python 全栈开发,Day134(爬虫系列之第1章-requests模块)
一、爬虫系列之第1章-requests模块
爬虫简介
概述

近年来,随着网络应用的逐渐扩展和深入,如何高效的获取网上数据成为了无数公司和个人的追求,在大数据时代,谁掌握了更多的数据,谁就可以获得更高的利益,而网络爬虫是其中最为常用的一种从网上爬取数据的手段。
网络爬虫,即Web Spider,是一个很形象的名字。如果把互联网比喻成一个蜘蛛网,那么Spider就是在网上爬来爬去的蜘蛛。网络蜘蛛是通过网页的链接地址来寻找网页的。从网站某一个页面(通常是首页)开始,读取网页的内容,找到在网页中的其它链接地址,然后通过这些链接地址寻找下一个网页,这样一直循环下去,直到把这个网站所有的网页都抓取完为止。如果把整个互联网当成一个网站,那么网络蜘蛛就可以用这个原理把互联网上所有的网页都抓取下来。
爬虫的价值
互联网中最有价值的便是数据,比如天猫商城的商品信息,链家网的租房信息,雪球网的证券投资信息等等,这些数据都代表了各个行业的真金白银,可以说,谁掌握了行业内的第一手数据,谁就成了整个行业的主宰,如果把整个互联网的数据比喻为一座宝藏,那我们的爬虫课程就是来教大家如何来高效地挖掘这些宝藏,掌握了爬虫技能, 你就成了所有互联网信息公司幕后的老板,换言之,它们都在免费为你提供有价值的数据。
爬虫的基本流程
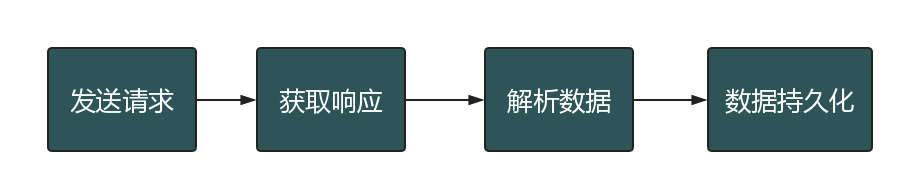
在爬虫的基本流程中,最难的不是解析数据,而是发送请求。为什么这么说呢?因为某些页面做了防爬虫机制,你连访问,都访问不了,那么剩下的流程就走不通了!
预备知识
HTTP请求由三部分组成,分别是:请求行,消息报头,请求正文。
HTTP响应也是由三个部分组成,分别是:状态行,消息报头,相应正文。
httpbin
如果一个人想学习爬虫技术,我会首先推荐他学会使用httpbin!
httpbin(官网|github)是一个很不错测试工具,你可以放心大胆的黑他,而不用担心他报复你。他有点像一个蜜罐,时刻等待着你的光临,然后根据你的请求,给你返回你想要的东西
直接访问页面: http://httpbin.org/get
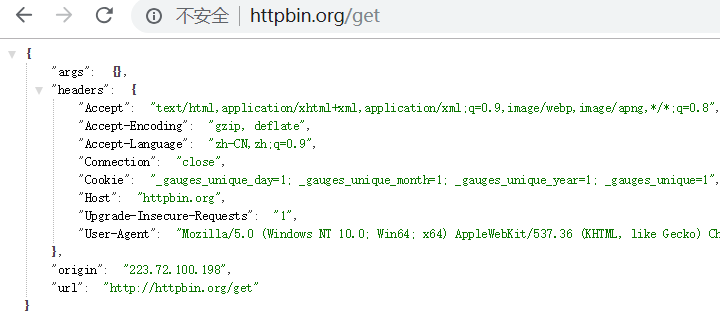
它将你的请求信息,直接展示到页面中!
args 表示get参数
headers 表示请求头
origin 表示 你所在网络运营商的公网IP地址
url 表示访问的url
带一个参数

requests模块
Requests 是使用 Apache2 Licensed 许可证的 HTTP 库。用 Python 编写,真正的为人类着想。
Python 标准库中的 urllib2 模块提供了你所需要的大多数 HTTP 功能,但是它的 API 太渣了。它是为另一个时代、另一个互联网所创建的。它需要巨量的工作,甚至包括各种方法覆盖,来完成最简单的任务。
在Python的世界里,事情不应该这么麻烦。
Requests 使用的是 urllib3,因此继承了它的所有特性。Requests 支持 HTTP 连接保持和连接池,支持使用 cookie 保持会话,支持文件上传,支持自动确定响应内容的编码,支持国际化的 URL 和 POST 数据自动编码。现代、国际化、人性化。
(以上转自Requests官方文档)
安装
pip install requests
基本语法
requests模块支持的请求:
import requests requests.get("http://httpbin.org/get") requests.post("http://httpbin.org/post") requests.put("http://httpbin.org/put") requests.delete("http://httpbin.org/delete") requests.head("http://httpbin.org/get") requests.options("http://httpbin.org/get")
上面列举了几种请求方式,最常用的还是get和post
get请求
1. 基本请求
import requests response=requests.get('https://www.jd.com/',) with open("jd.html","wb") as f: f.write(response.content)
2. 含参数请求
import requests response=requests.get('https://s.taobao.com/search?q=手机') response=requests.get('https://s.taobao.com/search',params={"q":"美女"})
直接访问: https://s.taobao.com/search?q=手机
这样是没有问题,但是后面的条件是动态的。应该使用params,即使有多个参数,它会自动拼接url。
举例:
import requests res = requests.get("https://s.taobao.com/search", params={"q": "美女"}, headers={ 'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/62.0.3202.75 Safari/537.36', } ) with open("res.html", "wb") as f: print(res.text) f.write(res.content)
使用Pycharm打开res.html,效果如下:

3. 含请求头请求
示例1:
import requests response=requests.get('https://dig.chouti.com/', headers={ 'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/62.0.3202.75 Safari/537.36', } )
示例2:

import requests res=requests.post('https://www.lagou.com/jobs/positionAjax.json', headers={ 'Referer':"https://www.lagou.com/jobs/list_python", 'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/63.0.3239.132 Safari/537.36', }, data={ 'first':True, 'pn':2, 'kd':'java高级开发' }, params={ 'gj': '3年及以下', 'px': 'default', 'yx': '25k-50k', 'city': '北京', 'needAddtionalResult': False, 'isSchoolJob': 0 } ) comapines_list=res.json() print(comapines_list)
4. 含cookies请求
import uuid import requests url = 'http://httpbin.org/cookies' cookies = dict(sbid=str(uuid.uuid4())) res = requests.get(url, cookies=cookies) print(res.json())
等同于,下面的代码
import uuid import requests url = 'http://httpbin.org/cookies' cookies = {"sbid":str(uuid.uuid4())} res = requests.get(url, cookies=cookies) print(res.json())
执行输出:
{'cookies': {'sbid': 'f51b0553-2fdc-49ee-a52d-f6fb7472d9ac'}}
比如某些网站,需要携带cookie,否则就拦截!
5. request.session()
import requests # res=requests.get("https://www.zhihu.com/explore") # print(res.cookies.get_dict()) session = requests.session() res1 = session.get("https://www.zhihu.com/explore") print(session.cookies.get_dict()) res2 = session.get("https://www.zhihu.com/question/30565354/answer/463324517", cookies={"abs": "123"})
举例:
import requests res = requests.get("https://www.zhihu.com/explore") print(res.cookies.get_dict()) # 查看响应体携带的cookie
执行输出:
{'_xsrf': 'QHfkaGFpX6OxaDGFcyJq8IeaEJWyYlDz', 'tgw_l7_route': '29b95235203ffc15742abb84032d7e75'}
比如一个网站,有3个页面,分别是a,b,c。
访问a时,响应返回 cookie为1。访问b时,响应返回 cookie为2。
当访问c时,必须要同时具有cookie为1和2的记录。否则拦截掉!
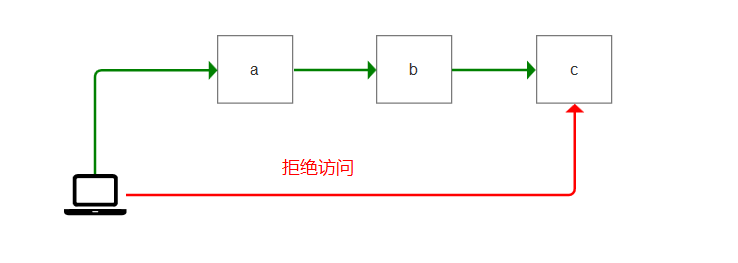
也就是说:必须要先访问a,b之后,才能访问c。
那么这个session的作用在于,每次访问的网页,只要响应信息,携带了cookie。它就会存储到session对象中!
那么我们使用下面的代码,就可以访问c页面了
import requests session = requests.session() res1 = session.get("https://www.xx.com/a") res2 = session.get("https://www.xx.com/b") res3 = session.get("https://www.xx.com/c") print(session.cookies.get_dict())
post请求
1. data参数
requests.post()用法与requests.get()完全一致,特殊的是requests.post()多了一个data参数,用来存放请求体数据
response=requests.post("http://httpbin.org/post",params={"a":"10"}, data={"name":"yuan"})
举例:
直接访问post页面,是被拦截的。因为浏览器访问是get请求
使用post访问访问
import requests res2 = requests.post(url='http://httpbin.org/post',headers={},cookies={},params={'a': "1"},data={"a":1234}) print(res2.text)
执行输出:

{ "args": { "a": "1" }, "data": "", "files": {}, "form": { "a": "1234" }, "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Connection": "close", "Content-Length": "6", "Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded", "Host": "httpbin.org", "User-Agent": "python-requests/2.19.1" }, "json": null, "origin": "223.72.99.154", "url": "http://httpbin.org/post?a=1" }
data为什么是空的呢?
是因为content-type,上面的代码,默认的请求头是:application/x-www-form-urlencoded,它只会放到form里面
如果要data里面有数据,必须是application/json才行!
2. 发送json数据
import requests res1 = requests.post(url='http://httpbin.org/post', data={'name': 'yuan'}) # 没有指定请求头,#默认的请求头:application/x-www-form-urlencoed print(res1.json()) res2 = requests.post(url='http://httpbin.org/post', json={'age': "22", }) # 默认的请求头:application/json) print(res2.json())
举例:
import requests res2 = requests.post(url='http://httpbin.org/post', json={'age': "22", }) # 默认的请求头:application/json) print(res2.text)
执行输出:

{ "args": {}, "data": "{\"age\": \"22\"}", "files": {}, "form": {}, "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Connection": "close", "Content-Length": "13", "Content-Type": "application/json", "Host": "httpbin.org", "User-Agent": "python-requests/2.19.1" }, "json": { "age": "22" }, "origin": "223.72.100.198", "url": "http://httpbin.org/post" }
data里面,就有数据了!
json={'age': "22", } 这句代码,它做了2件事情。
1. 指定content-type 为 application/json
2. 对数据做json序列化
response对象
(1) 常见属性
import requests respone=requests.get('https://sh.lianjia.com/ershoufang/') # respone属性 print(respone.text) print(respone.content) print(respone.status_code) print(respone.headers) print(respone.cookies) print(respone.cookies.get_dict()) print(respone.cookies.items()) print(respone.url) print(respone.history) print(respone.encoding)
举例1:
import requests response = requests.get('https://www.jd.com') print(response)
执行输出:
<Response [200]>
它返回的是一个 Response对象
举例2:
import requests response = requests.get('https://www.jd.com') print(response.status_code)
执行输出:200
举例3:
import requests response = requests.get('https://www.jd.com') print(response.url)
执行输出: https://www.jd.com/
举例4:
import requests response = requests.get('https://www.jd.com') print(response.text) print(type(response.text)) # str
执行输出:
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>京东(JD.COM)-正品低价、品质保障、配送及时、轻松购物!</title> ... </body> </html> <class 'str'>
可以发现,response.text 它是一个字符串
从网络接收过来的,一定是字节流。response.text 将它转化成了字符串!
举例5:
import requests response = requests.get('https://www.jd.com') print(response.encoding) # utf-8,目标网站编码
执行输出:utf-8
不是所有网站都是utf-8,比如汽车之家
import requests response = requests.get('https://www.autohome.com.cn/beijing/') print(response.encoding) # gb2312
执行输出:gb2312
它的网站编码是使用gb2312的!那么我们保持这个网站时,必须使用gb2312编码,否则数据是乱码的!
举例6:
import requests response = requests.get('https://www.jd.com/') print(response.content) # 源数据(字节流)
执行输出:
b'<!DOCTYPE HTML>\n<html lang="zh-CN">\n<head>\n ... </body>\n</html>\n'
它返回的是字节流,不存在于编码问题!
举例7:
import requests response = requests.get('https://www.jd.com/') with open("jd.html","w") as f: f.write(response.text)
执行输出:
UnicodeEncodeError: 'gbk' codec can't encode character '\ue600' in position 79125: illegal multibyte sequence
为什么会报错呢?
因为with open调用的是windows系统默认的编码,它的编码是gbk。而jd.com使用的是utf-8编码!
所以在使用gbk保存时,会报错!
所以,为了解决这个问题。with open必须指定编码为utf-8
import requests response = requests.get('https://www.jd.com/') with open("jd.html","w",encoding="utf-8") as f: f.write(response.text)
再次执行,就不会报错了!
使用Pycharm打开本地的jd.html,效果和官网是一摸一样的!

举例8:
比如访问一个网站,可能会有301跳转
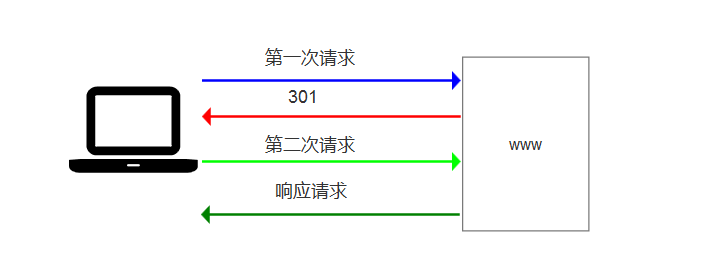
比如访问,链接网的二手房信息
使用http访问
http://bj.lianjia.com/ershoufang/
会跳转到https页面
https://bj.lianjia.com/ershoufang/
举例:
import requests res = requests.get("http://bj.lianjia.com/ershoufang/")print(res.history[0].url) print(res.url)
执行输出:
http://bj.lianjia.com/ershoufang/
https://bj.lianjia.com/ershoufang/
那么通过histroy,就可以得到访问历史了!它能得到重定向之前的url
(2) 编码问题
import requests response=requests.get('http://www.autohome.com/news') #response.encoding='gb2312' #汽车之家网站返回的页面内容为gb2312编码的,而requests的默认编码为ISO-8859-1,如果不设置成gbk则中文乱码 with open("res.html","w") as f: f.write(response.text)
执行报错:
UnicodeEncodeError: 'gbk' codec can't encode character '\xa1' in position 76: illegal multibyte sequence
更改代码
import requests response=requests.get('http://www.autohome.com/news') response.encoding='gbk' #汽车之家网站返回的页面内容为gb2312编码的,而requests的默认编码为ISO-8859-1,如果不设置成gbk则中文乱码 with open("res.html","w") as f: f.write(response.text)
执行代码,打开res.html,效果如下:
图片加载不出来,是因为做了防爬机制!
(3) 下载二进制文件(图片,视频,音频)
import requests response=requests.get('http://bangimg1.dahe.cn/forum/201612/10/200447p36yk96im76vatyk.jpg') with open("res.png","wb") as f: # f.write(response.content) # 比如下载视频时,如果视频100G,用response.content然后一下子写到文件中是不合理的 for line in response.iter_content(): f.write(line)
图片,视频,音频。都是二进制文件,必须使用wb模式写入。
response.iter_content() 表示,将响应体转换为迭代器。这样可以节省内存!缓解服务器压力!
(4) 解析json数据
import requests import json response=requests.get('http://httpbin.org/get') res1=json.loads(response.text) #太麻烦 res2=response.json() #直接获取json数据 print(res1==res2)
(5) Redirection and History
默认情况下,除了 HEAD, Requests 会自动处理所有重定向。可以使用响应对象的 history 方法来追踪重定向。Response.history 是一个 Response 对象的列表,为了完成请求而创建了这些对象。这个对象列表按照从最老到最近的请求进行排序。
>>> r = requests.get('http://github.com') >>> r.url 'https://github.com/' >>> r.status_code 200 >>> r.history [<Response [301]>]
另外,还可以通过 allow_redirects 参数禁用重定向处理:
>>> r = requests.get('http://github.com', allow_redirects=False) >>> r.status_code 301 >>> r.history []
最简单的防爬机制
一般网站,最简单的防爬虫机制,就是判断user-agent是否存在。不存在,则认为是恶意访问,比如爬虫。它会拦截掉,返回一个错误页面!
举例:
比如,直接访问:抽屉热搜
import requests res = requests.get("https://dig.chouti.com/") with open("res.html","wb") as f: f.write(res.content)
使用Pycharm打开res.html,效果如下:
加一个user-agent就可以解决
import requests res = requests.get("https://dig.chouti.com/", headers={ 'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/63.0.3239.132 Safari/537.36', },) with open("res.html","wb") as f: f.write(res.content)
使用Pycharm打开res.html,效果如下:
DRF为什么应用广泛
因为收,iPad,PC携带的user-agent是不一样的!前端根据不同的user-agent,返回不同的页面!
而后端API,针对同一个功能,返回的数据是统一的。
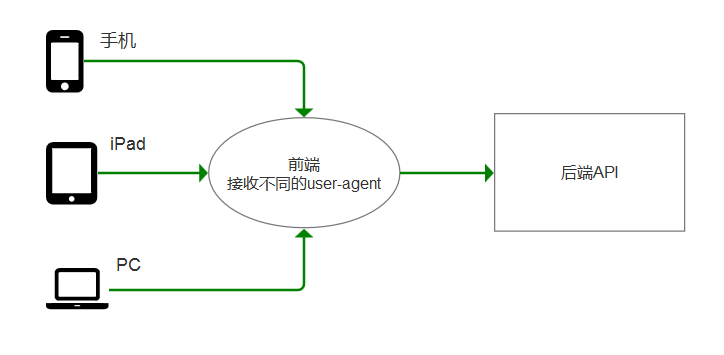
比如,访问jd.com,可以使用iPhone X访问

刷新页面,它会自动跳转到 m.jd.com
它的user-agent也变动了

应用案例
1、模拟GitHub登录,获取登录信息

import requests import re #请求1: r1=requests.get('https://github.com/login') r1_cookie=r1.cookies.get_dict() #拿到初始cookie(未被授权) authenticity_token=re.findall(r'name="authenticity_token".*?value="(.*?)"',r1.text)[0] #从页面中拿到CSRF TOKEN print("authenticity_token",authenticity_token) #第二次请求:带着初始cookie和TOKEN发送POST请求给登录页面,带上账号密码 data={ 'commit':'Sign in', 'utf8':'✓', 'authenticity_token':authenticity_token, 'login':'xx@xx.com', 'password':'xx' } #请求2: r2=requests.post('https://github.com/session', data=data, cookies=r1_cookie, # allow_redirects=False ) print(r2.status_code) #200 print(r2.url) #看到的是跳转后的页面:https://github.com/ print(r2.history) #看到的是跳转前的response:[<Response [302]>] print(r2.history[0].text) #看到的是跳转前的response.text with open("result.html","wb") as f: f.write(r2.content)
步骤解析
如果不登录,直接访问: https://github.com/
网页会提示,让你登录!
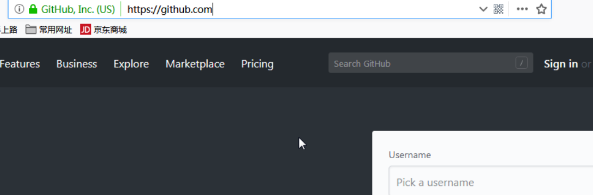
点击sign in,进入登录页面
登录成功之后,跳转到首页:https://github.com/
现在需要爬取页面:https://github.com/
那么直接用requests模块,访问 https://github.com/,是没有意义的!它肯定会拦截!
我们需要模拟 输入用户名和密码,点击 siin in按钮,进入首页的整个过程!
打开浏览器工具-->network,点击preserve log(保存记录)。
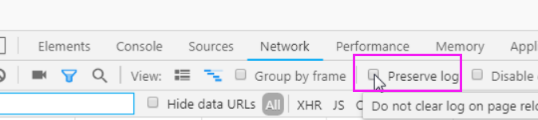
为什么要勾选这个呢?
因为登录之后,页面会刷新一次。所以network中的记录会被重新覆盖,那么我需要得到刷次之前的记录呢?
启用 preserve log,就可以看到了!
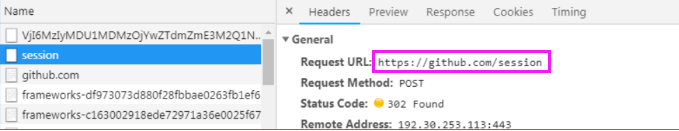
退出github账号,进入登录页面。打开浏览器工具,重新登录一次。查看network信息
这里面的 https://github.com/session,就是提交地址
再看响应信息中的Localtion,这就是调整地址。也就是首页!
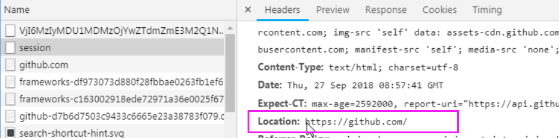
综上所述,我们就可以得出结论了!
模拟github登录示例 1. get 请求访问 https://github.com/login 2. post请求访问 https://github.com/session 3. get 请求访问 https://github.com/
正常登录,就是这3个过程!
有没有必要,从第一个位置,发送请求?
如果直接从 第二步开始,能访问到第三步,说明这样做可以。否则不可以!
测试一下吧,先来看From Data

它需要5个参数。密码是明文的,好吧,先不管它!
这3个,是干啥的呢?不管它,直接复制一下
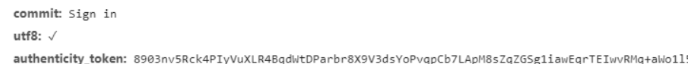
因为是form表单,需要使用data参数。

import requests session = requests.session() res = requests.post("https://github.com/session", data={ 'commit': 'Sign in', 'utf8': '✓', 'authenticity_token': "u89SiiF6aFWFHSOboNVn8w/hbHQIcu0AeoJUTR+OLRP01noYZiCbpJL8E7rex29S5AkJz+w+Te47NC1PwjtXaA==", 'login': 'xx@xx.com', 'password': 'xx' }) with open("res.html","wb") as f: f.write(res.content)
注意:需要改为自己的github账户
运行之后,使用Pycharm打开res.html,效果如下:
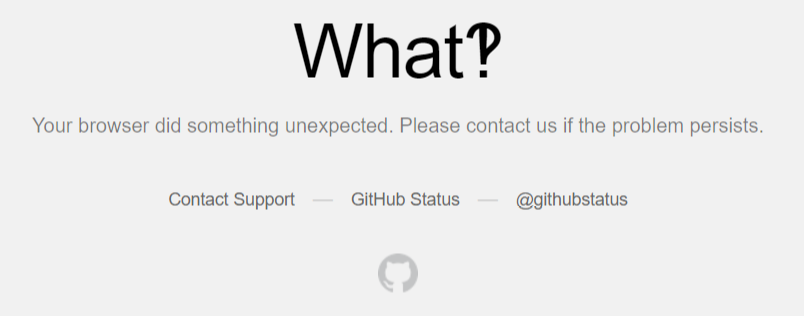
它提示访问非法,说明它已经知道你在爬取了!
怎么办呢?再加一个user-agent和Referer
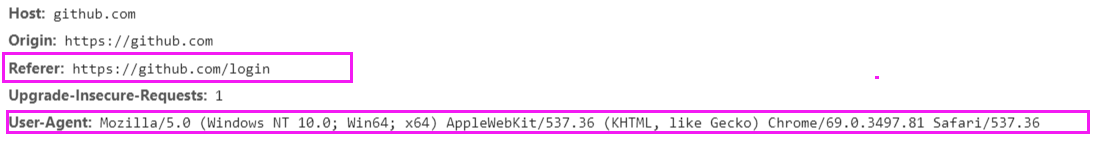
修改代码

import requests session = requests.session() res = requests.post("https://github.com/session", headers={ "Referer":"https://github.com/login", "User-Agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/69.0.3497.81 Safari/537.36" }, data={ 'commit': 'Sign in', 'utf8': '✓', 'authenticity_token': "u89SiiF6aFWFHSOboNVn8w/hbHQIcu0AeoJUTR+OLRP01noYZiCbpJL8E7rex29S5AkJz+w+Te47NC1PwjtXaA==", 'login': 'xx@xx.com', 'password': 'xx' }) with open("res.html","wb") as f: f.write(res.content)
执行代码,再次访问res.html。效果还是一样的!
既然请求头没有问题,那么就是数据有问题了!
打开login页面,搜索关键字 authenticity_token

刷新页面,再次查看
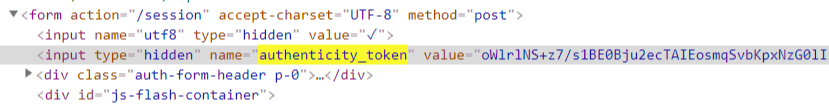
可以发现,它每次是不一样的!
注意:这个authenticity_token不是固定死的。每次访问页面,都是不一样的!
它和django的csrf组件,是一样的效果!
那么就卡在 token了。
只能往上推了,那就是登陆页面。
现在需要使用第一步了,必须找到token值
第一次请求:获取authenticity_token
第二次请求:模拟登录,成功重定向
获取authenticity_token
因为在页面上面,需要使用re模块来匹配
import requests import re r1=requests.get('https://github.com/login') r1_cookie=r1.cookies.get_dict() #拿到初始cookie(未被授权) authenticity_token=re.findall(r'name="authenticity_token".*?value="(.*?)"',r1.text)[0] #从页面中拿到CSRF TOKEN print(authenticity_token)
执行输出:
hLpkfrH6C3kyxB5CXj5adhE0hNOJzmFa4Z++y6Et6+POSA3bw4bsBy/jfp/LFawCch6oWNEZxBF3sKjpw2oFig==
最终代码

import requests import re session = requests.session() #请求1: r1=requests.get('https://github.com/login') r1_cookie=r1.cookies.get_dict() #拿到初始cookie(未被授权) authenticity_token=re.findall(r'name="authenticity_token".*?value="(.*?)"',r1.text)[0] #从页面中拿到CSRF TOKEN print(authenticity_token) #第二次请求:带着初始cookie和TOKEN发送POST请求给登录页面,带上账号密码 res = requests.post("https://github.com/session", headers={ "Referer":"https://github.com/login", "User-Agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/69.0.3497.81 Safari/537.36" }, data={ 'commit': 'Sign in', 'utf8': '✓', 'authenticity_token': authenticity_token, 'login': 'xx@xx.com', 'password': 'xx' },cookies=r1_cookie,) with open("res.html","wb") as f: f.write(res.content)
效果如下:
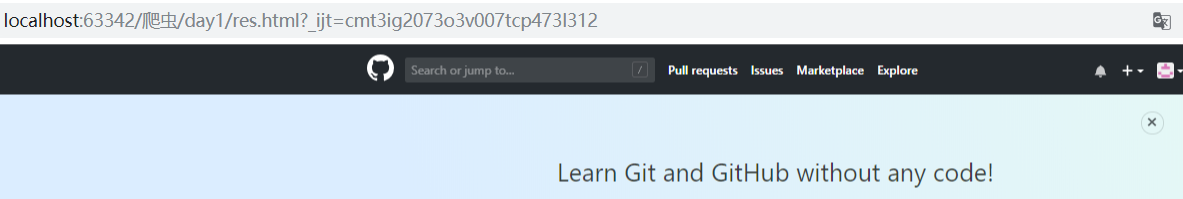
这个,才是真正的首页
2、爬取豆瓣电影信息

import requests import re import json import time from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor pool=ThreadPoolExecutor(50) def getPage(url): response=requests.get(url) return response.text def parsePage(res): com=re.compile('<div class="item">.*?<div class="pic">.*?<em .*?>(?P<id>\d+).*?<span class="title">(?P<title>.*?)</span>' '.*?<span class="rating_num" .*?>(?P<rating_num>.*?)</span>.*?<span>(?P<comment_num>.*?)评价</span>',re.S) iter_result=com.finditer(res) return iter_result def gen_movie_info(iter_result): for i in iter_result: yield { "id":i.group("id"), "title":i.group("title"), "rating_num":i.group("rating_num"), "comment_num":i.group("comment_num"), } def stored(gen): with open("move_info.txt","a",encoding="utf8") as f: for line in gen: data=json.dumps(line,ensure_ascii=False) f.write(data+"\n") def spider_movie_info(url): res=getPage(url) iter_result=parsePage(res) gen=gen_movie_info(iter_result) stored(gen) def main(num): url='https://movie.douban.com/top250?start=%s&filter='%num pool.submit(spider_movie_info,url) #spider_movie_info(url) if __name__ == '__main__': before=time.time() count=0 for i in range(10): main(count) count+=25 after=time.time() print("总共耗费时间:",after-before)
今日作业
1. 爬取拉钩python的所有职位信息,爬取3页即可!(有一个隐藏的反扒机制)
2. 爬取链家二手房源信息,爬取3页即可!
本文参考链接:
https://www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/9449430.html
作业解析
拉钩
1. 爬取拉钩python的所有职位信息
打开拉勾网,打开浏览器工具,输入pythton,点击搜索
网页链接是这个
https://www.lagou.com/jobs/list_python?px=default&city=全国#filterBox
打开浏览器工具-->Network-->XHR
查看第一个链接,点击Preview,它返回的是一个json数据。
将数据一点点展开,result就是我们要的数据了
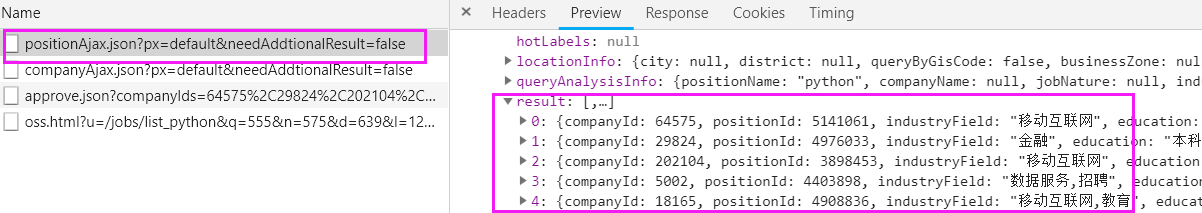
查看请求方式

查看请求参数
pn:表示分页数,kd:表示搜索关键字

接下来,就可以直接上代码了

import requests res = requests.post('https://www.lagou.com/jobs/positionAjax.json', headers={ 'Referer': "https://www.lagou.com/jobs/list_python", 'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/63.0.3239.132 Safari/537.36', }, data={ 'first': True, 'pn': 1, # 页码 'kd': 'python' # 关键字 }, params={ 'px': 'default', 'city': '全国', 'needAddtionalResult': False, } ) with open("lianjia.txt", "a", encoding="utf-8") as f: f.write(res.text + "\n")
参数解释:
我们要请求的地址是
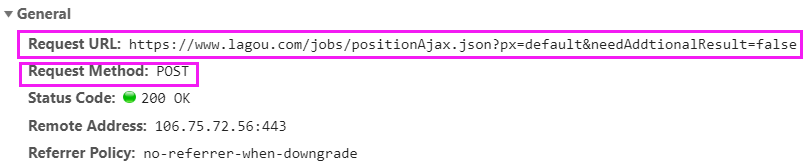
也就是这个
https://www.lagou.com/jobs/positionAjax.json?px=default&needAddtionalResult=false
因此,params参数,指定了参数px和needAddtionalResult
还有一个参数city,是从页面中获取的
https://www.lagou.com/jobs/list_python?px=default&city=全国#filterBox
headers指定了2个参数,Referer和User-Agent,是从这里获取的
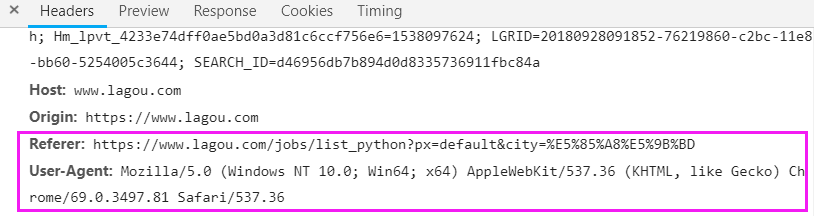
Referer 直接写前半段就可以了,后面的参数可以不要!
执行程序,查看lianjia.txt,它存储的就是一段json
再新建一个py文件,单独处理文件操作

import json with open('lianjia.txt', encoding="utf-8") as f: for line in f: dic = json.loads(line) for i in dic.get('content').get('positionResult').get('result'): print(i.get('positionName'), i.get('city'), i.get('createTime'), i.get('salary'), i.get('workYear'), i.get('education'), i.get('companyShortName'))
执行输出:
Python开发 上海 2018-09-26 14:43:36 13k-26k 3-5年 大专 德邦
...
将这2段代码,结合到一个py文件,最终代码如下:

import requests import time import json page = [x for x in range(1, 4)] # 只爬取3页 for i in page: res=requests.post('https://www.lagou.com/jobs/positionAjax.json', headers={ 'Referer':"https://www.lagou.com/jobs/list_python", 'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/63.0.3239.132 Safari/537.36', }, data={ 'first':True, 'pn':i, # 页码 'kd':'python' # 关键字 }, params={ 'px': 'default', 'city': '全国', 'needAddtionalResult': False, } ) with open("lianjia.txt","a",encoding="utf-8") as f: f.write(res.text+"\n") time.sleep(5) with open('lianjia.txt', encoding="utf-8") as f: for line in f: dic = json.loads(line) for i in dic.get('content').get('positionResult').get('result'): print(i.get('positionName'), i.get('city'), i.get('createTime'), i.get('salary'), i.get('workYear'), i.get('education'), i.get('companyShortName'))
执行输出:
Python开发 上海 2018-09-26 14:43:36 13k-26k 3-5年 大专 德邦
...
拉钩网的防爬机制,不能访问的太频繁。否则会封锁IP,这里我暂停了5秒
还有一种升级方案,使用session访问,它是没有做限制的!

import requests import time import json page = [x for x in range(1, 4)] # 只爬取3页 for i in page: session = requests.session() session.get("https://www.lagou.com/") session.get("https://www.lagou.com/jobs/list_python") res=session.post('https://www.lagou.com/jobs/positionAjax.json', headers={ 'Referer':"https://www.lagou.com/jobs/list_python", 'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/63.0.3239.132 Safari/537.36', }, data={ 'first':True, 'pn':i, # 页码 'kd':'python' # 关键字 }, params={ # 'gj': '3年及以下', 'px': 'default', # 'yx': '25k-50k', 'city': '北京', 'needAddtionalResult': False, # 'isSchoolJob': 0 } ) with open("lianjia.txt","a",encoding="utf-8") as f: f.write(res.text+"\n") # time.sleep(5) with open('lianjia.txt', encoding="utf-8") as f: for line in f: dic = json.loads(line) for i in dic.get('content').get('positionResult').get('result'): print(i.get('positionName'), i.get('city'), i.get('createTime'), i.get('salary'), i.get('workYear'), i.get('education'), i.get('companyShortName'))
执行脚本,效果同上!
链家
2. 爬取链家二手房源信息
这个网站,几乎没有XHR请求。无法直接得到我们想要的信息!它的信息,直接渲染到页面上了。
所以要获取房源信息,只有2个途径
1. 使用正则匹配
2. 使用模块或者框架解析html,比如BS和Xpath模块,还有scrapy
正则玩的不够6,模块和框架不会!。。。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix