value.int16Value; } int32_t ToInt32() const { if ( _type != Type::Int32 ) { throw TypeMismatchException("The type of value is not int32"); } return _value.int32Value; } int64_t ToInt64() const { if ( _type != Type::Int64 ) { throw TypeMismatchException("The type of value is not int64"); } return _value.int64Value; } char ToCharacter() const { if ( _type != Type::Character ) { throw TypeMismatchException("The type of value is not character"); } return _value.characterValue; } const std::string& ToString() const { if ( _type != Type::String ) { throw TypeMismatchException("The type of value is not string"); } return _stringValue; } friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Value& value) { if (value._type == Type::String) { os << "value:" << value._stringValue; } else if (value._type == Type::Int32) { os << "value:" << value._value.int32Value; } else if (value._type == Type::Double) { os << "value:" << value._value.doubleValue; } return os; } // 以下以int32和string为例进行测试 void SetInt32Value(int32_t value) { _type = Type::Int32; _value.int32Value = value; } void SetStringValue(std::string value) { _type = Type::String; _stringValue = value; } int32_t GetInt32Value() const {return _value.int32Value;} std::string GetStringValue() const {return _stringValue;} Type GetValueType() const {return _type;} private: Type _type; InnerValue _value; std::string _stringValue; }; #include <vector> class Values : public std::vector<Value> { public: Values() = default; Values(std::initializer_list<Value> list) : std::vector<Value>(list) { } Value& operator[](size_t index) { return std::vector<Value>::operator[](index); } const Value& operator[](size_t index) const { return std::vector<Value>::operator[](index); } };

#pragma once #include "IODevice.h" #include "Values.h" class IWriteble { public: virtual int32_t Write(ByteArrayWriter& Writer, const Value& value) = 0; virtual int32_t Read(ByteArrayReader& Reader, Value& value) = 0; }; class Int32Writeable : public IWriteble { public: Int32Writeable(){} int32_t Write(ByteArrayWriter& Writer, const Value& value) override { int32_t nValue = value.GetInt32Value(); return Writer.Write<int32_t>(nValue); } int32_t Read(ByteArrayReader& Reader, Value& value) override { int32_t nValue = Reader.Read<int32_t>(); value.SetInt32Value(nValue); return sizeof(int32_t); } }; class StringWriteable : public IWriteble { public: StringWriteable(){} int32_t Write(ByteArrayWriter& Writer, const Value& value) override { std::string stringValue = value.GetStringValue(); Writer.Write(stringValue.size()); Writer.Write(stringValue.c_str(), stringValue.size()); return sizeof(int32_t) + stringValue.size(); } int32_t Read(ByteArrayReader& Reader, Value& value) override { // 对于string类型,前4个字节为字符串的长度,后面为字符串的内容 int32_t nSize = Reader.Read<int32_t>(); ByteArray byteArray = Reader.Read(nSize); value.SetStringValue(byteArray.ToStdString()); return sizeof(int32_t) + byteArray.size(); // 注意这个位置不应该直接写nSize } }; #include <map> #include <memory> /*std::map<Value::Type, int32_t> CodeToTypeMap = { {Value::Type::Int32, 5}, {Value::Type::String, 9} }; // 根据数据类型得到对应的IWriteble std::map<int32_t, std::shared_ptr<IWriteble>> WriterMap = { {5, std::shared_ptr<IWriteble>(new Int32Writeable)}, {9, std::shared_ptr<IWriteble>(new StringWriteable)} };*/ //static std::map<int32_t, IWriteble*> WriterMap = //{ // {5, new Int32Writeable()}, // {9, new StringWriteable()} //}; class DataPachage { public: DataPachage() { CodeToTypeMap.insert({ Value::Type::Int32, 5 }); CodeToTypeMap.insert({ Value::Type::String, 9 }); WriterMap.insert({ 5, std::shared_ptr<IWriteble>(new Int32Writeable) }); WriterMap.insert({ 9, std::shared_ptr<IWriteble>(new StringWriteable) }); } ByteArray Serialize(const Values& values) { ByteArrayWriter Writer; for (Value value : values) { Value::Type type = value.GetValueType(); int32_t code = CodeToTypeMap[type]; std::shared_ptr<IWriteble> pInt32Writer = std::shared_ptr<IWriteble>(new Int32Writeable()); pInt32Writer->Write(Writer, code); std::shared_ptr<IWriteble> Writeable = WriterMap[code]; Writeable->Write(Writer, value); } return Writer.ToByteArray(); } Values DeSerialize(const ByteArray& byteArray) { Values values; int32_t i = 0; ByteArrayReader Reader(byteArray); int32_t pos = 0; while (( pos = Reader.Tell()) < byteArray.size()) { std::shared_ptr<IWriteble> pInt32Writer = std::shared_ptr<IWriteble>(new Int32Writeable()); Value value; pInt32Writer->Read(Reader, value); std::shared_ptr<IWriteble> Writeable = WriterMap[value.GetInt32Value()]; Writeable->Read(Reader, value); values.push_back(value); } return values; } private: std::map<Value::Type, int32_t> CodeToTypeMap; std::map<int32_t, std::shared_ptr<IWriteble>> WriterMap; };

#include "stdio.h" #include "Serialize.h" int main() { Values list = {5, "hello"}; std::cout << "序列化前Values值:" << std::endl; for (Value value : list) { std::cout << value << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; DataPachage data; ByteArray bytes = data.Serialize(list); Values list1 = data.DeSerialize(bytes); std::cout << "反序列化得到Values值:" << std::endl; for (Value value : list1) { std::cout << value << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; return 0; }



