python--Scrapy模块的使用
python--Scrapy模块的使用
Scrapy是一个为了爬取网站数据,提取结构性数据而编写的应用框架。 其可以应用在数据挖掘,信息处理或存储历史数据等一系列的程序中。
Scrapy 使用了 Twisted异步网络库来处理网络通讯。整体架构大致如下
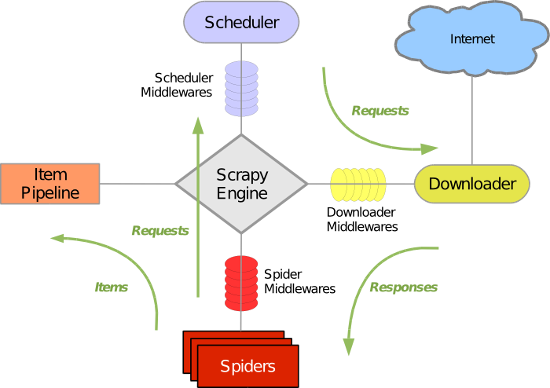
各个组件:
Scrapy引擎:
是框架核心,用来处理调度整个系统的数据流处理
Scheduler调度器:
用来接收引擎发送过来的请求,压入队列中,并在引擎再次请求时返回,就是在我们所要爬取的url全部放入一个优先队列中,由它来决定下一个处理的url是什么,同时他会自动将重复的url去除
注意:我们在创建一个项目时,在spider中会存在一个start_urls = ['http://dig.chouti.com/'],他将是我们的初始url,会在项目启动后被引擎放入调度器中开始处理
Downloader下载器:
用于下载网页内容,并将网页内容返回给蜘蛛(下载器是基于twisted实现)
Item解析器:
设置数据存储模板,用于结构化数据。为下一步的持久化数据做处理,类似于Django中的models,设置存储字段等数据,解析数据
Pipeline项目管道
负责处理爬虫从网页中抽取的实体,主要的功能是持久化实体、验证实体的有效性、清除不需要的信息。当页面被爬虫解析后,将被发送到项目管道,并经过几个特定的次序处理数据。
Downloader Middlewares下载器中间件
位于Scrapy引擎和下载器之间的框架,主要是处理Scrapy引擎与下载器之间的请求及响应。
Spider Middlewares爬虫中间件
介于Scrapy引擎和爬虫之间的框架,主要工作是处理蜘蛛的响应输入和请求输出。
Scheduler Middewares调度中间件
介于Scrapy引擎和调度之间的中间件,从Scrapy引擎发送到调度的请求和响应。
Scrapy运行流程
1.引擎从调度器中取出一个连接URL,用于接下来的抓取
2.引擎将URL封装为一个请求Request传给下载器
3.下载器将资源下载,封装为应答包Response
4.爬虫解析Response
5.解析出实体Item,将实体通过管道解析持久化操作
6.若是解析出URL,将其放入调度器中等待抓取
注意:第一步之前,是先去爬虫start_url中获取初始网址,进行操作
项目创建的基本命令
1.创建项目
|
1
|
scrapy startproject 项目名 |
|
1
|
scrapy startproject scrapyPro |
2.进入项目,创建爬虫
cd 项目名
scrapy genspider 项目列表名 初始url(后面可以修改)
cd scrapyPro
scrapy genspider chouti chouti.com
3.展示爬虫应用列表
scrapy list
chouti
4.运行爬虫应用
scrapy crawl 爬虫应用名称
scrapy crawl chouti --nolog #--nolog不打印日志
项目结构
project_name/ scrapy.cfg #项目的主配置文件 project_name/ __init__.py items.py #设置数据存储模板,用于结构化数据:类似于Django中models pipelines.py #数据处理行为:如数据的持久化 settings.py #配置文件:递归层数,并发数等 spiders/ #爬虫目录,我们可以创建多个爬虫在此 __init__.py 爬虫1.py 爬虫2.py 爬虫3.py
简单实例应用(获取抽屉的新闻标题和URL,并将其保存到文件,实现持久化操作)
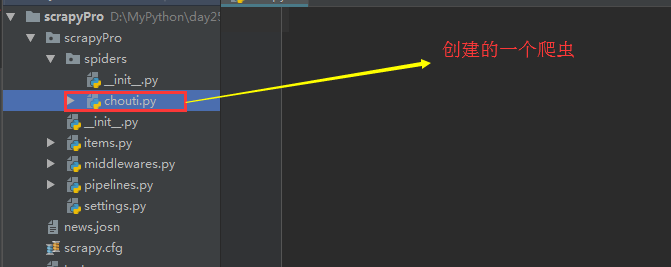
chouti爬虫的编写
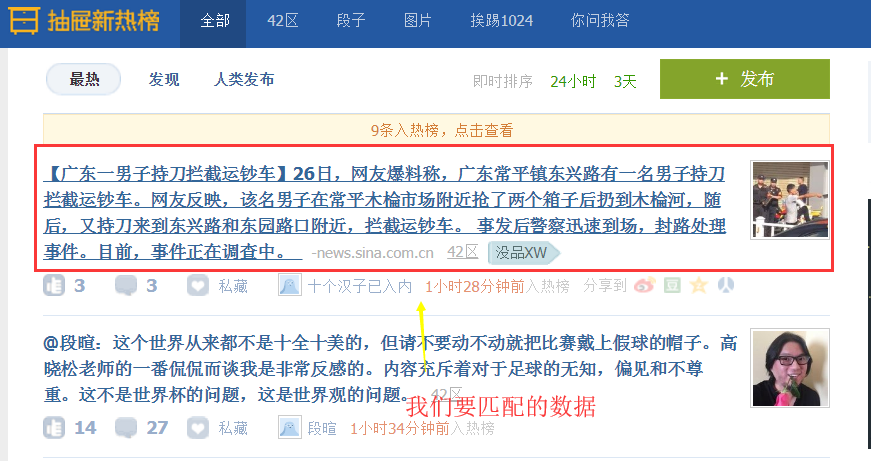
import scrapy,hashlib from scrapy.selector import Selector,HtmlXPathSelector from scrapy.http import Request import sys,io from ..items import ChoutiItem sys.stdout=io.TextIOWrapper(sys.stdout.buffer,encoding='gb18030') #设置原因:在windows下,我们需要在cmd命令行下启动项目,而cmd默认是gbk编码,而py3是utf-8为了保持编码一致,避免乱码,我们需要修改 class ChoutiSpider(scrapy.Spider): name = 'chouti' allowed_domains = ['chouti.com'] #允许采集的域名 start_urls = ['http://dig.chouti.com/'] #初始url def parse(self, response): #response.url/text/body/meta含有访问深度 item_objs = Selector(response=response).xpath("//div[@class='item']//a[@class='show-content color-chag']") #注意这里过滤class不能只选用一个,必须将全部的class加上 for item in item_objs: title = item.xpath("text()").extract_first().strip() href = item.xpath("@href").extract_first() #想要将数据持久化,必须在Item中设置数据字段 item_obj = ChoutiItem(title=title,href=href) # 将item对象传递给pipeline yield item_obj
items.py文件的编写:设置数据存储模板,之后才能够实现持久化处理
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define here the models for your scraped items # # See documentation in: # https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html import scrapy class ScrapyproItem(scrapy.Item): # define the fields for your item here like: # name = scrapy.Field() pass class ChoutiItem(scrapy.Item): # define the fields for your item here like: title = scrapy.Field() href = scrapy.Field()
pipeline.py文件编写:实现数据持久化操作
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define your item pipelines here # # Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting # See: https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html class ScrapyproPipeline(object): def process_item(self, item, spider): #写入文件中去 tpl = "%s\n%s\n\n"%(item['href'],item['title']) with open("news.josn",'a',encoding="utf-8") as fp: #注意文件编码 fp.write(tpl)
注意:我们要使使用Item解析实体和pipeline持久化关联,需要修改setting配置文件
ITEM_PIPELINES = { 'scrapyPro.pipelines.ScrapyproPipeline': 300, #后面300代表优先级 }
补充:Selector的操作
Selector(response=response).xpath('//a') #解析当前响应response下的所有子孙a标签 Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[2]') #获取所有的a标签下的第二个标签
Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[@id="i1"]') #获取属性id为il的标签 @后面跟属性
Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[@href="link.html"][@id="i1"]') #多个标签的连续筛选
Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[starts-with(@href, "link")]') #属性以指定的字符串开头
Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[contains(@href, "link")]') #属性中包含有指定字符串
Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[re:test(@id, "i\d+")]') #正则匹配数据
Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[re:test(@id, "i\d+")]/text()') #获取匹配标签下的文本数据
Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[re:test(@id, "i\d+")]/@href') #获取匹配标签的属性值
上面获取的都是解析对象,要想获取具体数据(字符串),我们需要使用
Selector(response=response).xpath('/html/body/ul/li/a/@href').extract() #提取所有的,是个列表 Selector(response=response).xpath('//body/ul/li/a/@href').extract_first() #提取第一个
注意:'//'代表子孙标签,'/'代表子标签,另外'./'代表当前标签下寻找
简单实例应用:获取抽屉页码
import scrapy,hashlib from scrapy.selector import Selector,HtmlXPathSelector from scrapy.http import Request class ChoutiSpider(scrapy.Spider): name = 'chouti' allowed_domains = ['chouti.com'] start_urls = ['http://dig.chouti.com/'] visited_urls = set() #用于存放我们获取的url的md5值,而且是集合去重 def md5(self,url): #将url转md5 ha_obj = hashlib.md5() ha_obj.update(bytes(url,encoding="utf-8")) key = ha_obj.hexdigest() return key def parse(self, response): page_objs = Selector(response=response).xpath("//div[@id='dig_lcpage']//a[@class='ct_pagepa']") #解析实体 for page in page_objs: href = page.xpath("@href").extract_first() ha_href = self.md5(href) if ha_href in self.visited_urls: pass else: self.visited_urls.add(ha_href) #将获取的url添加到集合 new_url = "https://dig.chouti.com%s"%href
yield Request(url=new_url,callback=self.parse) #请求新的url,获取下面的url 对于阻塞操作使用yield切换,实现异步
注意:默认是获取所有的页面100多页,我们可以在setting文件设置解析深度
DEPTH_LIMIT = 1 #深度为1,表示在当前页面向下再次解析一次
这是第二次,只会解析到14页
简单实例应用:获取校花网的图片和姓名,按照姓名进行持久化文件归类
xiaohua.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scrapy import hashlib from scrapy.http.request import Request from scrapy.selector import Selector,HtmlXPathSelector import scrapy.http.response.html from ..items import XiaohuaItem class XiaohuaSpider(scrapy.Spider): name = 'xiaohua' allowed_domains = ['xiaohua.com'] start_urls = ['http://www.xiaohuar.com/'] visited_url = set() visited_url_img = {} visited_url_title = {} def md5(self,url): hash_obj = hashlib.md5() hash_obj.update(bytes(url,encoding="utf-8")) return hash_obj.hexdigest() def parse(self, response): #获取首页中所有的人物的下一级url,过滤掉校草 xh_a = Selector(response=response).xpath("//ul[@class='twoline']/li") for xh in xh_a: a_url = xh.xpath("./a[@class='xhpic']/@href").extract_first() a_title = xh.xpath("./a/span/text()").extract_first() if a_title.find("校草") != -1: continue if not a_url.startswith("http"): a_url = "http://www.xiaohuar.com%s" % a_url ha_url = self.md5(a_url) if ha_url in self.visited_url: pass else: self.visited_url.add(ha_url) self.visited_url_title[ha_url]=a_title yield scrapy.Request(url=a_url,callback=self.parse,dont_filter=True) #下面是所有人物下一级url中去查找所有照片,注意:部分小照片和大照片的区别在于前面多了small,大照片只取前32位即可 #/d/file/20171202/small062adbed4692d28b77a45e269d8f19031512203361.jpg 小照片 #/d/file/20171202/ 062adbed4692d28b77a45e269d8f1903.jpg 大照片 xh_img = Selector(response=response).xpath("//div[@class='post_entry']") xh_img_a = xh_img.xpath("./ul//img/@src") if len(xh_img) == 0: xh_img = Selector(response=response).xpath("//div[@class='photo-Middle']/div") if len(xh_img) != 0: xh_img = xh_img[1] else: xh_img = Selector(response=response).xpath("//div[@class='photo-m']/div")[1] xh_img_a = xh_img.xpath("./table//img/@src") # 上面找到标签,下面开始对标签进行循环,获取所有照片url for xh_img_item in xh_img_a: xh_img_url = xh_img_item.extract() if xh_img_url.find("small"): tmp_list = xh_img_url.rsplit("/",1) tmp_name_list = tmp_list[1].replace("small","").split(".") xh_img_url = "/".join([tmp_list[0],".".join([tmp_name_list[0][:32],tmp_name_list[1]])]) if not xh_img_url.startswith("http"): xh_img_url = "http://www.xiaohuar.com%s" % xh_img_url #将所有照片加入字典 url:名字 self.visited_url_img[xh_img_url] = self.visited_url_title[self.md5(response.url)] #若是收集完成,那么两者的长度是一致的,开始进行持久化 if len(set(self.visited_url_img.values())) == len(self.visited_url) and len(self.visited_url) != 0: for xh_url in self.visited_url_img.items(): item_obj = XiaohuaItem(title=xh_url[1],img_url=xh_url[0]) yield item_obj
items.py
import scrapy class XiaohuaItem(scrapy.Item): title = scrapy.Field() img_url = scrapy.Field()
pipelines.py
import requests,os
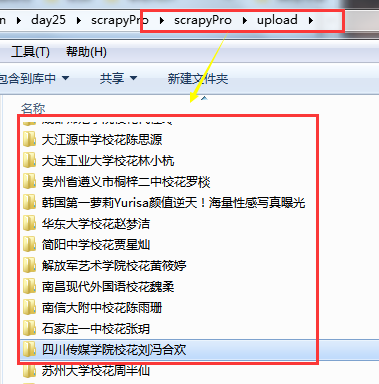
class XiaohuaPipeline(object): def process_item(self, item, spider): ''' title img_url ''' file_path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)),'upload',item['title']) if not os.path.isdir(file_path): os.makedirs(file_path) response = requests.get(item['img_url'],stream=False) with open(os.path.join(file_path,item['img_url'].rsplit("/",1)[1]),"wb") as fp: fp.write(response.content) return item
settings.py
ITEM_PIPELINES = { 'scrapyPro.pipelines.ScrapyproPipeline': 300, 'scrapyPro.pipelines.XiaohuaPipeline': 100, }
补充:request的回调函数不执行
原因:可能是我在设置allowed_domains允许域名中所设置的域名不是我们所爬取的网站域名
allowed_domains = ['xiaohua.com'] #域名不对,是xiaohuar.com start_urls = ['http://www.xiaohuar.com/']
设置allowed_domains的原因:
因为在网站中可能有外联,我们只是需要去访问该网站,而不是他的外联网站,所以设置allowed_domains是必须的,可以过滤掉外联的网站,要是希望获取外联网站,我们在该列表中添加上即可。
上面出错原因:
我们所爬取的网站时xiaohuar.com,而设置的域名是xiaohua.com所以爬取失败,在request中请求被拒绝
解决方法:(两者)
1.修改allowed_domains(推荐)
allowed_domains = ['xiaohuar.com']
2.在request中设置dont_filter(不对url进行过滤)
yield scrapy.Request(url=a_url,callback=self.parse,dont_filter=True)
推荐使用第一种:
我们可以在自定义类BaseDupeFilter(用于过滤url)中设置去重,数据收集等操作,使用dont_filter可能会有所影响
