进度模拟算法
一、实验目的
进程调度是处理机管理的核心内容。本实验要求用高级语言编写模拟进程调度程序,以便加深理解有关进程控制快、进程队列等概念,并体会和了解优先数算法和时间片轮转算法的具体实施办法。
二、实验要求
1.设计进程控制块PCB 的结构,通常应包括如下信息:
进程名、进程优先数(或轮转时间片数)、进程已占用的CPU 时间、进程到完成还需要的时间、进程的状态、当前队列指针等。
2.编写两种调度算法程序:
优先数调度算法程序
循环轮转调度算法程序
3.按要求输出结果。
三、实验过程
1.准备
在CSDN上查询相关资料,编写程序,测试
2、主要流程和源代码
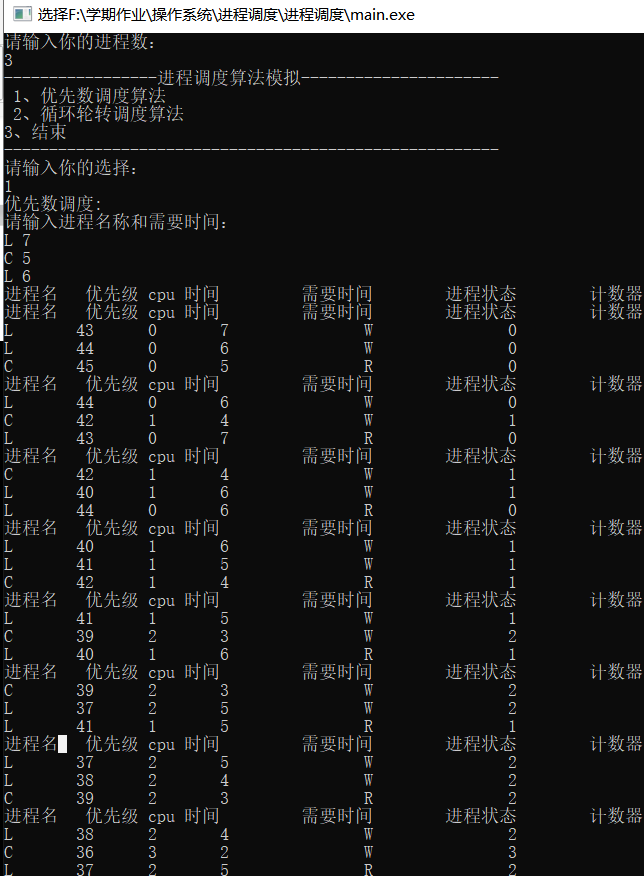
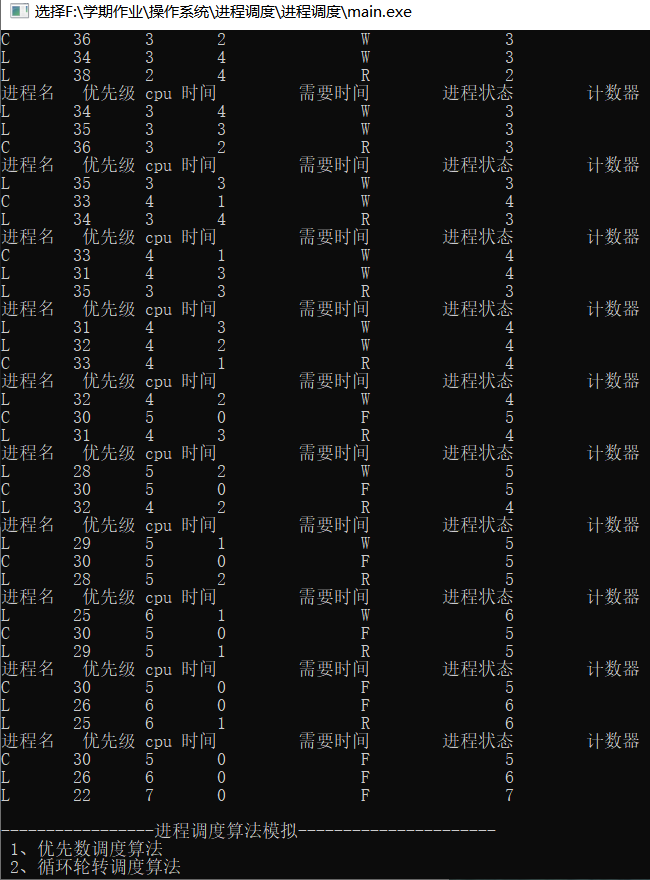
优先数调度算法主要流程:进程就绪队列按优先数大小从高到低排列,链首进程首先投入运行。进程每执行一次,进程需要的时间片数减1、该进程的优先数减3。这样,该进程如果在一个时间片中没有完成,其优先数降低一级。接着仍是用该进程降低一级后的优先数与就绪队列中链首进程的优先数进行比较,如果仍是该进程的优先数高或相同,便让该进程继续执行;否则,调度就绪队列的链首进程投入运行。原运行过的进程按其现行优先数大小插入就绪队列,且改变它们对应的进程状态,一直到所有进程都运行完各自的时间片数。
循环轮转调度算法的主要流程:
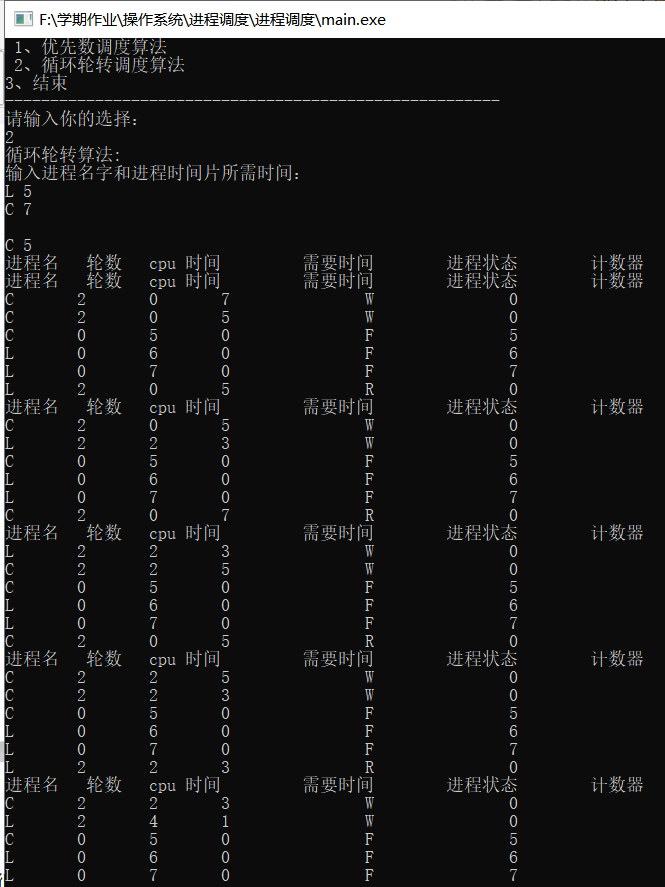
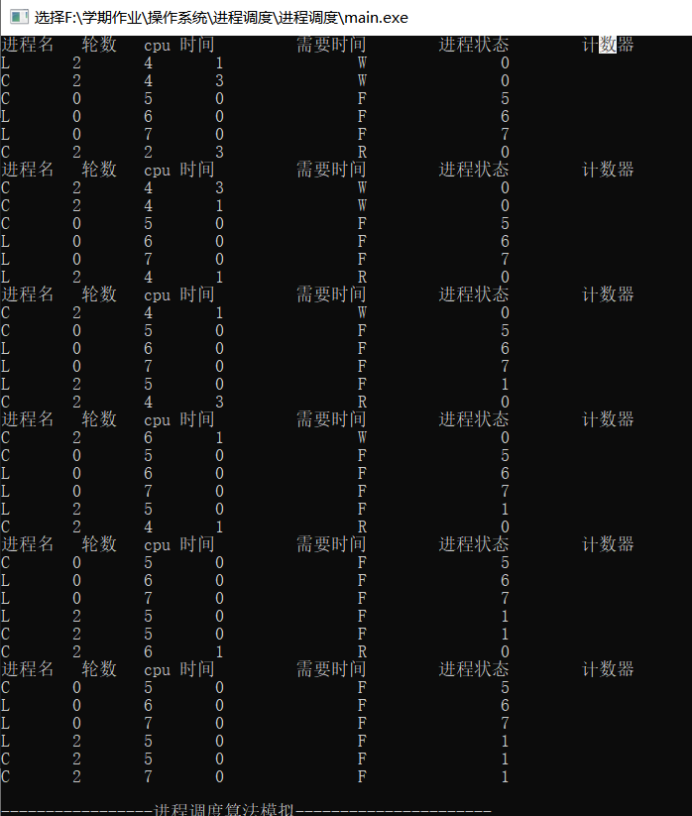
进程就绪队列按各进程进入的先后顺序排列。进程每次所需处理机的轮转式按其重要程度记入进程控制块中的轮转时间片数记录项。进程执行时,每运行一个时间片,进程还需要的时间片数减1,运行进程占用处理机的时间片数加1,然后比较占用CPU的时间片数是否与该进程的轮转时间片数相等,若相等则说明已达到轮转时间,应将现运行的进程排列就绪队列的末尾,调度队列上的首进程运行,且改变它们的进程状态,直至所有进程完成各自的时间片。
源代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
typedef struct node {
char name[20];
int prio;
int round;
int cputime;//CPU执行时间
int needtime; //进程执行所需要的时间
char state; //进程的状态,W——就绪态,R——执行态,F——完成态
int count;//记录执行的次数
struct node*next;
}PCB;
int num; PCB *ready = NULL, *run = NULL, *finish = NULL;
void GetFirst() //取得第一个就绪队列节点
{
run = ready;
if (ready != NULL)
{
run->state = 'R';
ready = ready->next;
run->next = NULL;
}
} //优先级输出队列
void Output1() {
PCB *p;
p = ready;
cout << "进程名\t 优先级\tcpu 时间\t 需要时间\t 进程状态\t 计数器" << endl;
while (p != NULL) {
cout << p->name << "\t" << p->prio << "\t" << p->cputime << "\t" << p->needtime << "\t\t" << p->state << "\t\t" << p->count << endl; p = p->next;
} p = finish;
while (p != NULL) {
cout << p->name << "\t" << p->prio << "\t" << p->cputime << "\t" << p->needtime << "\t\t" << p->state << "\t\t" << p->count << endl;
p = p->next;
} p = run;
while (p != NULL) {
cout << p->name << "\t" << p->prio << "\t" << p->cputime << "\t" << p->needtime << "\t\t" << p->state << "\t\t" << p->count << endl;
p = p->next;
}
}
//轮转法输出队列
void Output2() {
PCB *p; p = ready;
printf("进程名\t 轮数\tcpu 时间\t 需要时间\t 进程状态\t 计数器\n");
while (p != NULL) {
cout << p->name << "\t" << p->round << "\t" << p->cputime << "\t" << p->needtime << "\t\t" << p->state << "\t\t" << p->count << endl;
p = p->next;
} p = finish;
while (p != NULL) {
cout << p->name << "\t" << p->round << "\t" << p->cputime << "\t" << p->needtime << "\t\t" << p->state << "\t\t" << p->count << endl;
p = p->next;
} p = run;
while (p != NULL) {
cout << p->name << "\t" << p->round << "\t" << p->cputime << "\t" << p->needtime << "\t\t" << p->state << "\t\t" << p->count << endl;
p = p->next;
}
} //创建优先级队列,规定优先数越小,优先级越低
void InsertPrio(PCB *in) {
PCB *fst, *nxt;
fst = nxt = ready;
if (ready == NULL) { //如果队列为空,则为第一个元素
in->next = ready;
ready = in;
}
else {
//查到合适的位置进行插入
if (in->prio >= fst->prio)
{
in->next = ready; ready = in;
}
else {
//比第一个还要大,则插入到队头
while (fst->next != NULL) //移动指针查找第一个比它小的元素的位置进行插入
{
nxt = fst; fst = fst->next;
}
if (fst->next == NULL) //已经搜索到队尾,则其优先级数最小,将其插入到队尾 即可
{
in->next = fst->next; fst->next = in;
}
else { //插入到队列中
nxt = in; in->next = fst;
}
}
}
}
//将进程插入到就绪队列尾部
void InsertTime(PCB *in) {
PCB *fst; fst = ready; if (ready == NULL) { in->next = ready; ready = in; }
else
{
while (fst->next != NULL) { fst = fst->next; } in->next = fst->next; fst->next = in;
}
}
//将进程插入到完成队列尾部
void InsertFinish(PCB *in) {
PCB *fst; fst = finish;
if (finish == NULL)
{
in->next = finish; finish = in;
}
else {
while (fst->next != NULL)
{
fst = fst->next;
}
in->next = fst->next;
fst->next = in;
}
}
//优先级调度输入函数
void PrioCreate() {
PCB *tmp; int i;
cout << "请输入进程名称和需要时间:" << endl;
for (i = 0;i < num; i++)
{
if ((tmp = (PCB *)malloc(sizeof(PCB))) == NULL)
{
cerr << "malloc" << endl; exit(1);
}
cin >> tmp->name; getchar();
cin >> tmp->needtime;
tmp->cputime = 0;
tmp->state = 'W';
tmp->prio = 50 - tmp->needtime;
tmp->round = 0;
tmp->count = 0;
InsertPrio(tmp);
}
cout << "进程名\t 优先级\tcpu 时间\t 需要时间\t 进程状态\t 计数器" << endl;
}
//时间片输入函数
void TimeCreate()
{
PCB *tmp;
int i;
cout << "输入进程名字和进程时间片所需时间:" << endl;
for (i = 0;i < num; i++)
{
if ((tmp = (PCB *)malloc(sizeof(PCB))) == NULL) {
cerr << "malloc" << endl;
exit(1);
}
cin >> tmp->name;
getchar();
cin >> tmp->needtime;
tmp->cputime = 0;
tmp->state = 'W';
tmp->prio = 0;
tmp->round = 2;
tmp->count = 0;
InsertTime(tmp);
} printf("进程名\t 轮数\tcpu 时间\t 需要时间\t 进程状态\t 计数器\n");
}
//按照优先级调度,每次执行一个时间片
void Priority() {
int flag = 1;
GetFirst();
while (run != NULL) //设置其优先级,需要的时间越多,优先级越低 //按照优先级从高到低,插入到就绪队列
{
Output1();
while (flag) {
run->prio -= 3; //优先级减去三
run->cputime++; //CPU 时间片加一
run->needtime--;//进程执行完成的剩余时间减一
if (run->needtime == 0)//如果进程执行完毕,将进程状态置为 F,将其插入到完 成队列
{
run->state = 'F';
run->count++;
InsertFinish(run);
flag = 0;
}
else { //将进程状态置为 W,入就绪队列
run->state = 'W';
run->count++; //进程执行的次数加一
InsertTime(run);
flag = 0;
}
} flag = 1;
GetFirst();
}
}
void RoundRun()
{
int flag = 1;
GetFirst();
while (run != NULL)
{
Output2();
while (flag) {
run->count++;
run->cputime++;
run->needtime--;
if (run->needtime == 0) //进程执行完毕
{
//时间片轮转调度算法
//继续取就绪队列队头进程进入执行队列
run->state = 'F';
InsertFinish(run);
flag = 0;
}
else if (run->count == run->round)//时间片用完
{
run->state = 'W';
run->count = 0;
InsertTime(run);
flag = 0;
}
} flag = 1;
GetFirst();
}
}
int main(void) {
int n;
cout << "请输入你的进程数:" << endl;
cin >> num;
getchar();
cout << "-----------------进程调度算法模拟----------------------" << endl;
cout << " 1、优先数调度算法" << endl;
cout << " 2、循环轮转调度算法 " << endl;
cout << "-------------------------------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "请输入你的选择:" << endl;
cin >> n;
switch (n) {
case 1: cout << "优先数调度:" << endl;
PrioCreate();
Priority();
Output1();
break;
case 2: cout << "循环轮转算法:" << endl;
TimeCreate();
RoundRun(); //计数器清零,为下次做准备
Output2()
; break;
case 0:
exit(1);
break;
default:
cout << "输入错误" << endl;
break;
} cout << endl;
return 0;
}
3、遇到的主要问题和解决方法
本实验的进程的创建几乎是同时的,没有实现对于不同到达时间的进程的处理。
4、上机调试

四、实验结果
优先数算法

时间片轮转
五、实验总结
通过本次试验,我对优先数调度算法和时间片轮转调度算法实现的过程有了很清楚的理解。掌握了设计计数器来对进程执行状态的时间分析,从而使得进程调度得到具体化。对“链表插入”模型的运用和优先级的概念有了进一步的理解。



