Python字符串
从编码和常用字符串函数两方面进行总结
1. 编码
计算机里面,编码方法有很多种,英文的一般用ascii,而中文有unicode,utf-8,gbk,utf-16等等。
unicode是 utf-8,gbk,utf-16这些的父编码,这些子编码都能转换成unicode编码,然后转化成子编码,例如utf8可以转成unicode,再转gbk,但不能直接从utf8转gbk
所以,python中就有两个方法用来解码(decode)与编码(encode),解码是子编码转unicode,编码就是unicode转子编码
#encoding:UTF-8
从Python3.0以后,只要没有带前缀的字符串都是Unicode,将字符串对象编码为字节序列的方法有两种:
1. str.encode(encoding, errors)
2. bytes(source, encoding,errors)
2. 字符串格式化
字符串格式化和C++一样使用%,但在使用上有区别
#使用%对字符串进行格式化 msg = "hello" print("%s:%s" %(msg,"world")) # 若要显示百分号,必须使用%% print("%%%d" %(50))
(1)字符宽度和精度
“%10.2f” %pi #字符宽10,精度2
可以使用*(星号)作为字符宽度或者精度(或者两者都使用*)
import math
print("%0*.*f" %(7,3,math.pi))
>>> 003.142
(2)符号、对齐和0填充
在字符宽度和精度之前还可以放置一个标志,该标志可以是零、加号、减号或空格
减号(-)用来左对齐数值
空格(“ ”)在正数前加上空格
print("% 5d" %(10) +'\n'+"% 5d" %(-10))
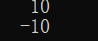
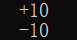
加号(+)表示不管是证书还是附属都标示出符号
print("%+5d" %(10) +'\n'+"%+5d" %(-10))
3. 字符串方法
lower()#大写转小写
upper() #小写转大写
swapcase() #大小写互换
capitalize() #首字母大写
ljust rjust center zfill expandtabs #字符串输出对齐
find rfind #字符串查找
index rindex #字符索引
count #字符出现的次数
replce strip lstrip rstrip #字符串替换
split rsplit lsplit
join(seq) #把seq代表的序列--字符串序列,用字符串S链接起来
startswith endswith #注意别写错
isalnum #是否全是字母和数字,并至少有一个字符
isalpha #是否全是字母,并至少有一个字符
isdigit #是否全是数字
isspace islower isupper istitle
#coding=utf-8 ''' 字符串基本操作 split join strip ''' str1 = "you are a super man" print (str1.split(" ", 2)) str2 = ["a", "b", "c"] print (("-").join(str2)) str3 = "8888888strip888888" print (str3.strip("8")) print (str3.lstrip("8")) print (str3.rstrip("8")) #str.replace(old, new[, max]) str4 = "aa bb aa cc aa dd aa" print (str4.replace("aa", "---", 3))
>>> ['you', 'are', 'a super man']
>>> a-b-c
>>> strip
>>> strip888888
>>> 8888888strip
>>> --- bb --- cc --- dd aa
strip()说明
(1)当rm为空时,默认删除空白符(包括'\n', '\r', '\t', ' ')
(2)这里的rm删除序列是只要边(开头或结尾)上的字符在删除序列内,就删除掉。
join() 方法用于将序列中的元素以指定的字符连接生成一个新的字符串


