数据结构之hash表
哈希(散列)技术既是一种存储方法,也是一种查找方法。然而它与线性表、树、图等结构不同的是,前面几种结构,数据元素之间都存在某种逻辑关系,可以用连线图示表示出来,而哈希技术的记录之间不存在什么逻辑关系,它只与关键字有关联。因此,哈希主要是面向查找的存储结构。哈希技术最适合的求解问题是查找与给定值相等的记录。

一、基本概念及原理
1.1 构造哈希函数的方法
构造哈希函数的目标在于使哈希地址尽可能均匀地分布在连续的内存单元地址上,以减少发生冲突的可能性,同时使计算尽可能简单以达到尽可能高的时间效率,这里主要看看两个构造哈希函数的方法。
(1)直接地址法
直接地址法取关键字的某个线性函数值为哈希地址,即h(key)=key 或 h(key)=a*key+b
其中,a、b均为常数,这样的散列函数优点就是简单、均匀,也不会产生冲突,但问题是这需要事先知道关键字的分布情况,适合查找表较小且连续的情况。由于这样的限制,在现实应用中,此方法虽然简单,但却并不常用。
(2)除留余数法
除留余数法采用取模运算(%)把关键字除以某个不大于哈希表表长的整数得到的余数作为哈希地址,它也是最常用的构造哈希函数的方法,其形式为:h(key)=key%p
![]()
本方法的关键就在于选择合适的p,p如果选得不好,就可能会容易产生同义词。
PS:根据前辈们的经验,若哈希表表长为m,通常p为小于或等于表长(最好接近m)的最小质数或不包含小于20质因子的合数。
1.2 解决哈希冲突的方法
(1)闭散列法
闭散列法时把所有的元素都存储在哈希表数组中,当发生冲突时,在冲突位置的附近寻找可存放记录的空单元。寻找“下一个”空位的过程则称为探测。上述方法可用如下公式表示为:

其中,h(key)为哈希函数,m为哈希表长度,di为递增的序列。根据di的不同,又可以分为几种探测方法:线性探测法、二次探测法以及双重散列法。
(2)开散列法
开散列法的常见形式是将所有关键字为同义词的记录存储在一个单链表中。我们称这种表为同义词子表,在散列表中只存储所有同义词子表的头指针。对于关键字集合{12,67,56,16,25,37,22,29,15,47,48,34},我们用前面同样的12为除数,进行除留余数法,可得到如下图所示的结构,此时,已经不存在什么冲突换址的问题,无论有多少个冲突,都只是在当前位置给单链表增加结点的问题。

该方法对于可能会造成很多冲突的散列函数来说,提供了绝不会出现找不到地址的保障。当然,这也就带来了查找时需要遍历单链表的性能损耗。在.NET中,链表的各个元素分散于托管堆各处,也会给GC垃圾回收带来压力,影响程序的性能。
1.3 闭散列实现哈希冲突
1.3.1 代码实现
#pragma once // 开放定址法解决hash冲突 /* 1.pair<k,v> 2.vector<pair<k,v>> 3.使用素数对齐坐哈希表的容量,降低哈希冲突 4.将负载因子控制在0.7-0.8范围内性能最高 5.支持任一类型hash算法 */ #include<string> #include <vector> #include<iostream> using namespace std; static size_t GetNextPrime(const size_t& value) { // 使用素数表对齐做哈希表的容量,降低哈希冲突 const int _PrimeSize = 28; static const unsigned long _PrimeList[_PrimeSize] = { 53ul, 97ul, 193ul, 389ul, 769ul, 1543ul, 3079ul, 6151ul, 12289ul, 24593ul, 49157ul, 98317ul, 196613ul, 393241ul, 786433ul, 1572869ul, 3145739ul, 6291469ul, 12582917ul, 25165843ul, 50331653ul, 100663319ul, 201326611ul, 402653189ul, 805306457ul, 1610612741ul, 3221225473ul, 4294967291ul }; for (size_t i = 0; i < _PrimeSize; ++i) { if (_PrimeList[i] > value) { return _PrimeList[i]; } } return _PrimeList[_PrimeSize - 1]; } template <class K> class CHashFunc { public: CHashFunc(){} size_t operator()(const K &key) { return key; } }; template<> // 显示专用化需要 class CHashFunc<string> { public: size_t BKDRHash(const char * str) { unsigned int seed = 131; // 31 131 1313 13131 131313 unsigned int hash = 0; while (*str) { hash = hash * seed + (*str++); } return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF); } size_t operator()(const string& key) { return BKDRHash(key.c_str()); } }; template<class K, class V,class HashFunc = CHashFunc<K>> class HashTab { public: HashTab() :m_nNumber(0){} typedef pair<K, V> Pair; struct Node { Pair p; bool bIsExist; }; enum {NOEXIST = 0,EXISTS}; bool Insert(const Pair &p) { CheckCapacity(); size_t nIndex = _HashFunc(p.first, m_Table.size()); while (m_Table[nIndex].bIsExist == EXISTS) { if (m_Table[nIndex].p.first == p.first) { return false; } nIndex++; if (nIndex == m_Table.size()) { nIndex = 0; } } m_Table[nIndex].p = p; m_Table[nIndex].bIsExist = EXISTS; m_nNumber++; return true; } V Find(const K&& key) { size_t nIndex = _HashFunc(key, m_Table.size()); if (m_Table[nIndex].p.first == key) { return m_Table[nIndex].p.second; } return 0; } private: // 检查负载因子,并用素数表初始化容器大小 void CheckCapacity() { if (0 == m_Table.size()) { m_Table.resize(GetNextPrime(0)); } else if (m_nNumber * 10 / m_Table.size() > 7) { vector <Node> NewVect; NewVect.resize(GetNextPrime(m_Table.size())); NewVect.assign(m_Table.begin(), m_Table.end()); m_Table.swap(NewVect); } } size_t _HashFunc(const K& key, const size_t& size) { HashFunc hash; return hash(key) % size; } private: vector <Node> m_Table; int m_nNumber; // 已存node数量 };
1.3.2 测试
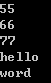
#include "HashTab.h" void main() { HashTab<int, int> hash; hash.Insert(pair<int,int>(5, 55)); hash.Insert(pair<int,int>(6, 66)); hash.Insert(pair<int,int>(7, 77)); cout << hash.Find(5) << endl; cout << hash.Find(6) << endl; cout << hash.Find(7) << endl; HashTab<string, string> hash1; hash1.Insert(pair<string, string>("a", "hello")); hash1.Insert(pair<string, string>("b", "word")); cout << hash1.Find("a") << endl; cout << hash1.Find("b") << endl; }