c++ 代码技巧
数学运算性能
大多数数据运算不存在性能问题,但是相对来说,整型的除法运算还是比较昂贵的。
参考下面的例子:
uint32_t BM_S1(uint64_t v) {
uint32_t result = 0;
do {
++result;
v /= 10;
} while (v);
return result;
}
uint32_t BM_S2(uint64_t v) {
uint32_t result = 1;
for (;;) {
if (v < 10) return result;
if (v < 100) return result + 1;
if (v < 1000) return result + 2;
if (v < 10000) return result + 3;
v /= 10000;
result += 4;
}
return result;
}
uint32_t BM_S3(uint64_t v) {
uint32_t result = 1;
for (;;) {
if (v < 10) return 1;
if (v < 100) return 2;
if (v < 1000) return 3;
if (v < 1000000000000) { // 10^12
if (v < 100000000) { // 10^7
if (v < 1000000) { // 10^6
if (v < 10000) {
return 4;
}
return 5 + (v >= 100000); // 10^5
}
return 7 + (v >= 10000000); // 10^7
}
if (v < 10000000000) { // 10^10
return 9 + (v >= 1000000000); // 10^9
}
return 11 + (v >= 100000000000); // 10^11
}
v /= 1000000000000;
result += 12;
}
return result;
}
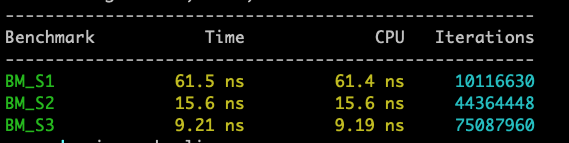
核心原因是因为 BM_S2 用比较和加法减少了除法运算,BM_S3通过搜索的方法进一步减少了除法操作。
运算速度可以参考下面:
* comparisons (1 clock cycle)
* (u)int add, subtract, bitops, shift (1 clock cycle)
* floating point add, sub (3~6 clock cycle)
* indexed array access (cache effects)
* (u)int32 mul (3~4 clock cycle)
* Floating point mul (4~8 clock cycle)
* Float Point division, remainder (14~45 clock cycle)
* (u)int division, remainder (40~80 clock cycle)
除法比乘法要慢很多,所以有些除法运算可以利用乘法来加快:
double y, a1, a2, b1, b2;
y = a1/b1 + a2/b2; // slow
double y, a1, a2, b1, b2;
y = (a1*b2 + a2*b1) / (b1*b2); // faster
cache line
目前的计算机系统,cache line 是 64 字节,基于cache line 可以做一些优化,从而减少内存读取次数。但是有些场景,cache line 反而会拖慢,例如下面的结构体:
struct S {
long long a;
long long b;
};
如果两个线程,一个写a,一个写b,这样会频发的触发内存和cache的交互。通过添加占位,让a和b不在一个cache line上,性能会更好。
struct S2 {
long long a;
long long nonp[8]; // 占位,a、b 加载到不同的缓存行
long long b;
};
选择删除vector中的某些元素
auto cond = [](int x) { return (x & 1 == 1); };
vec3.erase(std::remove_if(vec3.begin(), vec3.end(), cond), vec3.end());
时间复杂度是 O(n)
字符串拼接
void func1() {
std::string a = "hello";
std::string b = "world";
std::string c = "";
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
c = a + b;
}
}
void func2() {
std::string a = "hello";
std::string b = "world";
std::string c = "";
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
c += a;
c += b;
}
}
void func3() {
std::string a = "hello";
std::string b = "world";
std::string c = "";
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
c.append(a);
c.append(b);
}
}
void func4() {
std::stringstream ss;
std::string a = "hello";
std::string b = "world";
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
ss << a;
ss << b;
}
}
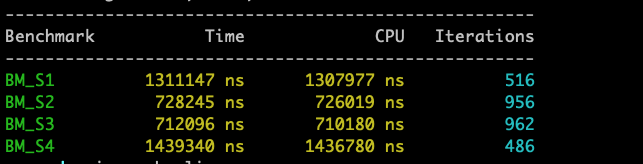
使用 += 和 append 的拼接效率是最高的。
字符串优化
#include <benchmark/benchmark.h>
#include <string>
#define BENCHMARKFUNC(func) \
static void BM_##func(benchmark::State& state) { \
for (auto _ : state) { \
std::string s = "BBHFGDHGFDTREHBGFYRTAGFYGIWERWQAGFJNBVNRETWEAHGFFFUJHRWEAGHDFG"; \
func(s); \
} \
} \
BENCHMARK(BM_##func);
std::string remove_1(std::string s) {
std::string result;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {
if (s[i] != 'A') {
result = result + s[i];
}
}
return result;
}
BENCHMARKFUNC(remove_1);
// std::string::length() 返回值是 size_t
std::string remove_2(std::string s) {
std::string result;
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {
if (s[i] != 'A') {
result = result + s[i];
}
}
return result;
}
BENCHMARKFUNC(remove_2);
// 复合赋值操作替换拼接操作,避免临时字符串
std::string remove_3(std::string s) {
std::string result;
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {
if (s[i] != 'A') {
result += s[i];
}
}
return result;
}
BENCHMARKFUNC(remove_3);
// 预留存储空间减少内存重新分配
std::string remove_4(std::string s) {
std::string result;
result.reserve(s.length());
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {
if (s[i] != 'A') {
result += s[i];
}
}
return result;
}
BENCHMARKFUNC(remove_4);
// 参数引用
std::string remove_5(const std::string& s) {
std::string result;
result.reserve(s.length());
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {
if (s[i] != 'A') {
result += s[i];
}
}
return result;
}
BENCHMARKFUNC(remove_5);
// 使用迭代器消除指针解引
// 初始化时调用end,缓存,避免后续重复计算
std::string remove_6(const std::string& s) {
std::string result;
result.reserve(s.length());
for (auto it = s.begin(), end = s.end(); it != end; ++it) {
if (*it != 'A') {
result += *it;
}
}
return result;
}
BENCHMARKFUNC(remove_6);
// 使用更好的算法
std::string remove_7(const std::string& s) {
std::string result;
result.reserve(s.length());
for (size_t b = 0, i = b; b < s.length(); b = i + 1) {
for (i = b; i < s.length(); ++i) {
if (s[i] == 'A') {
break;
}
}
result.append(s, b, i - b);
}
return result;
}
BENCHMARKFUNC(remove_7);
// 删除修改
std::string remove_inplace(std::string s) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.length();) {
if (s[i] == 'A') {
s.erase(i, 1);
} else {
++i;
}
}
return s;
}
BENCHMARKFUNC(remove_inplace);
BENCHMARK_MAIN();
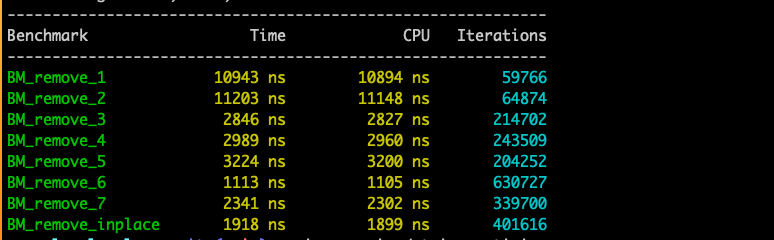
- remove_4 和 remove_5 的区别是参数传递改为引用。推测出现性能退化的原因,是remove_5中每次出现s,都会解引用,而在remove_4中不需要解引用,额外的开销导致性能下降。
- remove_7 相较remove_6的性能下降,说明for循环嵌套对性能影响较大
bench mark
之前一直用 https://quick-bench.com/ 做小段代码性能测试,但是最近这个网站挂了,还是在本地跑 benchmark 靠谱。
安装bench mark
git clone https://github.com/google/benchmark.git
git clone https://github.com/google/googletest.git benchmark/googletest
mkdir build && cd build
cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RELEASE ../benchmark
make -j4
# 如果想全局安装就接着运行下面的命令
sudo make install
demo
测试代码
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <benchmark/benchmark.h>
struct S {
long long a;
long long b;
};
struct S2 {
long long a;
long long nonp[8]; // 占位,a、b 加载到不同的缓存行
long long b;
};
void func1() {
S s;
std::thread t1([&]() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
s.a++;
}
});
std::thread t2([&]() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
s.b++;
}
});
t1.join();
t2.join();
}
void func2() {
S2 s;
std::thread t1([&]() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
s.a++;
}
});
std::thread t2([&]() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
s.b++;
}
});
t1.join();
t2.join();
}
static void BM_S(benchmark::State& state) {
for (auto _ : state) {
func1();
}
}
BENCHMARK(BM_S);
static void BM_S2(benchmark::State& state) {
for (auto _ : state) {
func2();
}
}
BENCHMARK(BM_S2);
BENCHMARK_MAIN();
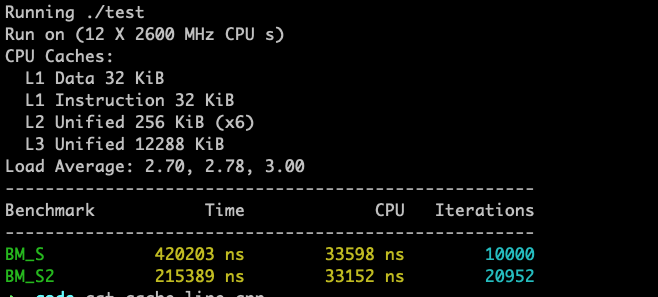
编译(mac os)
clang++ -Wall -std=c++14 cache_line.cpp -I /usr/local/include -L /usr/local/lib -L /usr/lib -pthread -lbenchmark -o test
执行结果