css中position 定位的兼容性,以及定位的使用及层级的应用
一、首先我们来看看定位的兼容性,当然是在IE6、7但是现在大多数公司都已经不考虑了 我们就作为一个了解吧:
1、在IE67下,子元素有相对定位的话,父级的overflow:hidden包不住子元素
解决办法: 给父级也加相对定位
2、在IE6下绝对定位元素的父级宽高是奇数的时候,元素的right值和bottom值会有1px的偏差
解决办法: 父级不要设置双数。
这里就不上代码给大家解释了,如果小伙伴们想具体了解请自行用代码到IE6\7上面去测试。
二、现在定位有三种position:relative 相对定位、position:absolute绝对定位、position:fixed固定定位、position:static默认定位、position:inherit继承定位,现在具体来描述一下这五种定位的特征:
1、position:relative 相对定位 相对于自身
1)不影响元素本身特性
2)不使元素脱离文档流 (移动之后原始位置会被保留)
3)如果没有定位偏移量,对元素本身没有任何影响
4)提升层级
2、position:absolute 绝对定位 相对于父级(如果父不设置relative,那么子会向上寻找祖先元素,看是否设置relative。如果有则相对于设置的relative来进行定位,如果没有,那么就相对于body窗口来定位。)
1)使元素脱离文档流
2)使内嵌元素支持宽高
3)块属性标签内容撑开宽高
4)如果有定位父级相对于父级发生偏移,没有父级相对于document发生偏移
5)相对定位是配合绝对定位使用的
6)提升层级
3、position:fixed; 固定定位
与绝对定位的特性基本一致,的差别是始终相对整个文档进行定位;
问题:IE6不支持固定定位;
4、static(默认值) ;
5、inherit(从父元素继承定位属性的值);
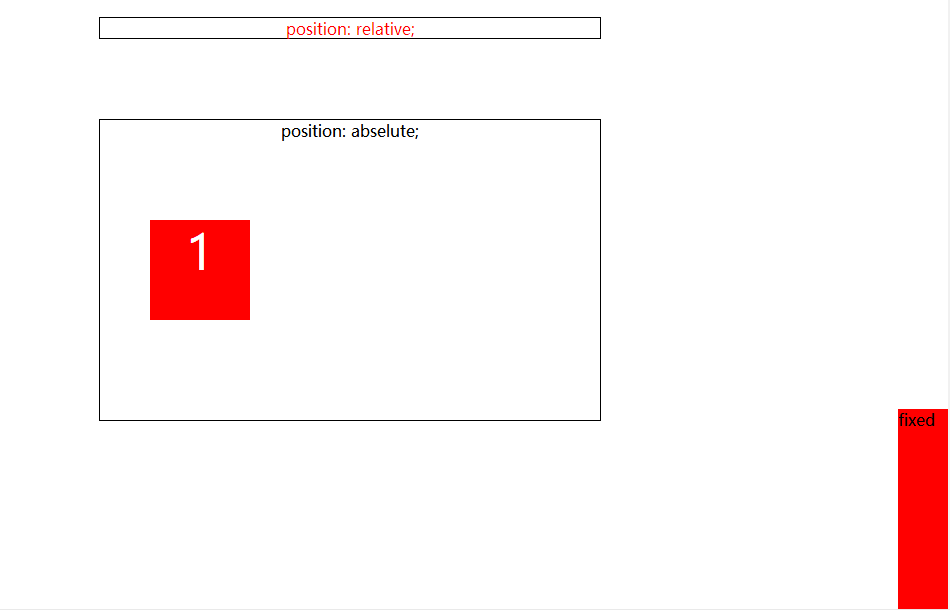
以下代码比较简单给大家展示一下前三种定位效果:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <!-- 1、position:relative 相对定位 相对于自身 1)不影响元素本身特性 2)不使元素脱离文档流 (移动之后原始位置会被保留) 3)如果没有定位偏移量,对元素本身没有任何影响 4)提升层级 2、position:absolute 绝对定位 相对于父级(如果父不设置relative,那么子会向上寻找祖先元素,看是否设置relative。如果有则相对于设置的relative来进行定位,如果没有,那么就相对于body窗口来定位。) 1)使元素脱离文档流 2)使内嵌元素支持宽高 3)块属性标签内容撑开宽高 4)如果有定位父级相对于父级发生偏移,没有父级相对于document发生偏移 5)相对定位是配合绝对定位使用的 6)提升层级 3、position:fixed; 固定定位 与绝对定位的特性基本一致,的差别是始终相对整个文档进行定位; 问题:IE6不支持固定定位; 4、static(默认值) | inherit(从父元素继承定位属性的值); 5、position:absolute;和position:fixed; 绝对定位元素子级的浮动可以不用写清浮动方法; --> <style> *{margin: 0;padding: 0;} #relative,#abselute{ position: relative; width: 500px; border: 1px solid #000000; text-align: center; } #relative{ left: 500px; top:20px; height: 20px; color: red;} #abselute{ left: 500px; top:100px; height: 300px; } #abselute div{ position: absolute; top: 100px; left: 50px; width: 100px; height: 100px; font-size: 48px; text-align: center; color: #fff; } #fixed{ width: 50px; height: 200px; position: fixed; right: 0; bottom: 0; background-color: red; } </style> </head> <body style="height: 2000px;"> <div id="relative">position: relative; </div> <div id="abselute">position: abselute; <div style="background: red;">1</div> </div> <div id="fixed">fixed</div> </body> </html>
三、层级的使用:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <!-- 定位元素默认后者层级高于前者,建议在兄弟标签之间使用; z-index:number; 定位层级(默认0) --> <style> *{margin: 0;padding: 0;} #abselute{ position: relative; top: 20px; left: 100px; width: 500px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid #000; } #abselute div{ font-size: 48px; text-align: center; color: #fff; position: absolute; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="abselute"> <div style="background: red;z-index: 1;">1</div>//这里使用了层级,我们就会优先看到红色背景的色块 <div style="background: yellow;">2</div> <div style="background: cyan;">3</div> </div> </body> </html>
如下图:

End




