java设计模式-----17、中介者模式
概念:
Mediator模式也叫中介者模式,是由GoF提出的23种软件设计模式的一种。Mediator模式是行为模式之一,在Mediator模式中,类之间的交互行为被统一放在Mediator的对象中,对象通过Mediator对象同其他对象交互,Mediator对象起着控制器的作用。
中介者模式其实就好比租房中介和相亲网站一样,房东将信息发布到租房中介,而租客可以中介挑选自己理想的房子,或者单身男女各自将自己的信息发布到相亲网站,同时也可以挑选符合自己条件的另一半。
拿相亲网站举个例子,首先不用中介者模式
相亲,肯定是人相亲,所以新建一个Person类,并提供一个getCompanion(Person person)方法
1 public abstract class Person { 2 private String name; 3 private int condition; 4 5 public Person(String name, int condition){ 6 this.name = name; 7 this.condition = condition; 8 } 9 10 public String getName() { 11 return name; 12 } 13 14 public void setName(String name) { 15 this.name = name; 16 } 17 18 public int getCondition() { 19 return condition; 20 } 21 22 public void setCondition(int condition) { 23 this.condition = condition; 24 } 25 26 //得到是否符合信息 27 public abstract void getCompanion(Person person); 28 }
人肯定是分为男人和女人,所以在新建Man与Woman类
1 public class Man extends Person { 2 3 public Man(String name, int condition) { 4 super(name, condition); 5 } 6 7 @Override 8 public void getCompanion(Person person) { 9 if(person instanceof Man){ 10 System.out.println("我不是gay"); 11 }else{ 12 if(person.getCondition() == this.getCondition()){ 13 System.out.println(this.getName()+"先生与"+person.getName()+"女士"+"非常般配"); 14 }else{ 15 System.out.println(this.getName()+"先生与"+person.getName()+"女士"+"不合适"); 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 }
1 public class Woman extends Person{ 2 3 public Woman(String name, int condition) { 4 super(name, condition); 5 } 6 7 @Override 8 public void getCompanion(Person person) { 9 if(person instanceof Woman){ 10 System.out.println("我不是gay"); 11 }else{ 12 if(person.getCondition() == this.getCondition()){ 13 System.out.println(this.getName()+"女士与"+person.getName()+"先生"+"非常般配"); 14 }else{ 15 System.out.println(this.getName()+"女士与"+person.getName()+"先生"+"不合适"); 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 }
在写一个客户端
1 public class MainCLass { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Person xiaoming = new Man("小明",1); 4 Person xiaoqiang = new Man("小强",2); 5 6 Person xiaohong = new Woman("小红",1); 7 8 xiaoming.getCompanion(xiaohong); 9 10 xiaoqiang.getCompanion(xiaohong); 11 12 xiaoming.getCompanion(xiaoqiang); 13 } 14 }
运行结果:
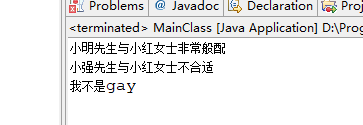
可以看到,这种形式判断对方是否合适都交给了男女双方自己来解决,自己去寻找是否符合条件的,像大海捞针一样,不管是男,女人,甚至不是人都要挨个去比较。
同时这样Man和Woman之间存在了一个交互行为,大大提高了代码的耦合性,如果这两个类中都有自己特定的方法需要对方调用时,只要一方修改,另一方就需要跟着修改。两个类紧紧联系到了一起,这样的设计是很不好的。
下面,正式进入中介者模式
中介者模式结构图
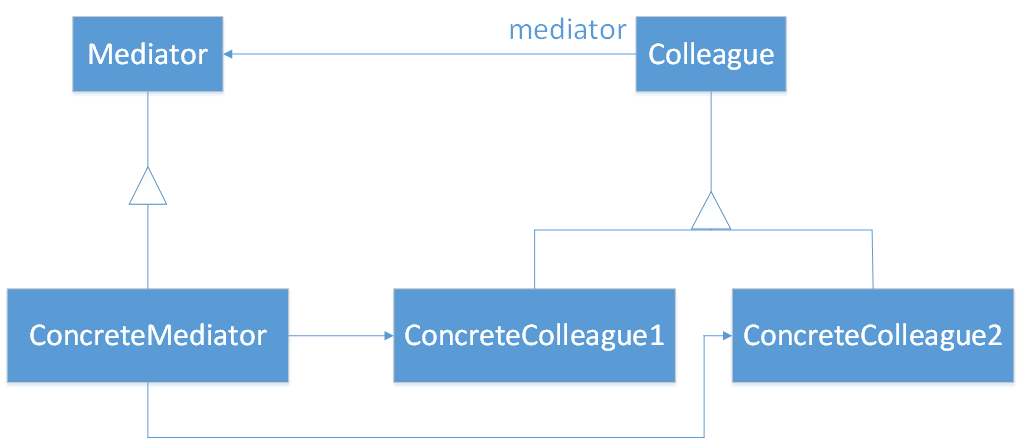
中介者模式的角色和职责
1、Mediator:中介者类的抽象父类
抽象中介者角色定义统一的接口,用于各角色(男和女)之间的通信。
2、ConcreteMediator:具体中介者角色
具体中介者角色,通过协调各角色(男和女)实现协作行为,因此它必须依赖于各个角色。
3、Colleague:关联类的抽象父类
每一个角色都知道中介者角色,而且与其它的角色通信的时候,一定要通过中介者角色来协作。
每个类(Person)的行为分为二种(男和女):一种是男女本身的行为,这种行为叫做自发行为(Self-Method);第二种是必须依赖中介者才能完成的行为,叫做依赖行为(Dep-Method)。
4、concreteColleague:具体的关联类(Man和Woman)。
下面,用代码实现中介者模式
首先新建一个Mediator
1 public abstract class Mediator { 2 private Man man; 3 private Woman woman; 4 5 public Man getMan() { 6 return man; 7 } 8 public void setMan(Man man) { 9 this.man = man; 10 } 11 public Woman getWoman() { 12 return woman; 13 } 14 public void setWoman(Woman woman) { 15 this.woman = woman; 16 } 17 18 //比较条件的方法 19 public abstract void getCompanion(Person person); 20 }
在新建一个ConcreteMediator:具体中介者角色
1 public class BlindDateMediator extends Mediator{ 2 @Override 3 public void getCompanion(Person person) { 4 if(person instanceof Man) { 5 this.setMan((Man)person); 6 } else { 7 this.setWoman((Woman)person); 8 } 9 10 //如果是同性 11 if(this.getMan() == null || this.getWoman() == null) { 12 System.out.println("我不是gay"); 13 }else { 14 //条件合适 15 if(this.getMan().getCondition() == this.getWoman().getCondition()) { 16 System.out.println(this.getMan().getName() + "先生与" + this.getWoman().getName() + "女士很般配"); 17 //条件不合适 18 }else { 19 System.out.println(this.getMan().getName() + "先生" + this.getWoman().getName() + "女士不合适"); 20 } 21 } 22 23 //比较之后,将条件置空,不然会影响下一次比较 24 this.setMan(null); 25 this.setWoman(null); 26 } 27 }
接下来,新建Person,Man与Woman
1 public abstract class Person { 2 private String name; 3 private int condition; 4 private Mediator mediator; 5 6 public Person(String name, int condition, Mediator mediator){ 7 this.name = name; 8 this.condition = condition; 9 this.mediator = mediator; 10 } 11 12 public String getName() { 13 return name; 14 } 15 16 public void setName(String name) { 17 this.name = name; 18 } 19 20 public int getCondition() { 21 return condition; 22 } 23 24 public void setCondition(int condition) { 25 this.condition = condition; 26 } 27 28 public Mediator getMediator() { 29 return mediator; 30 } 31 32 public void setMediator(Mediator mediator) { 33 this.mediator = mediator; 34 } 35 36 //得到是否符合信息 37 public abstract void getCompanion(Person person); 38 }
1 public class Man extends Person { 2 3 public Man(String name, int condition, Mediator mediator) { 4 super(name, condition, mediator); 5 } 6 7 @Override 8 public void getCompanion(Person person) { 9 this.getMediator().setMan(this); 10 this.getMediator().getCompanion(person); 11 } 12 }
1 public class Woman extends Person{ 2 3 public Woman(String name, int condition, Mediator mediator) { 4 super(name, condition, mediator); 5 } 6 7 @Override 8 public void getCompanion(Person person) { 9 this.getMediator().setWoman(this); 10 this.getMediator().getCompanion(person); 11 } 12 }
最后是客户端
1 public class MainCLass { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Mediator mediator = new BlindDateMediator(); 4 Person xiaoming = new Man("小明",1,mediator); 5 Person lisi = new Man("李四",2,mediator); 6 Person xiaohong = new Woman("小红",1,mediator); 7 8 xiaoming.getCompanion(xiaohong); 9 10 lisi.getCompanion(xiaohong); 11 12 xiaoming.getCompanion(lisi); 13 } 14 }
运行结果如下:

中介者模式的优缺点
优点:
1,将系统按功能分割成更小的对象,符合类的最小设计原则
2,对关联对象的集中控制
3,减小类的耦合程度,明确类之间的相互关系:当类之间的关系过于复杂时,其中任何一个类的修改都会影响到其他类,不符合类的设计的开闭原则 ,而Mediator模式将原来相互依存的多对多的类之间的关系简化为Mediator控制类与其他关联类的一对多的关系,当其中一个类修改时,可以对其他关联
类不产生影响(即使有修改,也集中在Mediator控制类)。
4,有利于提高类的重用性
缺点:
中介者会膨胀得很大,而且逻辑复杂,原本N个对象直接的相互依赖关系转换为中介者和同事类的依赖关系,同事类越多,中介者的逻辑就越复杂。



