python 全栈开发,Day72(昨日作业讲解,昨日内容回顾,Django多表创建)
昨日作业讲解
1.图书管理系统
实现功能:book单表的增删改查
1.1 新建一个项目bms,创建应用book。过程略...
1.2 手动创建static目录,并在目录里面创建css文件夹,修改settings.py,设置static的目录位置

STATICFILES_DIRS=[ os.path.join(BASE_DIR,"static") ]
修改templates的目录位置

TEMPLATES = [ { 'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates', 'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')], 'APP_DIRS': True, 'OPTIONS': { 'context_processors': [ 'django.template.context_processors.debug', 'django.template.context_processors.request', 'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth', 'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages', ], }, }, ]
注册app

INSTALLED_APPS = [ 'django.contrib.admin', 'django.contrib.auth', 'django.contrib.contenttypes', 'django.contrib.sessions', 'django.contrib.messages', 'django.contrib.staticfiles', 'book', ]
下载bootstrap.css放到static目录下的css目录里面
https://cdn.bootcss.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css
修改models.py,设计表

from django.db import models # Create your models here. class Book(models.Model): title=models.CharField(max_length=32,unique=True) price=models.DecimalField(max_digits=8,decimal_places=2,null=True) pub_date=models.DateField() publish=models.CharField(max_length=32) is_pub=models.BooleanField(default=True)
注意:这里没有加id字段,django会自动创建id字段,并设置主键自增,类型为int
默认的是sqlite3数据库,直接用它就可以了。它是基于文件的,不需要用户名和密码。
执行2个命令
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
就可以创建sqlite数据库
点击Pycharm右侧的数据库,添加sqlite
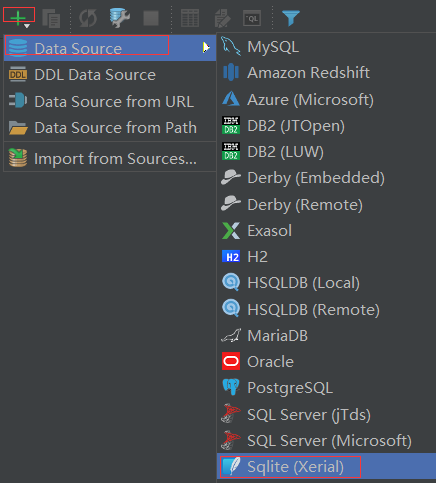
点击下载驱动
开始安装
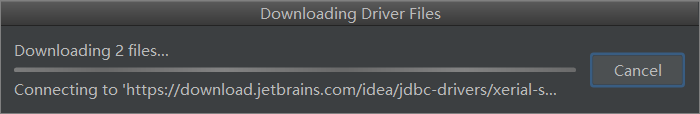
选择file文件,点击测试连接,点击Ok
展开右边的数据库,打开book_book

编辑urls.py,新增url

from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path,re_path from book import views urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('', views.index), path('index/', views.index), path('books/add/', views.add), path('books/manage/', views.manage), re_path('books/delete/(?P<id>\d+)', views.delete), re_path('books/modify/(?P<id>\d+)', views.modify), ]
path('', views.index),表示输入url: http://127.0.0.1:8001 可以直接跳转首页
修改views.py,增加视图函数

from django.shortcuts import render,redirect,HttpResponse from book import models # Create your views here. def index(request): #首页 ret = models.Book.objects.all().exists() # 判断表是否有记录 if ret: book_list=models.Book.objects.all() # 查询表的所有记录 return render(request,"index.html",{"book_list":book_list}) else: hint = '<script>alert("没有书籍,请添加书籍");window.location.href="/books/add"</script>' return HttpResponse(hint) # js跳转到添加页面 def add(request): # 添加 if request.method=="POST": # print(request.POST) title=request.POST.get("title") price=request.POST.get("price") pub_date=request.POST.get("pub_date") publish=request.POST.get("publish") is_pub=request.POST.get("is_pub") #插入一条记录 obj=models.Book.objects.create(title=title,price=price,publish=publish,pub_date=pub_date,is_pub=is_pub) print(obj.title) hint = '<script>alert("添加成功");window.location.href="/index/"</script>' return HttpResponse(hint) # js跳转到首页 return render(request,"add.html") # 默认渲染添加页面 def delete(request,id): # 删除 ret = models.Book.objects.filter(id=id).delete() # 返回元组 if ret[0]: # 取值为1的情况下 hint = '<script>alert("删除成功");window.location.href="/index/"</script>' return HttpResponse(hint) else: # 取值为0的情况下 hint = '<script>alert("删除失败");window.location.href="/index/"</script>' return HttpResponse(hint) def manage(request): # 管理页面 ret = models.Book.objects.all().exists() if ret: book_list = models.Book.objects.all() #加载管理页面 return render(request, "manage.html", {"book_list": book_list}) else: hint = '<script>alert("没有书籍,请添加书籍");window.location.href="/books/add"</script>' return HttpResponse(hint) def modify(request,id): # 修改 if request.method == "POST": title = request.POST.get("title") price = request.POST.get("price") pub_date = request.POST.get("pub_date") publish = request.POST.get("publish") is_pub = request.POST.get("is_pub") #更新一条记录 ret = models.Book.objects.filter(id=id).update(title=title, price=price, publish=publish, pub_date=pub_date, is_pub=is_pub) # print(ret) if ret: # 判断返回值为1 hint = '<script>alert("修改成功");window.location.href="/index/"</script>' return HttpResponse(hint) # js跳转 else: # 返回为0 hint = '<script>alert("修改失败");window.location.href="/index/"</script>' return HttpResponse(hint) # js跳转 book = models.Book.objects.get(id=id) # 默认获取id值 return render(request, "modify.html", {"book": book}) # 渲染指定id的记录
创建templates目录,在templates目录下创建base.html
注意:这个是模板页面

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> {% block title %} <title>title</title> {% endblock title %} <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/css/bootstrap.min.css"> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .header { width: 100%; height: 60px; background-color: #369; } .title { line-height: 60px; color: white; font-weight: 100; margin-left: 20px; font-size: 20px; } .container{ margin-top: 20px; } .table th, .table td { text-align: center; vertical-align: middle!important; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="header"> <p class="title"> 图书管理系统 </p> </div> <div class="container"> <div class="row"> <div class="col-md-3"> <div class="panel panel-danger"> <div class="panel-heading"><a href="/index/">查看书籍</a></div> <div class="panel-body"> Panel content </div> </div> <div class="panel panel-success"> <div class="panel-heading"><a href="/books/add/">添加书籍</a></div> <div class="panel-body"> Panel content </div> </div> <div class="panel panel-warning"> <div class="panel-heading"><a href="/books/manage/">管理书籍</a></div> <div class="panel-body"> Panel content </div> </div> </div> <div class="col-md-9"> {% block content %} {% endblock %} </div> </div> </div> </body> </html>
创建index.html,它是首页

{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block title %}
<title>查看书籍</title>
{% endblock title %}
{% block content %}
<h3>查看书籍</h3>
<table class="table table-hover table-striped ">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>名称</th>
<th>价格</th>
<th>出版日期</th>
<th>出版社</th>
<th>是否出版</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for book in book_list %}
<tr>
<td>{{ book.title }}</td>
<td>{{ book.price }}</td>
<td>{{ book.pub_date|date:"Y-m-d" }}</td>
<td>{{ book.publish }}</td>
<td>
{% if book.is_pub %}
已出版
{% else %}
未出版
{% endif %}
</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
{% endblock content %}
创建add.html,它是添加页面

{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block title %}
<title>添加书籍</title>
{% endblock title %}
{% block content %}
<h3>添加书籍</h3>
<form action="" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">书籍名称</label>
<input type="text" name="title" class="form-control">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">价格</label>
<input type="text" name="price" class="form-control">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">出版日期</label>
<input type="date" name="pub_date" class="form-control">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">出版社</label>
<input type="text" name="publish" class="form-control">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">是否出版</label>
<select name="is_pub" id="" class="form-control">
<option value="1">已出版</option>
<option value="0" selected="selected">未出版</option>
</select>
</div>
<input type="submit" class="btn btn-success pull-right" value="添加">
</form>
{% endblock content %}
创建manage.html,它是管理页面

{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block title %}
<title>管理书籍</title>
{% endblock title %}
{% block content %}
<h3>管理书籍</h3>
<table class="table table-hover table-striped ">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>名称</th>
<th>价格</th>
<th>出版日期</th>
<th>出版社</th>
<th>是否出版</th>
<th>删除</th>
<th>编辑</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for book in book_list %}
<tr>
<td>{{ book.title }}</td>
<td>{{ book.price }}</td>
<td>{{ book.pub_date|date:"Y-m-d" }}</td>
<td>{{ book.publish }}</td>
<td>
{% if book.is_pub %}
已出版
{% else %}
未出版
{% endif %}
</td>
<td>
<a href="/books/delete/{{ book.id }}" >
<button type="button" class="btn btn-danger" data-toggle="modal" id="modelBtn">删除</button>
</a>
</td>
<td>
<a href="/books/modify/{{ book.id }}">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-success" data-toggle="modal">编辑</button>
</a>
</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
{% endblock content %}
创建modify.html,它是修改页面

{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block title %}
<title>修改书籍</title>
{% endblock title %}
{% block content %}
<h3>修改书籍</h3>
<form action="" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">书籍名称</label>
<input type="text" name="title" class="form-control" value="{{ book.title }}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">价格</label>
<input type="text" name="price" class="form-control" value="{{ book.price }}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">出版日期</label>
<input type="date" name="pub_date" class="form-control" value="{{ book.pub_date|date:"Y-m-d" }}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">出版社</label>
<input type="text" name="publish" class="form-control" value="{{ book.publish }}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">是否出版</label>
<select name="is_pub" id="" class="form-control">
{% if book.is_pub %}
<option value="1" selected="selected">已出版</option>
<option value="0">未出版</option>
{% else %}
<option value="1">已出版</option>
<option value="0" selected="selected">未出版</option>
{% endif %}
</select>
</div>
<input type="submit" class="btn btn-default pull-right" value="修改">
</form>
{% endblock content %}
启动django项目,访问首页
添加一条数据
提示添加成功
效果如下:
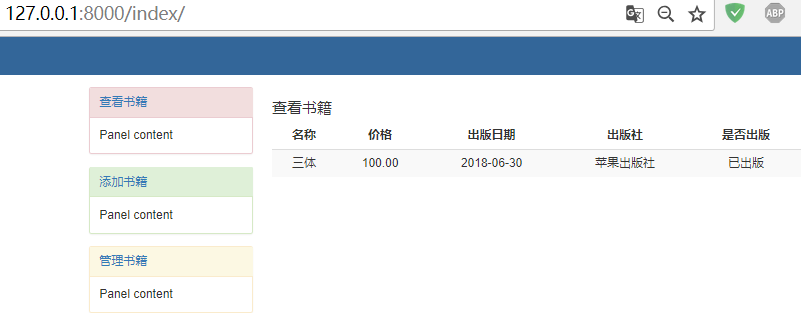
点击左侧的管理书籍
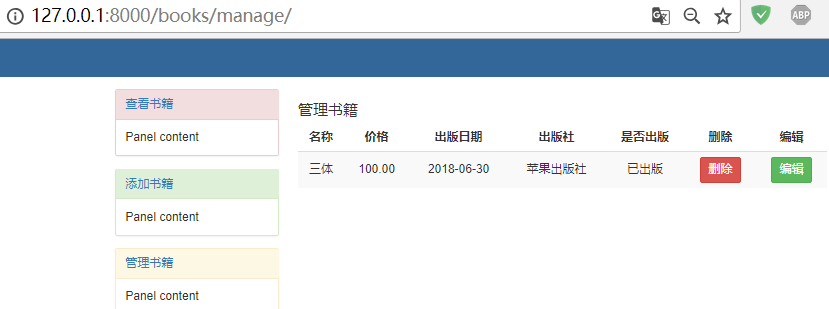
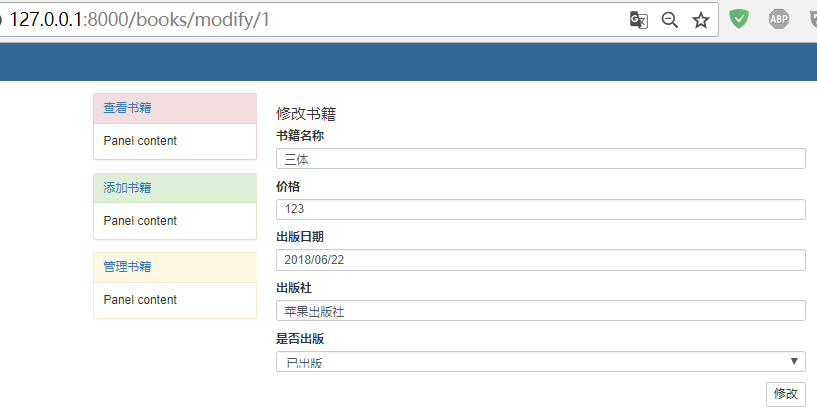
点击编辑按钮,修改价格和日期
提示修改成功
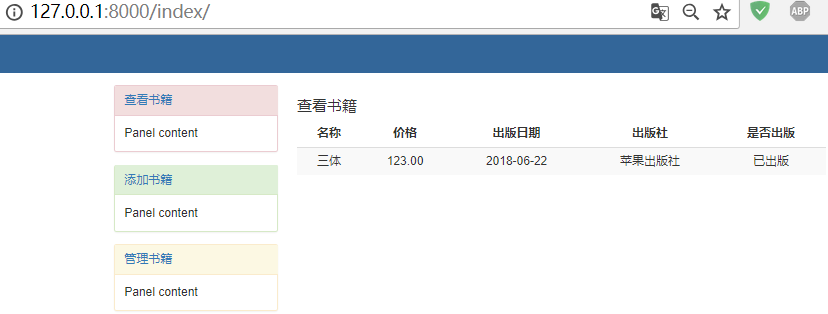
查看首页,发现数据更改过来了!
2.查询练习
答案:

1 查询苹果出版社过的价格大于200的书籍 Book.objects.filter(price__gt=200,publish="苹果出版社",is_pub=True) 2 查询2017年6月出版的所有以py开头的书籍名称 Book.objects.filter(title__startswith="py",pub_date__year=2017,pub_date__month=6) 3 查询价格为50,100或者150的所有书籍名称及其出版社名称 Book.objects.filter(price__in=[50,100,150]).values("title","publish") 4 查询价格在100到200之间的所有书籍名称及其价格 Book.objects.filter(price__range=[100,200]).values("title","price") 5 查询所有人民出版社出版的书籍的价格(从高到低排序,去重) Book.objects.filter(publish="人民出版社").order_by("prcie").reverse().values("prcie").distinct() 6 查询价格大于200的书籍的个数 Book.objects.filter(price__gt=200).count() 7 查询价格不等于100的所有书籍 Book.objects.exclude(prcie=100) 8 查询苹果出版社出版的书籍中的第3-7本(前提存在足够数量的书籍) Book.objects.filter(publish="苹果出版社")[2:7]
昨日内容回顾:

单表操作 class Book(models.Model): title=models.CharField(max_length=32,unique=True) price=models.DecimalField(max_digits=8,decimal_places=2,null=True)# 999999.99 pub_date=models.DateField() publish=models.CharField(max_length=32) is_pub=models.BooleanField(default=True) def __str__(self): return self.title 添加记录: 添加记录方式1: Book.objects.create(title="三体",....) 添加记录方式1: book=Book(title="三体",....) book.save() 查询记录: 查询API: 1 Book.objects.all() # querysey [obj,....] 2 Book.objects.filter(title="三体") # querysey [obj,....] queryset.filter() # 返回值 queryset 3 Book.objects.exclude(title="三体") # querysey [obj,....] 4 Book.objects.all().first() # obj 5 Book.objects.all().last() # obj 6 Book.objects.all()[0] # obj 7 Book.objects.get(title="三体") # obj ################################################# 8 queryset.order_by() # 返回值 queryset 9 queryset.reverse() # 返回值 queryset 10 queryset.count() # 返回值 int (queryset的终止函数) Book.objects.all().filter(price__gt=100).order_by("pirce").count() 11 queryset.exist() # 返回值是布尔值 ################################################# 12 queryset.values("price") # 返回值 queryset [{"price":123},{"price":124},{"price":13}] 13 queryset.valueslist("price") # 返回值 queryset [(123,),(124,),(345,)] 14 queryset.distinct("price") # 返回值 queryset 模糊查询 __ Book.objects.filter(price__in=[100,200,300]) Book.objects.filter(price__gt=100) Book.objects.filter(price__lt=100) Book.objects.filter(price__range=[100,200]) Book.objects.filter(title__contains="x") Book.objects.filter(title__icontains="x") Book.objects.filter(title__startswith="py") Book.objects.filter(pub_date__year=2012)
models.py里面的Book类,就是一个model对象。
对象可以调用属性字段,queryset可以调用对应的方法
下面这种,就属于链式操作。因为queryset可以调用API接口,只要前一个接口的返回值是queryset,它可以可以一直调用API接口,除非遇到返回值不是queryset的情况下,链式操作,才可以终止。因为count的返回值是int,所以到这里,就结束了!不能再调用API接口了!
Book.objects.all().filter(price__gt=100).order_by("pirce").count()
distinct是去重操作,看下面的代码,执行是没有意义的。因为每一条记录,都是唯一的。
Book.objects.all().distinct()
icontains表示不区分大小写。
三、Django多表创建
如何确定表关系?
表关系是在2张表之间建立的,没有超过2个表的情况。
那么相互之间有2条关系线,先来判断一对多的关系。
如果其中一张表的记录能够对应另外一张表的多条记录,那么关系线成立!
如果只有一条线成立,那么就是一对多的关系。
如果有2条线成立,那么就是多对多的关系。
一对多
比如book和publish。一本书不能对应多个出版社(常规是这样的,否则就盗版了),那么不成立。
一个出版社可以对应多本书,关系线成立。所以book和publish表的关系是一对多的关系
多对多
多对多的关系,就是2张表互相对应多条记录。
比如book和author。一本书可以有多个作者,一个作者可以写多本!
一对一
一对一的关系,就很简单了,彼此唯一。
比如author和authordetail是一对一的关系。
如何建立关联
一对多:
一旦确定一对多的关系:在多的表中创建关联字段
多对多:
一旦确定多对多的关系:创建第三张关系表
一对一:
一旦确定一对一的关系 : 创建关联字段(任意一张表创建都可以)
一般情况下,在重要的表创建关联字段
3种表关系的演进
一对多
看下面一张book表
| id | title | price | pub_date | publish |
| 1 | 西游记 | 123 | 1743-04-12 | 苹果出版社 |
如果需要查询出版社的邮箱呢?再加一列
| id | title | price | pub_date | publish | |
| 1 | 西游记 | 123 | 1743-04-12 | 苹果出版社 | 123@qq.com |
查询出版社的地址呢?再加一列
| id | tiitle | price | pub_date | publish | addr | |
| 1 | 西游记 | 123 | 1743-04-12 | 苹果出版社 | 123@qq.com | 北京 |
添加2条记录
| id | title | price | pub_date | publish | addr | |
| 1 | 西游记 | 123 | 1743-04-12 | 苹果出版社 | 123@qq.com | 北京 |
| 2 | 水浒传 | 456 | 1743-04-12 | 苹果出版社 | 123@qq.com | 北京 |
| 3 | 红楼梦 | 678 | 1743-04-12 | 橘子出版社 | 123@qq.com | 北京 |
问题来了:出版社,邮箱,地址,都重复了!这边非常浪费磁盘空间!
怎么解决这个问题呢?那么多表,就是为了解决问题,而诞生的。
将上面的单表,拆分成2张表。
book表,关联字段为publish_id
| id | title | price | pub_date | publish_id |
| 1 | 西游记 | 123 | 1743-04-12 | 1 |
| 2 | 水浒传 | 456 | 1743-04-12 | 1 |
| 3 | 红楼梦 | 678 | 1743-04-12 | 2 |
publish表
| id | name | addr | |
| 1 | 苹果出版社 | 123@qq.com | 北京 |
| 2 | 橘子出版社 | 456@qq.com | 南京 |
这样就可以节省空间
举例:查询西游记的出版社的邮箱
使用子查询(一次查询结果作为另一个查询的条件)
多对多
book和author是多对多的关系
一本书可以有多个作者,一个作者可以写多本!
常规做法,可能是这样的
book表
| id | title | price | pub_date | publish | author_id |
| 1 | 西游记 | 123 | 1743-04-12 | 1 | 1,2 |
| 2 | 水浒传 | 456 | 1743-04-12 | 1 | 1,2 |
author表
| id | name | age | book_id |
| 1 | xiao | 23 | 1,2 |
| 2 | zhang | 24 | 1,2 |
上面的方案不好,为什么呢?取字段的值,还得用split方法,用逗号分隔。它的返回结果是列表,再对列表进行循环。这样太麻烦了!所以,必须得创建第三张关系表
book表
| id | title | price | pub_date | publish_id |
| 1 | 西游记 | 123 | 1743-04-12 | 1 |
| 2 | 水浒传 | 456 | 1743-04-12 | 2 |
author表
| id | name | age | ad_id |
| 1 | xiao | 23 | 1 |
| 2 | zhang | 24 | 2 |
book_author(关系表)
关系表有且只有3个字段,分别是id,book_id(book表主键),author_id(author表主键)
| id | book_id | author_id |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 2 | 2 |
| 4 | 2 | 2 |
举例:查询西游记所有的作者
思路:先查询西游记的主键id,在关系表中查询id=book_id。最后通过author_id查询author表的作者!
一对一
author和authordetail是一对一的关系
一个作者对应唯一的详细信息
由于authordetail表是author表的延伸,所以在author表创建关联字段
author表
ad_id是关联字段,关联字段的值必须唯一,需要设置唯一属性
| id | name | age | ad_id |
| 1 | xiao | 25 | 1 |
| 2 | zhang | 26 | 2 |
authordetail表
gf表示女朋友,tel表示电话。
| id | gf | tel |
| 1 | 赵丽颖 | 110 |
| 2 | 刘诗诗 | 111 |
看下面一张图,这是5个表的关系图
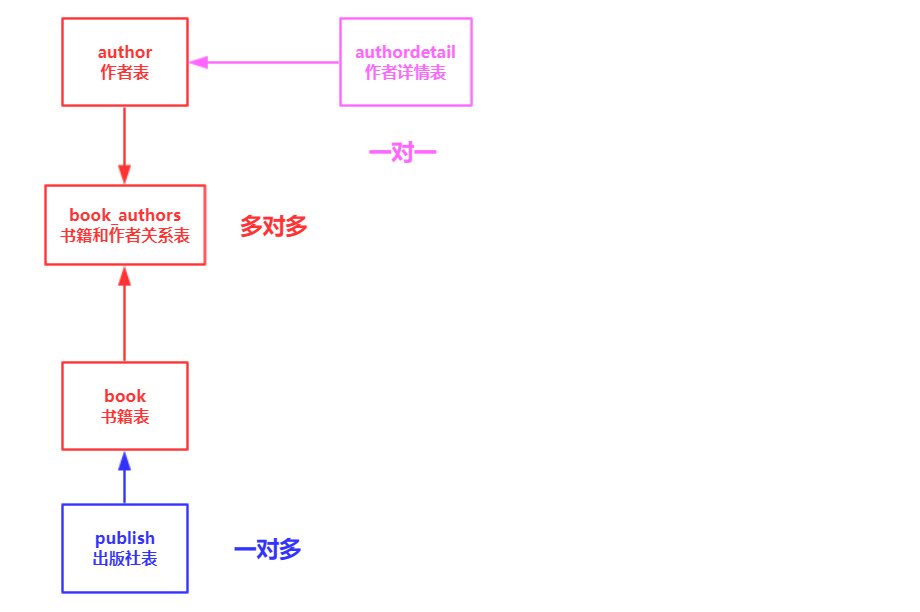
它是一个完整的系统,包含了3种表关系。
三、多表创建
创建模型
实例:我们来假定下面这些概念,字段和关系
作者模型:一个作者有姓名和年龄。
作者详细模型:把作者的详情放到详情表,包含生日,手机号,家庭住址等信息。作者详情模型和作者模型之间是一对一的关系(one-to-one)
出版商模型:出版商有名称,所在城市以及email。
书籍模型: 书籍有书名和出版日期,一本书可能会有多个作者,一个作者也可以写多本书,所以作者和书籍的关系就是多对多的关联关系(many-to-many);一本书只应该由一个出版商出版,所以出版商和书籍是一对多关联关系(one-to-many)。
有5个表,这里面有3种关系,分别是一对一,一对多,多对多
正常的sql建表

#作者表 CREATE TABLE `author` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(32) NOT NULL, `age` int(11) NOT NULL, `ad_id` int(11) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), UNIQUE KEY `ad_id` (`ad_id`), CONSTRAINT `author_ad_id_384abbeb_fk_authordetail_id` FOREIGN KEY (`ad_id`) REFERENCES `authordetail` (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; #作者详情表 CREATE TABLE `authordetail` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `gf` varchar(32) NOT NULL, `tel` varchar(32) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; #书籍表 CREATE TABLE `book` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `title` varchar(32) NOT NULL, `price` decimal(8,2) DEFAULT NULL, `pub_date` date NOT NULL, `publish_id` int(11) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), UNIQUE KEY `title` (`title`), KEY `book_publish_id_d96d3535_fk_publish_id` (`publish_id`), CONSTRAINT `book_publish_id_d96d3535_fk_publish_id` FOREIGN KEY (`publish_id`) REFERENCES `publish` (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; #书籍和作者关系表 CREATE TABLE `book_authors` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `book_id` int(11) NOT NULL, `author_id` int(11) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), UNIQUE KEY `book_authors_book_id_author_id_36f1e11a_uniq` (`book_id`,`author_id`), KEY `book_authors_author_id_5acae95a_fk_author_id` (`author_id`), CONSTRAINT `book_authors_author_id_5acae95a_fk_author_id` FOREIGN KEY (`author_id`) REFERENCES `author` (`id`), CONSTRAINT `book_authors_book_id_19c7077f_fk_book_id` FOREIGN KEY (`book_id`) REFERENCES `book` (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; #出版社表 CREATE TABLE `publish` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(32) NOT NULL, `email` varchar(32) NOT NULL, `addr` varchar(32) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
使用ORM创建表
ORM如果遇到关联字段,会自动添加_id后缀
一对一关系表
authordetail表

class AuthorDetail(models.Model): gf=models.CharField(max_length=32) tel=models.CharField(max_length=32)
authordetail表虽然没有定义id字段,但是ORM创建表时,会自动添加id字段,设置主键。字段类型为int,设置自增属性!
author表

class Author(models.Model): name=models.CharField(max_length=32) age=models.IntegerField() # 与AuthorDetail建立一对一的关系 # ad=models.ForeignKey(to="AuthorDetail",to_field="id",on_delete=models.CASCADE,unique=True) ad=models.OneToOneField(to="AuthorDetail",to_field="id",on_delete=models.CASCADE,)
OneToOneField 表示创建一对一关系。
to 表示需要和哪张表创建关系
to_field 表示关联字段
on_delete=models.CASCADE 表示级联删除。假设a表删除了一条记录,b表也还会删除对应的记录。
ad表示关联字段,但是ORM创建表的时候,会自动添加_id后缀。那么关联字段为ad_id
注意:创建一对一关系,会将关联字添加唯一属性。比如:ad_id
一对多关系表
publish表

class Publish(models.Model): name=models.CharField(max_length=32) email=models.CharField(max_length=32) addr=models.CharField(max_length=32)
book表

class Book(models.Model): title=models.CharField(max_length=32,unique=True) price=models.DecimalField(max_digits=8,decimal_places=2,null=True) pub_date=models.DateField() # 与Publish建立一对多的关系,外键字段建立在多的一方 publish=models.ForeignKey(to="Publish",to_field="id",on_delete=models.CASCADE) # 与Author表建立多对多的关系,ManyToManyField可以建在两个模型中的任意一个,自动创建关系表book_authors authors=models.ManyToManyField(to="Author")
ForeignKey 表示建立外键
to 表示需要和哪张表创建关系
to_field 表示关联字段
on_delete=models.CASCADE 表示级联删除。使用ForeignKey必须要加on_delete。否则报错。这是2.x规定的
ManyToManyField 表示建立多对多的关系。它只需要一个to参数,表示和哪张表创建多对多关系!
这里是在book模型下定义了多对多关系,它会自动创建一张额外的关系表。表的名字就是当前模型的名字(book)+关系的属性名(等式左边的属性名authors)。
也就是会创建表book_authors,它只有3个字段,分别是:本身表的id,boo表主键id,authors表主键id。
book_authors表,应该是这个样子的!
| id | book_id | author_id |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 2 | 2 |
| 4 | 2 | 2 |
多对多
book和author是多对多的关系,在上面已经创建好了。
注意:book模型类,会创建2张表。一个是book本身的表,一个是book和author的关系表
使用ORM模型创建表,完整代码如下:

from django.db import models # Create your models here. class Book(models.Model): title=models.CharField(max_length=32,unique=True) price=models.DecimalField(max_digits=8,decimal_places=2,null=True) pub_date=models.DateField() # 与Publish建立一对多的关系,外键字段建立在多的一方 publish=models.ForeignKey(to="Publish",to_field="id",on_delete=models.CASCADE) # 与Author表建立多对多的关系,ManyToManyField可以建在两个模型中的任意一个,自动创建关系表book_authors authors=models.ManyToManyField(to="Author") class Publish(models.Model): name=models.CharField(max_length=32) email=models.CharField(max_length=32) addr=models.CharField(max_length=32) class Author(models.Model): name=models.CharField(max_length=32) age=models.IntegerField() # 与AuthorDetail建立一对一的关系 # ad=models.ForeignKey(to="AuthorDetail",to_field="id",on_delete=models.CASCADE,unique=True) ad=models.OneToOneField(to="AuthorDetail",to_field="id",on_delete=models.CASCADE,) class AuthorDetail(models.Model): gf=models.CharField(max_length=32) tel=models.CharField(max_length=32)
注意:模型类的每一个属性,并不一定会创建字段。有些会创建表,比如ManyToManyField
生成表如下:
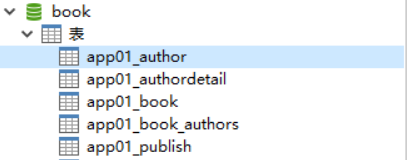
注意事项:
- 表的名称
myapp_modelName,是根据 模型中的元数据自动生成的,也可以覆写为别的名称 id字段是自动添加的- 对于外键字段,Django 会在字段名上添加"_id" 来创建数据库中的列名
- 这个例子中的
CREATE TABLESQL 语句使用PostgreSQL 语法格式,要注意的是Django 会根据settings 中指定的数据库类型来使用相应的SQL 语句。 - 定义好模型之后,你需要告诉Django _使用_这些模型。你要做的就是修改配置文件中的INSTALL_APPSZ中设置,在其中添加
models.py所在应用的名称。 - 外键字段 ForeignKey 有一个 null=True 的设置(它允许外键接受空值 NULL),你可以赋给它空值 None 。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix