网络通信——HTTP接口访问——移动数据格式JSON

网络通信的交互数据格式有两大类,分别是JSON和XML 。
对于App来说,基本采用JSON格式与服务器通信。
JSON相比XML的优势主要有两个:
(1)手机流量很贵,表达同样的信息,JSON串比XML串短很多。
(2) JSON串解析得更快,也更省电,XML不但慢而且耗电。

(1)整个JSON串由一对花括号包裹,并且内部的每个结构都以花括号包起来;
(2)参数格式类似键值对,其中键名与键值之间以冒号分隔,形如“键名:键值”;
(3)两个键值对之间以逗号分隔;
(4)键名需要用双引号括起来,键值为数字的话则无需双引号,为字符串的话仍需双引号;
(5)JSON数组通过方括号表达,方括号内部依次罗列各个元素,具体格式形如“数组的键名:[元素1,元素2,元素3]”;


================================================================================================
引入:
// https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.google.code.gson/gson
implementation group: 'com.google.code.gson', name: 'gson', version: '2.8.8'
布局:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" > <Button android:id="@+id/btn_origin_json" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="原始JSON串" android:textColor="@color/black" android:textSize="17sp" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_convert_json" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="转换JSON串" android:textColor="@color/black" android:textSize="17sp" /> </LinearLayout> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_json" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:paddingLeft="5dp" android:paddingRight="5dp" android:text="这里查看JSON串的构造和解析结果" android:textColor="@color/black" android:textSize="17sp" /> </LinearLayout>
UserInfo
package com.example.myapplication.bean; public class UserInfo { public String name; // 姓名 public int age; // 年龄 public long height; // 身高 public float weight; // 体重 public UserInfo(String name, int age, long height, float weight) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.height = height; this.weight = weight; } }
主代码;
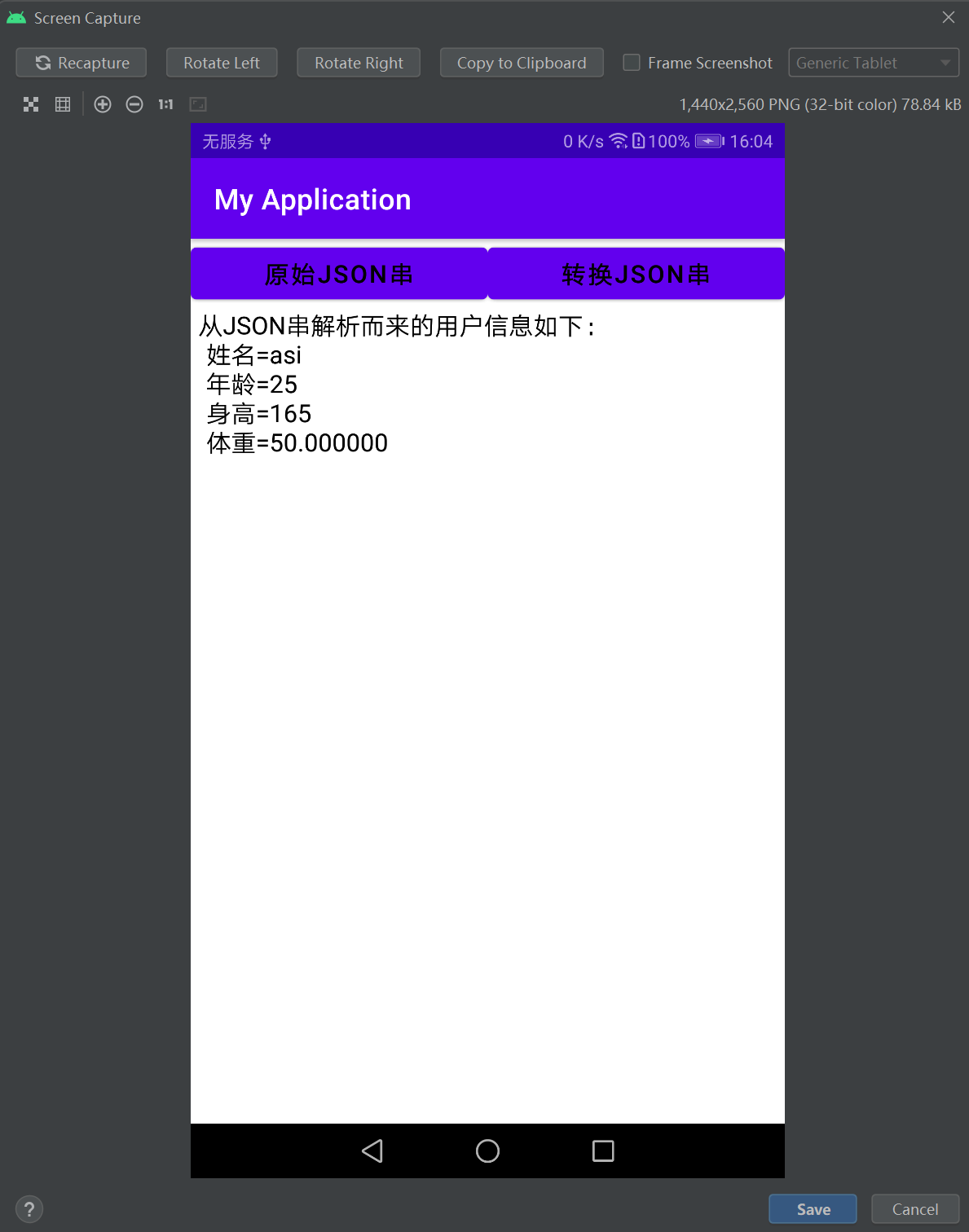
package com.example.myapplication; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.widget.TextView; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import com.example.myapplication.bean.UserInfo; import com.google.gson.Gson; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener { private TextView tv_json; // 声明一个文本视图对象 private UserInfo mUser; // 声明一个用户信息对象 private String mJsonStr; // JSON格式的字符串 @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); mUser = new UserInfo("asi", 25, 165L, 50.0f); // 创建用户实例 mJsonStr = new Gson().toJson(mUser); // 把用户实例转换为JSON串 tv_json = findViewById(R.id.tv_json); findViewById(R.id.btn_origin_json).setOnClickListener(this); findViewById(R.id.btn_convert_json).setOnClickListener(this); } @Override public void onClick(View v) { if (v.getId() == R.id.btn_origin_json) { mJsonStr = new Gson().toJson(mUser); // 把用户实例转换为JSON字符串 tv_json.setText("JSON串内容如下:\n" + mJsonStr); } else if (v.getId() == R.id.btn_convert_json) { // 把JSON串转换为UserInfo类型的对象 UserInfo newUser = new Gson().fromJson(mJsonStr, UserInfo.class); String desc = String.format("\n\t姓名=%s\n\t年龄=%d\n\t身高=%d\n\t体重=%f", newUser.name, newUser.age, newUser.height, newUser.weight); tv_json.setText("从JSON串解析而来的用户信息如下:" + desc); } } }







分类:
工作需要———安卓app学习






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!