多线程中join()的用法
Thread中,join()方法的作用是调用线程等待该线程完成后,才能继续用下运行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | public class TestThread5 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Runner0 run5 = new Runner0(); Thread th5 = new Thread(run5); th5.start(); th5.join();//join()方法用在此处是为了等待主线程结束后运行子线程 for(int i=0;i<5;i++){ System.out.println("子线程:"+i); } }} class Runner0 implements Runnable{ public void run(){ for(int i=0;i<5;i++) System.out.println("主线程:"+i); } } |
上述代码的运行结构如下所示:
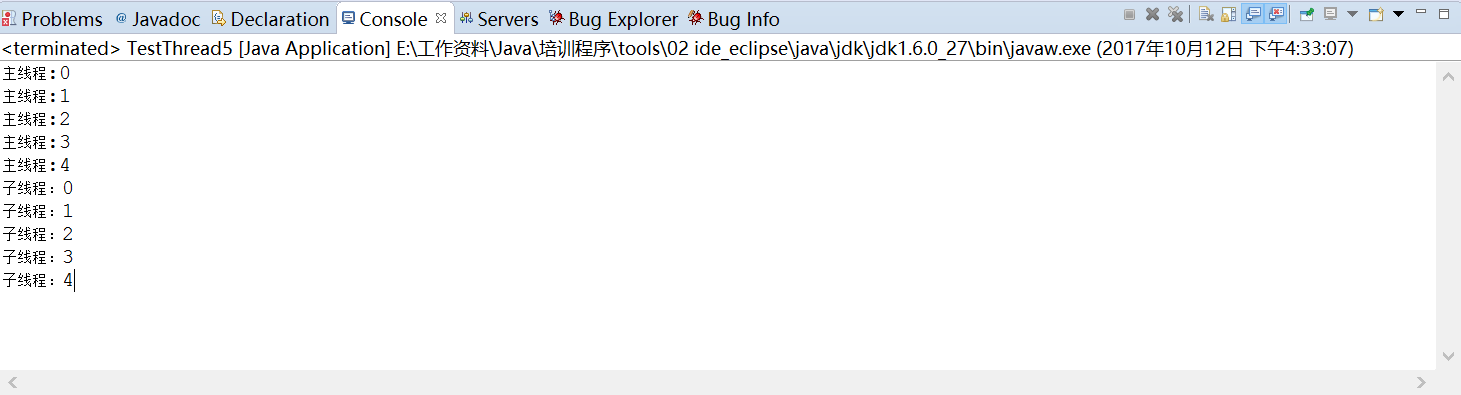
当然,如果不使用join()方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | public class TestThread6{ public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Runner0 run5 = new Runner0(); Thread th5 = new Thread(run5); th5.start();// th5.join(); for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ System.out.println("子线程:"+i); } }} class Runner0 implements Runnable{ public void run(){ for(int i=0;i<4;i++) System.out.println("主线程:"+i); } } |
如上代码注释掉jion()方法,
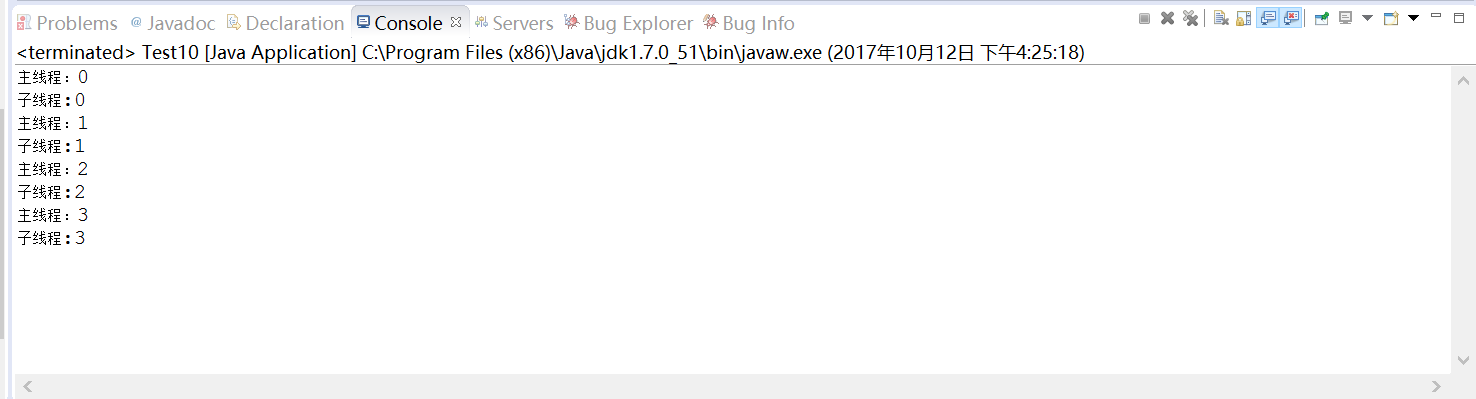
根据上面两个不同的代码,输出的不同,很容易就能理解join()方法。
yian






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· C#/.NET/.NET Core技术前沿周刊 | 第 29 期(2025年3.1-3.9)