HashMap详解
一. 关于 HashMap 常见的内容:
描述: 实现了 Map<K, V> 接口;元素以键值对的形式存储;key不可重复;key和value都可以为null,但是key只能有一个为null;无序存储,不能通过时间或者其他排序方式对其元素进行排序;不是线程安全的集合.
继承以及实现关系:
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable { }
Map<K, V> 接口定义了 Map 的方法和一些默认实现, AbstractMap<K,V> 实现了 Map<K,V> 接口,对其中一些方法添加了实现, Cloneable 接口表示可以克隆, Serializable接口表示可以序列化,可以用做数据传输.
二. HashMap 的实现原理:
HashMap 是通过数组和链表以及红黑树(后面简称树)来实现的, 每一个键值对都存放在一个实现了 Map.Entity<K, V> 的 Node<K,V> 节点中.
HashMap 中维护一个数组,这个数组就是哈希表,数组长度就是哈希表的容量, 哈希表示根据元素的key的哈希值通过算法获得一个不大于数组长度的数字作为元素在数组中位置的下标,每次取元素也是根据哈希值和相同的算法找到相应的下标志,从数组该下标处取.由于使用有限长的哈希值,其表示的内容必然是有限个,而可以存放的内容是无限的,必然会有同一个哈希值对应多个元素,便是hash冲突(后面会有详细解释)
图片演示:
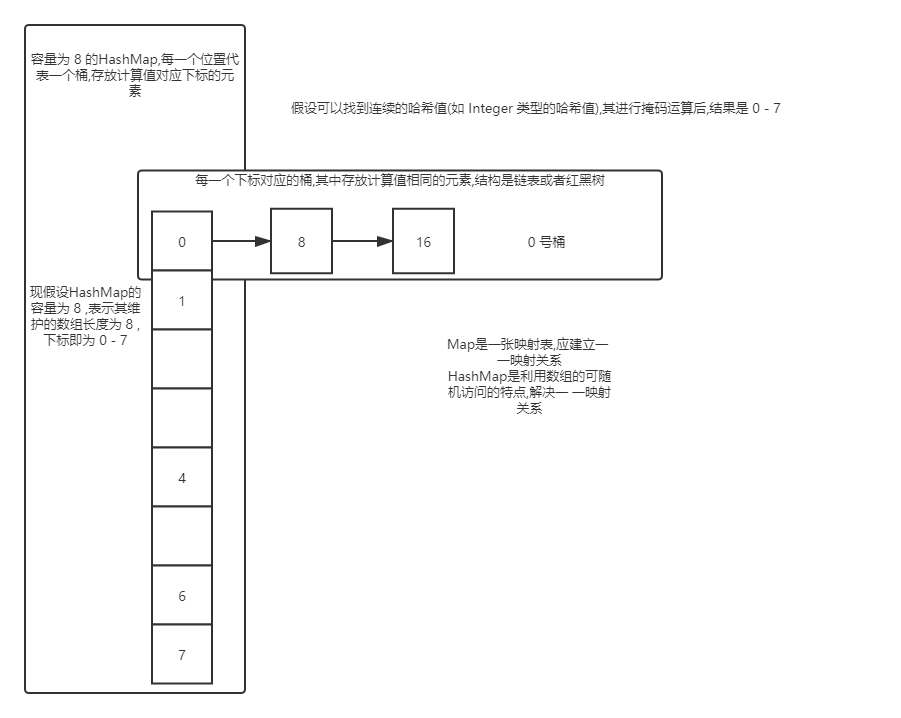
以上图片仅为了演示结构和原理,对容量等细节没有考虑和说明
三. HashMap 中定义的常量,属性和节点
常量:
/** * The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two. * 默认初始容量 16 */ static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; /** * 最大容量 * MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30. */ static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; /** * 默认加载因子 float型 0.75 */ static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; /** * 需要转为树的临界值 8 ,当某一个桶中的链表节点数大于 8 则转为树 */ static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; /** * 需要重新转为链表的临界值 6 ,当某一个桶中的树节点数小于 6 则转为链表 */ static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; /** * 允许转为树的最小容量 64 */ static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
常量描述: 默认初始化容量:是在使用无初始化容量构造时,创建的初始数组容量大小,此种构造在新建时并不会创建数组,而是在进行首次存放元素时才会进行数组初始化
最大容量: 标准扩容(即常规的扩容方式,每次扩容是上一次容量的两倍)的最大容量,如果容量大于了这个值,则将容量扩容至 Integer.MAX_VALUE
默认加载因子: 在使用无加载因子构造时使用的默认的加载因子
树化临界值: 当某个桶中的链表节点数大于此值时,则转化为树
链表化临界值: 当某个桶中的链表节点数小于此值时,则转为链表
最小树化容量: 只有当当前散列表中的容量大于等的此值时,才允许将符合要求的链表转为树,否则就只进行扩容操作
属性:
// 表(节点数组) transient Node<K,V>[] table; // 节点集合 transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet; // 大小:map中键值对的数量 transient int size; // 结构上的修改次数 (添加或者删除, 查询或者修改值不会造成结构变化) transient int modCount; // 临界值 int threshold; // 加载因子 final float loadFactor; // 键集合 transient Set<K> keySet; // 值集合 transient Collection<V> values;
属性描述:
表: table就是一个 Node<K,V> 数组,数组的长度就是散列表的容量,每一个数组元素就表示一个桶
节点集合: 存放所有节点的集合
大小: 当前散列表中目前元素个数
修改次数: 记录进行结构化修改的次数,用于判断同步,比较期望值和操作后的值是否一致,来判断是否同步
临界值: 用于判断是否需要扩容的临界值,当前值为当前容量乘以加载因子
加载因子: 用于计算散列表每次扩容的临界值
键集合和值集合:定义在 AbstractMap 中相关实现也是
节点:

1 static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { 2 // hash值 3 final int hash; 4 // 键 5 final K key; 6 // 值 7 V value; 8 // 下一个节点 9 Node<K,V> next; 10 11 // 节点全参构造 12 Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { 13 this.hash = hash; 14 this.key = key; 15 this.value = value; 16 this.next = next; 17 } 18 19 public final K getKey() { return key; } 20 public final V getValue() { return value; } 21 public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; } 22 23 // 获取hash值 24 public final int hashCode() { 25 return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value); 26 } 27 28 // 设置值,返回原值 29 public final V setValue(V newValue) { 30 V oldValue = value; 31 value = newValue; 32 return oldValue; 33 } 34 35 public final boolean equals(Object o) { 36 if (o == this) 37 return true; 38 if (o instanceof Map.Entry) { 39 Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o; 40 if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) && 41 Objects.equals(value, e.getValue())) 42 return true; 43 } 44 return false; 45 } 46 } static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { 47 // hash值 48 final int hash; 49 // 键 50 final K key; 51 // 值 52 V value; 53 // 下一个节点 54 Node<K,V> next; 55 56 // 节点全参构造 57 Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { 58 this.hash = hash; 59 this.key = key; 60 this.value = value; 61 this.next = next; 62 } 63 64 public final K getKey() { return key; } 65 public final V getValue() { return value; } 66 public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; } 67 68 // 获取hash值 69 public final int hashCode() { 70 return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value); 71 } 72 73 // 设置值,返回原值 74 public final V setValue(V newValue) { 75 V oldValue = value; 76 value = newValue; 77 return oldValue; 78 } 79 80 public final boolean equals(Object o) { 81 if (o == this) 82 return true; 83 if (o instanceof Map.Entry) { 84 Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o; 85 if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) && 86 Objects.equals(value, e.getValue())) 87 return true; 88 } 89 return false; 90 } 91 }
链表节点描述:
用于存放每个键值对的键和值以及对应的哈希值和下一个节点
注意: 1.由上面的节点代码可以看出, JAVA中的散列表的元素为链表时是单向链表,因为只有指向下一个节点的next属性
2.节点的构造只有一个全参构造,所以在HashMap中才会出现next为null时仍要写的情况

1 static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> { 2 TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links 3 TreeNode<K,V> left; 4 TreeNode<K,V> right; 5 TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion 6 boolean red; 7 TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) { 8 super(hash, key, val, next); 9 } 10 11 /** 12 * Returns root of tree containing this node. 13 */ 14 final TreeNode<K,V> root() { 15 for (TreeNode<K,V> r = this, p;;) { 16 if ((p = r.parent) == null) 17 return r; 18 r = p; 19 } 20 } 21 22 /** 23 * Ensures that the given root is the first node of its bin. 24 */ 25 static <K,V> void moveRootToFront(Node<K,V>[] tab, TreeNode<K,V> root) { 26 int n; 27 if (root != null && tab != null && (n = tab.length) > 0) { 28 int index = (n - 1) & root.hash; 29 TreeNode<K,V> first = (TreeNode<K,V>)tab[index]; 30 if (root != first) { 31 Node<K,V> rn; 32 tab[index] = root; 33 TreeNode<K,V> rp = root.prev; 34 if ((rn = root.next) != null) 35 ((TreeNode<K,V>)rn).prev = rp; 36 if (rp != null) 37 rp.next = rn; 38 if (first != null) 39 first.prev = root; 40 root.next = first; 41 root.prev = null; 42 } 43 assert checkInvariants(root); 44 } 45 } 46 47 /** 48 * Finds the node starting at root p with the given hash and key. 49 * The kc argument caches comparableClassFor(key) upon first use 50 * comparing keys. 51 */ 52 final TreeNode<K,V> find(int h, Object k, Class<?> kc) { 53 TreeNode<K,V> p = this; 54 do { 55 int ph, dir; K pk; 56 TreeNode<K,V> pl = p.left, pr = p.right, q; 57 if ((ph = p.hash) > h) 58 p = pl; 59 else if (ph < h) 60 p = pr; 61 else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk))) 62 return p; 63 else if (pl == null) 64 p = pr; 65 else if (pr == null) 66 p = pl; 67 else if ((kc != null || 68 (kc = comparableClassFor(k)) != null) && 69 (dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) != 0) 70 p = (dir < 0) ? pl : pr; 71 else if ((q = pr.find(h, k, kc)) != null) 72 return q; 73 else 74 p = pl; 75 } while (p != null); 76 return null; 77 } 78 79 /** 80 * Calls find for root node. 81 */ 82 final TreeNode<K,V> getTreeNode(int h, Object k) { 83 return ((parent != null) ? root() : this).find(h, k, null); 84 } 85 86 /** 87 * Tie-breaking utility for ordering insertions when equal 88 * hashCodes and non-comparable. We don't require a total 89 * order, just a consistent insertion rule to maintain 90 * equivalence across rebalancings. Tie-breaking further than 91 * necessary simplifies testing a bit. 92 */ 93 static int tieBreakOrder(Object a, Object b) { 94 int d; 95 if (a == null || b == null || 96 (d = a.getClass().getName(). 97 compareTo(b.getClass().getName())) == 0) 98 d = (System.identityHashCode(a) <= System.identityHashCode(b) ? 99 -1 : 1); 100 return d; 101 } 102 103 /** 104 * Forms tree of the nodes linked from this node. 105 */ 106 // 树化 107 final void treeify(Node<K,V>[] tab) { 108 TreeNode<K,V> root = null; 109 // 遍历双向链表 110 for (TreeNode<K,V> x = this, next; x != null; x = next) { 111 next = (TreeNode<K,V>)x.next; 112 x.left = x.right = null; 113 // 首次赋值根节点 114 if (root == null) { 115 x.parent = null; 116 x.red = false; 117 root = x; 118 } 119 else { 120 // 当前节点key 121 K k = x.key; 122 // 当前节点hash 123 int h = x.hash; 124 Class<?> kc = null; 125 for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) { 126 int dir, ph; 127 K pk = p.key; 128 // 当前节点hash小,左节点 129 if ((ph = p.hash) > h) 130 dir = -1; 131 // 当前节点hash大,右节点 132 else if (ph < h) 133 dir = 1; 134 else if ((kc == null && 135 (kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) || 136 (dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) 137 dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk); 138 // 定义当前节点的父节点 139 TreeNode<K,V> xp = p; 140 if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) { 141 x.parent = xp; 142 if (dir <= 0) 143 xp.left = x; 144 else 145 xp.right = x; 146 root = balanceInsertion(root, x); 147 break; 148 } 149 } 150 } 151 } 152 moveRootToFront(tab, root); 153 } 154 155 /** 156 * Returns a list of non-TreeNodes replacing those linked from 157 * this node. 158 */ 159 final Node<K,V> untreeify(HashMap<K,V> map) { 160 Node<K,V> hd = null, tl = null; 161 for (Node<K,V> q = this; q != null; q = q.next) { 162 Node<K,V> p = map.replacementNode(q, null); 163 if (tl == null) 164 hd = p; 165 else 166 tl.next = p; 167 tl = p; 168 } 169 return hd; 170 } 171 172 /** 173 * Tree version of putVal. 174 */ 175 final TreeNode<K,V> putTreeVal(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab, 176 int h, K k, V v) { 177 Class<?> kc = null; 178 boolean searched = false; 179 TreeNode<K,V> root = (parent != null) ? root() : this; 180 for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) { 181 int dir, ph; K pk; 182 if ((ph = p.hash) > h) 183 dir = -1; 184 else if (ph < h) 185 dir = 1; 186 else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk))) 187 return p; 188 else if ((kc == null && 189 (kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) || 190 (dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) { 191 if (!searched) { 192 TreeNode<K,V> q, ch; 193 searched = true; 194 if (((ch = p.left) != null && 195 (q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null) || 196 ((ch = p.right) != null && 197 (q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null)) 198 return q; 199 } 200 dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk); 201 } 202 203 TreeNode<K,V> xp = p; 204 if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) { 205 Node<K,V> xpn = xp.next; 206 TreeNode<K,V> x = map.newTreeNode(h, k, v, xpn); 207 if (dir <= 0) 208 xp.left = x; 209 else 210 xp.right = x; 211 xp.next = x; 212 x.parent = x.prev = xp; 213 if (xpn != null) 214 ((TreeNode<K,V>)xpn).prev = x; 215 moveRootToFront(tab, balanceInsertion(root, x)); 216 return null; 217 } 218 } 219 } 220 221 /** 222 * Removes the given node, that must be present before this call. 223 * This is messier than typical red-black deletion code because we 224 * cannot swap the contents of an interior node with a leaf 225 * successor that is pinned by "next" pointers that are accessible 226 * independently during traversal. So instead we swap the tree 227 * linkages. If the current tree appears to have too few nodes, 228 * the bin is converted back to a plain bin. (The test triggers 229 * somewhere between 2 and 6 nodes, depending on tree structure). 230 */ 231 final void removeTreeNode(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab, 232 boolean movable) { 233 int n; 234 if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) 235 return; 236 int index = (n - 1) & hash; 237 TreeNode<K,V> first = (TreeNode<K,V>)tab[index], root = first, rl; 238 TreeNode<K,V> succ = (TreeNode<K,V>)next, pred = prev; 239 if (pred == null) 240 tab[index] = first = succ; 241 else 242 pred.next = succ; 243 if (succ != null) 244 succ.prev = pred; 245 if (first == null) 246 return; 247 if (root.parent != null) 248 root = root.root(); 249 if (root == null 250 || (movable 251 && (root.right == null 252 || (rl = root.left) == null 253 || rl.left == null))) { 254 tab[index] = first.untreeify(map); // too small 255 return; 256 } 257 TreeNode<K,V> p = this, pl = left, pr = right, replacement; 258 if (pl != null && pr != null) { 259 TreeNode<K,V> s = pr, sl; 260 while ((sl = s.left) != null) // find successor 261 s = sl; 262 boolean c = s.red; s.red = p.red; p.red = c; // swap colors 263 TreeNode<K,V> sr = s.right; 264 TreeNode<K,V> pp = p.parent; 265 if (s == pr) { // p was s's direct parent 266 p.parent = s; 267 s.right = p; 268 } 269 else { 270 TreeNode<K,V> sp = s.parent; 271 if ((p.parent = sp) != null) { 272 if (s == sp.left) 273 sp.left = p; 274 else 275 sp.right = p; 276 } 277 if ((s.right = pr) != null) 278 pr.parent = s; 279 } 280 p.left = null; 281 if ((p.right = sr) != null) 282 sr.parent = p; 283 if ((s.left = pl) != null) 284 pl.parent = s; 285 if ((s.parent = pp) == null) 286 root = s; 287 else if (p == pp.left) 288 pp.left = s; 289 else 290 pp.right = s; 291 if (sr != null) 292 replacement = sr; 293 else 294 replacement = p; 295 } 296 else if (pl != null) 297 replacement = pl; 298 else if (pr != null) 299 replacement = pr; 300 else 301 replacement = p; 302 if (replacement != p) { 303 TreeNode<K,V> pp = replacement.parent = p.parent; 304 if (pp == null) 305 root = replacement; 306 else if (p == pp.left) 307 pp.left = replacement; 308 else 309 pp.right = replacement; 310 p.left = p.right = p.parent = null; 311 } 312 313 TreeNode<K,V> r = p.red ? root : balanceDeletion(root, replacement); 314 315 if (replacement == p) { // detach 316 TreeNode<K,V> pp = p.parent; 317 p.parent = null; 318 if (pp != null) { 319 if (p == pp.left) 320 pp.left = null; 321 else if (p == pp.right) 322 pp.right = null; 323 } 324 } 325 if (movable) 326 moveRootToFront(tab, r); 327 } 328 329 /** 330 * Splits nodes in a tree bin into lower and upper tree bins, 331 * or untreeifies if now too small. Called only from resize; 332 * see above discussion about split bits and indices. 333 * 334 * @param map the map 335 * @param tab the table for recording bin heads 336 * @param index the index of the table being split 337 * @param bit the bit of hash to split on 338 */ 339 final void split(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab, int index, int bit) { 340 TreeNode<K,V> b = this; 341 // Relink into lo and hi lists, preserving order 342 TreeNode<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null; 343 TreeNode<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null; 344 int lc = 0, hc = 0; 345 for (TreeNode<K,V> e = b, next; e != null; e = next) { 346 next = (TreeNode<K,V>)e.next; 347 e.next = null; 348 if ((e.hash & bit) == 0) { 349 if ((e.prev = loTail) == null) 350 loHead = e; 351 else 352 loTail.next = e; 353 loTail = e; 354 ++lc; 355 } 356 else { 357 if ((e.prev = hiTail) == null) 358 hiHead = e; 359 else 360 hiTail.next = e; 361 hiTail = e; 362 ++hc; 363 } 364 } 365 366 if (loHead != null) { 367 if (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) 368 tab[index] = loHead.untreeify(map); 369 else { 370 tab[index] = loHead; 371 if (hiHead != null) // (else is already treeified) 372 loHead.treeify(tab); 373 } 374 } 375 if (hiHead != null) { 376 if (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) 377 tab[index + bit] = hiHead.untreeify(map); 378 else { 379 tab[index + bit] = hiHead; 380 if (loHead != null) 381 hiHead.treeify(tab); 382 } 383 } 384 } 385 386 /* ------------------------------------------------------------ */ 387 // Red-black tree methods, all adapted from CLR 388 389 static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> rotateLeft(TreeNode<K,V> root, 390 TreeNode<K,V> p) { 391 TreeNode<K,V> r, pp, rl; 392 if (p != null && (r = p.right) != null) { 393 if ((rl = p.right = r.left) != null) 394 rl.parent = p; 395 if ((pp = r.parent = p.parent) == null) 396 (root = r).red = false; 397 else if (pp.left == p) 398 pp.left = r; 399 else 400 pp.right = r; 401 r.left = p; 402 p.parent = r; 403 } 404 return root; 405 } 406 407 static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> rotateRight(TreeNode<K,V> root, 408 TreeNode<K,V> p) { 409 TreeNode<K,V> l, pp, lr; 410 if (p != null && (l = p.left) != null) { 411 if ((lr = p.left = l.right) != null) 412 lr.parent = p; 413 if ((pp = l.parent = p.parent) == null) 414 (root = l).red = false; 415 else if (pp.right == p) 416 pp.right = l; 417 else 418 pp.left = l; 419 l.right = p; 420 p.parent = l; 421 } 422 return root; 423 } 424 425 static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> balanceInsertion(TreeNode<K,V> root, 426 TreeNode<K,V> x) { 427 x.red = true; 428 for (TreeNode<K,V> xp, xpp, xppl, xppr;;) { 429 if ((xp = x.parent) == null) { 430 x.red = false; 431 return x; 432 } 433 else if (!xp.red || (xpp = xp.parent) == null) 434 return root; 435 if (xp == (xppl = xpp.left)) { 436 if ((xppr = xpp.right) != null && xppr.red) { 437 xppr.red = false; 438 xp.red = false; 439 xpp.red = true; 440 x = xpp; 441 } 442 else { 443 if (x == xp.right) { 444 root = rotateLeft(root, x = xp); 445 xpp = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.parent; 446 } 447 if (xp != null) { 448 xp.red = false; 449 if (xpp != null) { 450 xpp.red = true; 451 root = rotateRight(root, xpp); 452 } 453 } 454 } 455 } 456 else { 457 if (xppl != null && xppl.red) { 458 xppl.red = false; 459 xp.red = false; 460 xpp.red = true; 461 x = xpp; 462 } 463 else { 464 if (x == xp.left) { 465 root = rotateRight(root, x = xp); 466 xpp = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.parent; 467 } 468 if (xp != null) { 469 xp.red = false; 470 if (xpp != null) { 471 xpp.red = true; 472 root = rotateLeft(root, xpp); 473 } 474 } 475 } 476 } 477 } 478 } 479 480 static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> balanceDeletion(TreeNode<K,V> root, 481 TreeNode<K,V> x) { 482 for (TreeNode<K,V> xp, xpl, xpr;;) { 483 if (x == null || x == root) 484 return root; 485 else if ((xp = x.parent) == null) { 486 x.red = false; 487 return x; 488 } 489 else if (x.red) { 490 x.red = false; 491 return root; 492 } 493 else if ((xpl = xp.left) == x) { 494 if ((xpr = xp.right) != null && xpr.red) { 495 xpr.red = false; 496 xp.red = true; 497 root = rotateLeft(root, xp); 498 xpr = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.right; 499 } 500 if (xpr == null) 501 x = xp; 502 else { 503 TreeNode<K,V> sl = xpr.left, sr = xpr.right; 504 if ((sr == null || !sr.red) && 505 (sl == null || !sl.red)) { 506 xpr.red = true; 507 x = xp; 508 } 509 else { 510 if (sr == null || !sr.red) { 511 if (sl != null) 512 sl.red = false; 513 xpr.red = true; 514 root = rotateRight(root, xpr); 515 xpr = (xp = x.parent) == null ? 516 null : xp.right; 517 } 518 if (xpr != null) { 519 xpr.red = (xp == null) ? false : xp.red; 520 if ((sr = xpr.right) != null) 521 sr.red = false; 522 } 523 if (xp != null) { 524 xp.red = false; 525 root = rotateLeft(root, xp); 526 } 527 x = root; 528 } 529 } 530 } 531 else { // symmetric 532 if (xpl != null && xpl.red) { 533 xpl.red = false; 534 xp.red = true; 535 root = rotateRight(root, xp); 536 xpl = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.left; 537 } 538 if (xpl == null) 539 x = xp; 540 else { 541 TreeNode<K,V> sl = xpl.left, sr = xpl.right; 542 if ((sl == null || !sl.red) && 543 (sr == null || !sr.red)) { 544 xpl.red = true; 545 x = xp; 546 } 547 else { 548 if (sl == null || !sl.red) { 549 if (sr != null) 550 sr.red = false; 551 xpl.red = true; 552 root = rotateLeft(root, xpl); 553 xpl = (xp = x.parent) == null ? 554 null : xp.left; 555 } 556 if (xpl != null) { 557 xpl.red = (xp == null) ? false : xp.red; 558 if ((sl = xpl.left) != null) 559 sl.red = false; 560 } 561 if (xp != null) { 562 xp.red = false; 563 root = rotateRight(root, xp); 564 } 565 x = root; 566 } 567 } 568 } 569 } 570 } 571 572 /** 573 * Recursive invariant check 574 */ 575 static <K,V> boolean checkInvariants(TreeNode<K,V> t) { 576 TreeNode<K,V> tp = t.parent, tl = t.left, tr = t.right, 577 tb = t.prev, tn = (TreeNode<K,V>)t.next; 578 if (tb != null && tb.next != t) 579 return false; 580 if (tn != null && tn.prev != t) 581 return false; 582 if (tp != null && t != tp.left && t != tp.right) 583 return false; 584 if (tl != null && (tl.parent != t || tl.hash > t.hash)) 585 return false; 586 if (tr != null && (tr.parent != t || tr.hash < t.hash)) 587 return false; 588 if (t.red && tl != null && tl.red && tr != null && tr.red) 589 return false; 590 if (tl != null && !checkInvariants(tl)) 591 return false; 592 if (tr != null && !checkInvariants(tr)) 593 return false; 594 return true; 595 } 596 }
树节点描述:
树节点有两个结构,一是双向链表,树节点的定义中既有指向上一节点的引用变量也有指向下一节点的引用变量(下一节点的变量定义是继承过来的);二是树结构(红黑树),既有父级节点引用变量,也有左右子节点的引用变量,还有变量指明该节点是否是红节点. 树这一节点中有很多内容,本人就在此挖个坑,等本人把树吃透后来填(博客园:xiao_lin_unit于2021-03-10挖)
四. 一些重要方法
1. hash
1 static final int hash(Object key) { 2 int h; 3 return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); 4 }
描述: 此方法是JAVA的HashMap中获取哈希值的方法,此处不纠结hash算法的值是怎样计算的,不同语言有不同的hash实现(主要是此处计算算法我也不知道是要实现什么效果的逻辑),将此方法放在此处是想说明为什么HashMap中的key可以有null,因为key为null时,返回的hash值直接是 0 .
2.tableSizeFor
1 // 结果是返回一个不小于给定值的最小2的整次幂数,用作表容量 2 static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) { 3 int n = cap - 1; 4 n |= n >>> 1; // n = n | n >>> 1 从n的最高有效位(第一个 1 )开始的 2 位都为 1 (如果位数大于等于 2) 5 n |= n >>> 2; // n = n | n >>> 2 基于上一步,结果是从n的最高有效位(第一个 1 )开始的 4 位都为 1 (如果位数大于等于 4) 6 n |= n >>> 4; // n = n | n >>> 4 基于上一步,结果是从n的最高有效位(第一个 1 )开始的 8 位都为 1 (如果位数大于等于 8) 7 n |= n >>> 8; // n = n | n >>> 8 基于上一步,结果是从n的最高有效位(第一个 1 )开始的 16 位都为 1 (如果位数大于等于 16) 8 n |= n >>> 16; // n = n | n >>> 16 基于上一步,结果是从n的最高有效位(第一个 1 )开始的所有位都为 1 9 // 以上算法会从 cap - 1 的有效最高位开始,后续位全部为 1 10 // 如果小于0,就为1 ,否则如果大于等于最大容量,就为最大容量,否则就为不小于给定值的最小2的整次幂数 11 return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1; 12 }
描述: 上述方法中添加了注释, 对 n 的操作是无符号右移和按位或运算,结果是返回了一个大于给定值同时又是 2 的整次幂的最小值
右移和或运算流程举例如下:
/* 一个 int 类型的值 n ,获取其二进制数,如: n = 0000 0000 0000 1010 0000 1100 0000 0000 (随便敲的,我也没计算是多少) n >>> 1 0000 0000 0000 0101 0000 0110 0000 0000 n |= n >>> 1(按位或运算,有 1 则 1) n = 0000 0000 0000 1111 0000 1110 0000 0000 n >>> 2 0000 0000 0000 0011 1100 0011 1000 0000 n |= n >>> 2 n = 0000 0000 0000 1111 1100 1111 1000 0000 n >>> 4 0000 0000 0000 0000 1111 1100 1111 1000 n |= n >>> 4 0000 0000 0000 1111 1111 1111 1111 1000 ... 0000 0000 0000 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 经过方法中描述的 5 次运算后,任何一个数都可以的到一个从最高有效位开始至结束全部为 1 的数
*/
注意:1.是符合要求的任意一个数,哪怕 n 是 2 的整次幂(二进制数只有一个 1 )
2.由上述操作的到的数字加 1 之后,得到一个 2 的整次幂数, 这个数必然会大于给定的数,因为任意一个给定数,将其从最高有效位开始至结束位的所有位都置为 1 得到的数必然会大于等于该数,加 1 之后必然大于该数
3.为什么 n 要等于 给定值 cap 减 1 :影响该算法的结果的关键在于最高有效位位置:如果 cap 不是 2 的整次幂,则值是否减 1 是没有影响的;如果 cap 是 2 的整次幂,如果不减 1 ,最高有效位就是cap 的最高有效位,方法的返回值就是 cap 的两倍,如果减 1 ,最高有效位就是 cap 的最高有效位的下一位,方法的返回值就是 cap 值;
3.构造方法:
1 public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { 2 if (initialCapacity < 0) 3 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + 4 initialCapacity); 5 if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) 6 initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; 7 if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) 8 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + 9 loadFactor); 10 this.loadFactor = loadFactor; 11 // 不小于目标容量的最小 2 的整次幂 12 this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity); 13 } 14 15 public HashMap(int initialCapacity) { 16 this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); 17 } 18 19 20 public HashMap() { 21 this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted 22 } 23 24 public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { 25 this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; 26 putMapEntries(m, false); 27 }
描述:非集合构造方法中并没有创建散列表(节点数组)的操作,只是进行了加载因子和临界值的赋值,散列表的创建是在首次赋值时进行创建的
4.resize
1 final Node<K,V>[] resize() { 2 // 旧表 3 Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table; 4 // 旧表容量 5 int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length; 6 // 旧表临界值 7 int oldThr = threshold; 8 // 定义初始化信标容量和临界值 9 int newCap, newThr = 0; 10 // 旧容量大于 0 如果不是新new的哈希表的首次添加元素,则一定会执行此分支,结果是,每次扩容结果为之前容量的两倍或者是最大 11 if (oldCap > 0) { 12 // 旧表容量大于最大容量,临界值定义为最大整数,旧表已经是最大容量表,不能再扩容,返回原表即可 13 if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { 14 threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 15 return oldTab; 16 } 17 // 否则新的容量为旧容量左移一位(旧容量的两倍),并且小于最大容量且旧容量大于等于默认初始化值 18 else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && 19 oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) 20 // 新临界值为旧临界值左移一位(旧临界值的两倍) 21 newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold 22 } 23 // 旧容量不大于 0 且旧临界值大于 0 24 // TODO 什么情况下执行此分支? 25 else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold 初始化容量放置在临界值中 26 // 新容量为旧的临界值 27 newCap = oldThr; 28 // 旧容量不大于 0 且旧临界值不大于 0 ,新new的哈希表首次添加元素时执行 29 else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults 从零开始初始化使用默认值 30 newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; 31 newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); 32 } 33 // 新临界值为 0 ,即旧容量不大于 0 且旧临界值大于 0 的情况 34 // TODO 什么情况下会执行该分支 35 if (newThr == 0) { 36 // 计算新临界值 37 float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor; 38 newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? 39 (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); 40 } 41 threshold = newThr; 42 @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) 43 Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap]; 44 table = newTab; 45 if (oldTab != null) { 46 // 遍历数组中所有的链表 47 for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) { 48 Node<K,V> e; 49 // 该桶上有节点 50 if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) { 51 // 元素置空? 52 oldTab[j] = null; 53 //该桶只有一个节点 54 if (e.next == null) 55 // 重新hash,并将元素放到桶中 56 newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e; 57 // 如果由多个节点,先判断有没有转化为树 58 else if (e instanceof TreeNode) 59 ((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap); 60 // 链 61 else { // preserve order 62 // 在表中位置不发生变化的元素头节点和当前节点 63 Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null; 64 // 在表中位置发生了变化的元素头节点和当前节点 65 Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null; 66 // 下一个节点 67 Node<K,V> next; 68 // 遍历链表中所有的元素 69 do { 70 next = e.next; 71 // 由于容量值除了最高位为 1 以外,其他位全为 0 ,所以,如果 & 运算结果位 0 ,那么 oldCap 的最高位对应的 e.hash 的该位为 0 72 if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) { 73 if (loTail == null) 74 loHead = e; 75 else 76 loTail.next = e; 77 loTail = e; 78 } 79 else { 80 if (hiTail == null) 81 hiHead = e; 82 else 83 hiTail.next = e; 84 hiTail = e; 85 } 86 } while ((e = next) != null); 87 // 将链表放到数组对应下标位置 88 if (loTail != null) { 89 loTail.next = null; 90 newTab[j] = loHead; 91 } 92 if (hiTail != null) { 93 hiTail.next = null; 94 newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead; 95 } 96 } 97 } 98 } 99 } 100 return newTab; 101 }
描述:1.结果是返回了扩容后的新散列表
2. e.hash & (cap - 1) 这个运算: 前文中提及,每一个节点中都会保存该节点key对应的hash值, 使用容量减一(cap - 1)作为掩码,可以使任意的值计算得到一个小于 cap 的值,这个值在 0 到 (cap - 1)之间,也刚好契合数组下标
原因: cap 是一个 2 的整次幂数, 减一之后得到的数 n 是最高有效位之前全为 0 ,从最高有效位开始全为 1 ,进行 & 运算(有 0 则 0)后得到的结果 m ,最高有效位之前全部为 0 ,所以 m 不可能大于 n,必然小于 n + 1
3.为什么建议在大致知道要添加到散列表中数量时,传入容量值: resize过程中会对散列表中的元素重新哈希寻找位置,不断的resize很耗费性能,使用容量构造可以减少或者避免重新哈希
5.putVal
1 final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, 2 boolean evict) { 3 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; 4 // 如果没有表,初始化容量(默认值) 5 if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) 6 n = (tab = resize()).length; 7 // 节点对应数组下标位置元素为 null ,即不存在该元素 8 if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) 9 // 新建一个节点 10 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); 11 else { 12 // 存放 key 相同的旧节点,不为 null 表示存在旧节点,为 null 表示不存在 13 Node<K,V> e; K k; 14 // 如果hash值相同并且key也相同 15 if (p.hash == hash && 16 ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 17 // 将该节点赋给 e 18 e = p; 19 else if (p instanceof TreeNode) 20 e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); 21 // 不相同,遍历链表 22 else { 23 for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { 24 // 如果链表中某一节点的 next 为 null 不存在值为该 key 的节点,就新建一个节点,跳出循环 25 if ((e = p.next) == null) { 26 // 新建一个节点 27 p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); 28 // 如果达到了树化临界值,就进行树化 29 if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st 30 treeifyBin(tab, hash); 31 break; 32 } 33 // 如果节点的hash值相同并且key也相同,存在值未该 key 的节点,就跳出循环 34 if (e.hash == hash && 35 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 36 break; 37 // 否则指针后移 38 p = e; 39 } 40 } 41 // 存在值为该 key 的节点,返回原来的值 42 if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key 43 V oldValue = e.value; 44 if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) 45 e.value = value; 46 afterNodeAccess(e); 47 return oldValue; 48 } 49 } 50 // 如果是新添加节点,则修改次数和大小自增,如果大小大于临界值,就重新计算容量 51 ++modCount; 52 if (++size > threshold) 53 resize(); 54 afterNodeInsertion(evict); 55 return null; 56 }
描述: 添加元素的主要方法.会先判断是否已经有了散列表,如果没有会先创建散列表;如果目标key已经存在相应的节点,就将原值替换并返回
6.putMapEntries
1 final void putMapEntries(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m, boolean evict) { 2 // 获取大小 3 int s = m.size(); 4 if (s > 0) { 5 // 如果还没有table 6 if (table == null) { // pre-size 7 // 大小除以加载因子加 1 ,加 1 是为了下一步强制类型转换时消除小数的影响 8 float ft = ((float)s / loadFactor) + 1.0F; 9 // 获取用于计算容量的数字 10 int t = ((ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? 11 (int)ft : MAXIMUM_CAPACITY); 12 // 如果大于临界值,重新计算容量 13 if (t > threshold) 14 threshold = tableSizeFor(t); 15 } 16 // 否则如果大于临界值 17 else if (s > threshold) 18 // 扩容 19 resize(); 20 for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet()) { 21 K key = e.getKey(); 22 V value = e.getValue(); 23 putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, evict); 24 } 25 } 26 }
描述: 添加节点的主要方法,主要用于集合构造和putAll,clone方法中也用到了
7.removeNode
1 final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value, 2 boolean matchValue, boolean movable) { 3 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index; 4 if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && 5 (p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { 6 Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v; 7 // 桶中头节点 8 if (p.hash == hash && 9 ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 10 node = p; 11 else if ((e = p.next) != null) { 12 if (p instanceof TreeNode) 13 node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key); 14 else { 15 // 遍历查找 16 do { 17 if (e.hash == hash && 18 ((k = e.key) == key || 19 (key != null && key.equals(k)))) { 20 node = e; 21 break; 22 } 23 p = e; 24 } while ((e = e.next) != null); 25 } 26 } 27 if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value || 28 (value != null && value.equals(v)))) { 29 if (node instanceof TreeNode) 30 ((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable); 31 else if (node == p) 32 tab[index] = node.next; 33 else 34 p.next = node.next; 35 // 修改次数自增,大小自减 36 ++modCount; 37 --size; 38 afterNodeRemoval(node); 39 return node; 40 } 41 } 42 return null; 43 }
描述:移除一个节点,先找桶判断有没有节点,节点数量是否大于 1 ,返回删除的节点
8.getNode
1 final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) { 2 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k; 3 // 数组存在并且 key 对应的桶位置不为 null 4 if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && 5 (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { 6 // 如果第一个节点就是该节点,则返回 7 if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node 8 ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 9 return first; 10 // 如果有下一个节点 11 if ((e = first.next) != null) { 12 if (first instanceof TreeNode) 13 return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); 14 // 遍历该桶的链表节点,比较是否相同 15 do { 16 if (e.hash == hash && 17 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 18 return e; 19 } while ((e = e.next) != null); 20 } 21 } 22 return null; 23 }
描述:查找节点,返回定位节点
9.treeifyBin
1 final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) { 2 int n, index; Node<K,V> e; 3 // 未达到最小树化容量(64)就只进行扩容 4 if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY) 5 resize(); 6 // 表中在该桶中有节点(不判断数量,默认该桶中的节点数大于等于8) 7 else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { 8 // 头和尾 9 TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null; 10 // 遍历链表,结果是的到一个双向链表 11 do { 12 TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null); 13 // 赋值头节点 14 if (tl == null) 15 hd = p; 16 else { 17 // 新节点的前一个节点是尾节点 18 p.prev = tl; 19 // 尾节点的下一个节点是新节点 20 tl.next = p; 21 } 22 // 每次都将尾节点更新(尾指针后移) 23 tl = p; 24 // 指针后移 25 } while ((e = e.next) != null); 26 // 树化 27 if ((tab[index] = hd) != null) 28 hd.treeify(tab); 29 } 30 }
描述:将桶进行树化的方法,从中可以找到判断当前散列表容量是否大于最小树化容量,如果小于就只进行扩容
五.常用方法
1.put
1 public V put(K key, V value) { 2 return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); 3 }
2.putAll
1 public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { 2 putMapEntries(m, true); 3 }
上面两个方法都是存放元素,直接调用存放元素值或者节点的方法
3.get
1 public V get(Object key) { 2 Node<K,V> e; 3 return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value; 4 }
4.containsKey
1 public boolean containsKey(Object key) { 2 return getNode(hash(key), key) != null; 3 }
5.replace
1 public V replace(K key, V value) { 2 Node<K,V> e; 3 if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) != null) { 4 V oldValue = e.value; 5 e.value = value; 6 afterNodeAccess(e); 7 return oldValue; 8 } 9 return null; 10 }
上面三个方法是直接调用查找节点的方法,然后进行后续操作
6.remove
1 public V remove(Object key) { 2 Node<K,V> e; 3 return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ? 4 null : e.value; 5 }
移除方法是直接调用移除节点的方法
7.containsValue
1 public boolean containsValue(Object value) { 2 Node<K,V>[] tab; V v; 3 if ((tab = table) != null && size > 0) { 4 for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) { 5 for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { 6 if ((v = e.value) == value || 7 (value != null && value.equals(v))) 8 return true; 9 } 10 } 11 } 12 return false; 13 }
8.clear
1 public void clear() { 2 Node<K,V>[] tab; 3 // 修改次数自增 4 modCount++; 5 if ((tab = table) != null && size > 0) { 6 // 遍历清空表 7 size = 0; 8 for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) 9 tab[i] = null; 10 } 11 }
9.forEach
1 public void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) { 2 Node<K,V>[] tab; 3 if (action == null) 4 throw new NullPointerException(); 5 if (size > 0 && (tab = table) != null) { 6 int mc = modCount; 7 for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) { 8 for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) 9 action.accept(e.key, e.value); 10 } 11 if (modCount != mc) 12 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 13 } 14 }
上面三个方法是直接遍历整个集合,注意与containsKey的实现区别,key可以通过哈希值直接获取
10.keySet
1 public Set<K> keySet() { 2 Set<K> ks = keySet; 3 if (ks == null) { 4 ks = new KeySet(); 5 keySet = ks; 6 } 7 return ks; 8 }
11.values
1 public Collection<V> values() { 2 Collection<V> vs = values; 3 if (vs == null) { 4 // 5 vs = new Values(); 6 values = vs; 7 } 8 return vs; 9 }
12.entrySet
1 public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() { 2 Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> es; 3 return (es = entrySet) == null ? (entrySet = new EntrySet()) : es; 4 }
13.isEmpty
1 public boolean isEmpty() { 2 return size == 0; 3 }
14.size
1 public int size() { 2 return size; 3 }
以上五个方法是直接对散列表属性进行操作
受限于个人水平,如有错误或者补充望请告知(博客园:xiao_lin_unit)






