斯坦福机器学习ex1.1(python)
使用的工具:NumPy和Matplotlib
NumPy是全书最基础的Python编程库。除了提供一些高级的数学运算机制以外,还具备非常高效的向量和矩阵运算功能。这些对于机器学习的计算任务是尤为重要的。因为不论是数据的特征表示也好,还是参数的批量设计也好,都离不开更加快捷的矩阵和向量计算。而NumPy更加突出的是它内部独到的设计,使得处理这些矩阵和向量计算比起一般程序员自行编写,甚至是Python自带程序库的运行效率都要高出许多。
Matplotlib是一款Python编程环境下免费试用的绘图工具包,其工作方式和绘图命令几乎和matlab类似。
操作步骤:
1.数据初始化,将数据存放到x,y当中。
print("Plotting Data...\n") fr=open('ex1data1.txt') arrayLines=fr.readlines() numberOfLines=len(arrayLines) x=np.zeros((numberOfLines,1)) y=np.zeros((numberOfLines,1)) index=0 for line in arrayLines: line = line.strip() listFormLine = line.split(",") x[index, :] = listFormLine[:1] y[index] = listFormLine[-1] index += 1
2.求取代价函数(cost function)
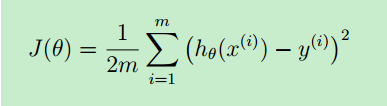
def computeCost(X,y,theta): m=X.shape[0] XMatrix=np.mat(X) yMatrix=np.mat(y) thetaMatrix=np.mat(theta) J=1/(2*float(m))*sum((np.array(XMatrix*thetaMatrix-yMatrix))**2) return J
3.采取梯度下降算法进行计算,首先将theta0与theta1都初始化为0,再使alpha为0.01,进行计算
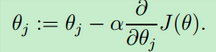
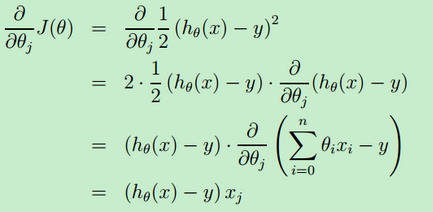
def gradientDescent(X,y,theta,alpha,iterations): m=len(y) J_history=np.zeros((iterations,1)) theta_s=theta.copy() for i in range(iterations): theta[0]=theta[0]-(alpha/m)*np.sum(np.mat(X)*np.mat(theta_s)-np.mat(y)) p1=np.mat(X)*np.mat(theta_s)-np.mat(y) p2=X[:,1]*p1 theta[1]=theta[1]-(alpha/m)*p2 theta_s=theta.copy() J_history[i,:]=computeCost(X,y,theta) return theta
4.将数据可视化显示
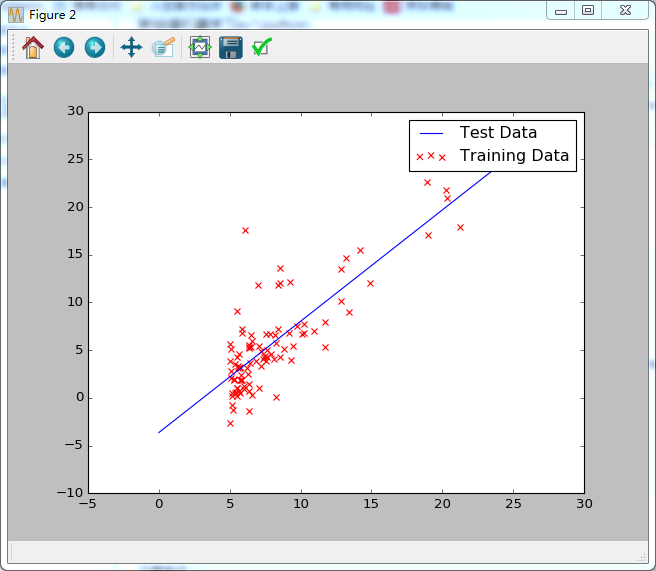
详细代码:https://github.com/xingxiaoyun/StanfordMachineLearning/blob/master/ex1.py



