网络爬虫必备知识之urllib库
就库的范围,个人认为网络爬虫必备库知识包括urllib、requests、re、BeautifulSoup、concurrent.futures,接下来将结合爬虫示例分别对urllib库的使用方法进行总结
1. urllib库全局内容
官方文档地址:https://docs.python.org/3/library/urllib.html
urllib库是python的内置HTTP请求库,包含以下各个模块内容:
(1)urllib.request:请求模块
(2)urllib.error:异常处理模块
(3)urllib.parse:解析模块
(4)urllib.robotparser:robots.txt解析模块
以下所有示例都以http://example.webscraping.com/网站为目标,网站预览:

2. urllib.request.urlopen
(1)函数原型
def urlopen(url, data=None, timeout=socket._GLOBAL_DEFAULT_TIMEOUT, *, cafile=None, capath=None, cadefault=False, context=None):
该函数功能简单,进行简单的网站请求,不支持复杂功能如验证、cookie和其他HTTP高级功能,若要支持这些功能必须使用build_opener()函数返回的OpenerDirector对象,后面介绍,埋个伏笔
(2)先写个简单的例子
import urllib.request url = "http://example.webscraping.com/" response = urllib.request.urlopen(url,timeout=1) print("http status:", response.status)

(3)data参数使用
data参数用于post请求,比如表单提交,如果没有data参数则是get请求
import urllib.parse import urllib.request data = urllib.parse.urlencode({'name':'张三', 'password':'666777'}).encode('utf-8') print(data) response = urllib.request.urlopen('http://httpbin.org/post', data=data) print(response.read())
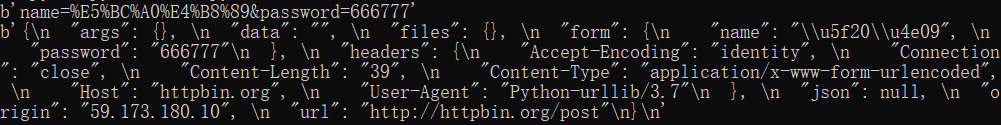
首先解释下urlencode的用法,将key-value的键值对转换为我们想要的格式,返回的是a=1&b=2这样的字符串,解码使用unquote(),应为urltilib没有提供urldecode
data1 = urllib.parse.urlencode({'name':'张三', 'password':'666777'}).encode('utf-8')
print(data1)
data2 = urllib.parse.unquote(data1.decode('utf-8'))
print(data2)

(4)timeout参数
在某些网络情况不好或服务器出现异常的情况下,这个时候我们需要设置一个超时时间,否则程序会一直等待下去
(5)urlopen函数返回响应对象
response = urllib.request.urlopen(url,timeout=1) for key,value in response.__dict__.items(): print(key,":", value)

返回<class 'http.client.httpresponse'="">对象,我们可以response.status获取返回状态,response.read()获得响应题的内容
3. urllib.request.build_opener
前面说过了urlopen不支持headers、cookie和HTTP的高级用法,那解决的方法就是使用build_opener()函数来定义自己的opener对象
(1)函数原型
build_opener([handler1[,headler2[,....]]])
参数都是特殊处理程序对象的实例,下表列出了所有可用的处理程序对象:
| CacheFTPHandler | 具有持久FTP连续的FTP处理程序 |
| FileHandler | 打开本地文件 |
| FTPHandler | 通过FTP打开URL |
| HTTPBasicAuthHandler | 基本的HTTP验证处理 |
| HTTPCookieProcessor | 处理HTTP cookie |
| HTTPDefaultErrorHandler | 通过引发HTTPError异常来处理HTTP错误 |
| HTTPDigestAuthHandler | HTTP摘要验证处理 |
| HTTPHandler | 通过HTTP打开URL |
| HTTPRedirectHandler | 处理HTTP重定向 |
| HTTPSHandler | 通过安全HTTP打开url |
| ProxyHandler | 通过代理重定向请求 |
| ProxyBasicAuthHandler | 基本的代理验证 |
| ProxyDigestAuthHandler | 摘要代理验证 |
| UnknownHandler | 处理所有未知URL的处理程序 |
(2)opener对象创建
这里以设置cookie和添加代理服务器为例进行说明
有时候爬取网站需要携带cookie信息访问,这个时候需要设置cookie,同时大多数网站都会检测某一段事件某个IP的访问次数,如果访问次数过多,它会禁止你的访问,这个时候需要设置代理服务器来爬取数据。
proxy = urllib.request.ProxyHandler( { 'http': 'http://127.0.0.1:9743', 'https': 'https://127.0.0.1:9743' }) cjar = http.cookiejar.CookieJar() opener = urllib.request.build_opener(urllib.request.HTTPHandler, urllib.request.HTTPCookieProcessor(cjar))
(3)headers设置
headers即为请求头,很多网站为了防止程序爬虫爬网站照成网站瘫痪,会需要携带一些headers头部信息才能访问,最常见的是user-agent参数
打开网站,按F12,点网络我们会看到下面内容:

headers = { 'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:63.0)Gecko/20100101 Firefox/63.0)', 'Accept':'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8', 'Connection':'keep-alive', 'Host':'example.webscraping.com'}
header的设置这里介绍两种方法:
a. 通过urllib.request.Request对象
request = urllib.request.Request(url,headers=headers)
b. 通过OpenerDirector对象的add_headers属性
headers = { 'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:63.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/63.0)', 'Accept':'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8', 'Connection':'keep-alive', 'Host':'example.webscraping.com'} cjar = http.cookiejar.CookieJar() opener = urllib.request.build_opener(urllib.request.HTTPHandler,urllib.request.HTTPCookieProcessor(cjar)) header_list = [] for key,value in headers.items(): header_list.append(key) header_list.append(value) opener.add_handler = [header_list]
(4)OpenDirector的open()函数
函数原型:
def open(self, fullurl, data=None, timeout=socket._GLOBAL_DEFAULT_TIMEOUT):
里面有一部分代码:
if isinstance(fullurl, str): req = Request(fullurl, data) else: req = fullurl if data is not None: req.data = data
说明fullurl既可以是url,也可以是urllib.request.Request对象
使用:
request = urllib.request.Request(url) response = opener.open(request, timeout=1)
综合代码:
def DownLoad(url): headers = { 'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:63.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/63.0)', 'Accept':'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8', 'Connection':'keep-alive', 'Host':'example.webscraping.com'} proxy = urllib.request.ProxyHandler( { 'http': 'http://127.0.0.1:9743', 'https': 'https://127.0.0.1:9743' }) cjar = http.cookiejar.CookieJar() opener = urllib.request.build_opener(urllib.request.HTTPHandler,urllib.request.HTTPCookieProcessor(cjar)) header_list = [] for key,value in headers.items(): header_list.append(key) header_list.append(value) opener.add_handler = [header_list] try: request = urllib.request.Request(url) response = opener.open(request, timeout=1) print(response.__dict__) except urllib.error.URLError as e: if hasattr(e, 'code'): print ("HTTPErro:", e.code) elif hasattr(e, 'reason'): print ("URLErro:", e.reason)
4. url.error异常处理
很多时候我们通过程序访问网页的时候,有的页面可能会出错,类似404,500的错误,这个时候就需要我们捕获异常,从上面的最后代码已经看到了urllib.error的使用
except urllib.error.URLError as e: if hasattr(e, 'code'): print ("HTTPErro:", e.code) elif hasattr(e, 'reason'): print ("URLErro:", e.reason)
HTTPError是URLError的子类
URLError里只有一个属性:reason,即抓异常的时候只能打印错误信息,类似上面的例子
HTTPError里有三个属性:code,reason,headers,即抓异常的时候可以获得code,reson,headers三个信息
5. urllib.parse
前面已经介绍过了urllib.parse.urlencode的使用,接下来再介绍三个函数:urlparse、urlunparse、urljoin
(1)urlparse
函数原型:
def urlparse(url, scheme='', allow_fragments=True):
"""Parse a URL into 6 components: <scheme>://<netloc>/<path>;<params>?<query>#<fragment> Return a 6-tuple: (scheme, netloc, path, params, query, fragment). Note that we don't break the components up in smaller bits (e.g. netloc is a single string) and we don't expand % escapes."""
意思就的对你传入的url进行拆分,包括协议,主机地址,端口,路径,字符串,参数,查询,片段
![]()
- protocol 协议,常用的协议是http
- hostname 主机地址,可以是域名,也可以是IP地址
- port 端口 http协议默认端口是:80端口,如果不写默认就是:80端口
- path 路径 网络资源在服务器中的指定路径
- parameter 参数 如果要向服务器传入参数,在这部分输入
- query 查询字符串 如果需要从服务器那里查询内容,在这里编辑
- fragment 片段 网页中可能会分为不同的片段,如果想访问网页后直接到达指定位置,可以在这部分设置
(2)urlunparse
功能和urlparse功能相反,用于将各组成成分拼接成URL
函数原型:
def urlunparse(components):
from urllib.parse import urlunparse print(urlunparse(('https','www.baidu.com','index.html','name','a=123','')))

(3)urljoin
函数的作用就是url拼接,后面的优先级高于前面
函数原型:
def urljoin(base, url, allow_fragments=True): """Join a base URL and a possibly relative URL to form an absolute interpretation of the latter."""
例:
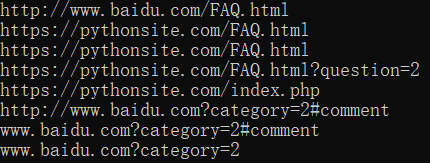
from urllib.parse import urljoin print(urljoin('http://www.baidu.com', 'FAQ.html')) print(urljoin('http://www.baidu.com', 'https://pythonsite.com/FAQ.html')) print(urljoin('http://www.baidu.com/about.html', 'https://pythonsite.com/FAQ.html')) print(urljoin('http://www.baidu.com/about.html', 'https://pythonsite.com/FAQ.html?question=2')) print(urljoin('http://www.baidu.com?wd=abc', 'https://pythonsite.com/index.php')) print(urljoin('http://www.baidu.com', '?category=2#comment')) print(urljoin('www.baidu.com', '?category=2#comment')) print(urljoin('www.baidu.com#comment', '?category=2'))
6. urllib.robotparser
该模块用于robots.txt内容解析
例:
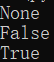
from urllib.robotparser import RobotFileParser rp = RobotFileParser() rp.set_url('http://example.webscraping.com/robots.txt') print(rp.read()) url = 'http://example.webscraping.com' user_agent = 'BadCrawler' print(rp.can_fetch(user_agent,url)) user_agent = 'GoodCrawler' print(rp.can_fetch(user_agent,url))
输出: