手写简易SpringMVC框架,包含@PathVariable
SpringMVC简介
SpringMVC是当前最优秀的MVC框架,自从Spring 2.5版本发布后,由于支持注解配置,易用性有了大幅度的提高。Spring 3.0更加完善,实现了对Struts 2的超越。现在越来越多的开发团队选择了Spring MVC。
- Spring为展现层提供的基于MVC设计理念的优秀的Web框架,是目前最主流的MVC框架之一
- Spring3.0后全面超越Struts2,成为最优秀的MVC框架
- Spring MVC通过一套MVC注解,让POJO成为处理请求的控制器,而无须实现任何接口。
- 支持REST风格的URL请求
- 采用了松散耦合可插拔组件结构,比其他MVC框架更具扩展性和灵活性
SpringMVC运行流程
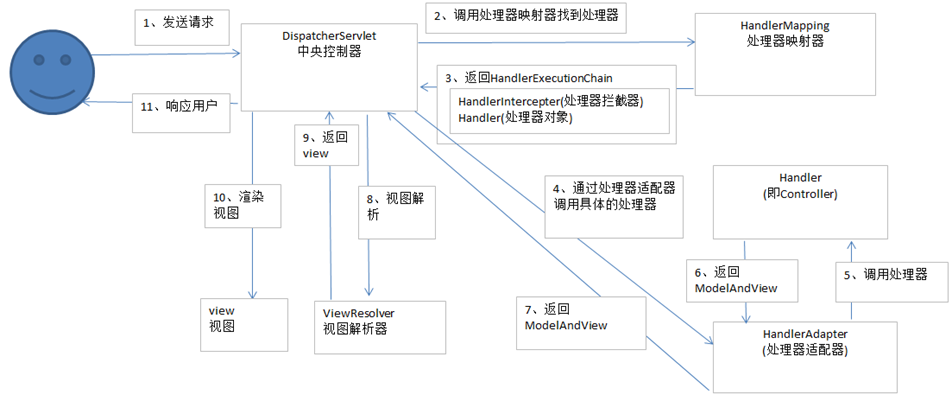
执行过程如图所示:
⑴用户发送请求至前端控制器DispatcherServlet。
⑵ DispatcherServlet收到请求调用HandlerMapping处理器映射器。
⑶ 处理器映射器根据请求url找到具体的处理器,生成处理器对象及处理器拦截器(如果有则生成)一并返回给DispatcherServlet。
⑷ DispatcherServlet通过HandlerAdapter处理器适配器调用处理器。
⑸ 执行处理器(Controller,也叫后端控制器)。
⑹ Controller执行完成返回ModelAndView。
⑺ HandlerAdapter将controller执行结果ModelAndView返回给DispatcherServlet。
⑻ DispatcherServlet将ModelAndView传给ViewReslover视图解析器。
⑼ ViewReslover解析后返回具体View。
⑽ DispatcherServlet对View进行渲染视图(即将模型数据填充至视图中)。
⑾ DispatcherServlet响应用户。
从上面可以看出,DispatcherServlet有接收请求,响应结果,转发等作用。有了DispatcherServlet之后,可以减少组件之间的耦合度。
SpringMVC九大组件
HandlerMapping
是用来查找Handler的。在SpringMVC中会有很多请求,每个请求都需要一个Handler处理,具体接收到一个请求之后使用哪个Handler进行处理,这就是HandlerMapping需要做的事。
HandlerAdapter
从名字上看,它就是一个适配器。因为SpringMVC中的Handler可以是任意的形式,只要能处理请求就ok,但是Servlet需要的处理方法的结构却是固定的,都是以request和response为参数的方法。如何让固定的Servlet处理方法调用灵活的Handler来进行处理呢?这就是HandlerAdapter要做的事情。
小结:Handler是用来干活的工具;HandlerMapping用于根据需要干的活找到相应的工具;HandlerAdapter是使用工具干活的人。
HandlerExceptionResolver
其它组件都是用来干活的。在干活的过程中难免会出现问题,出问题后需要有一个专门的角色对异常情况进行处理,在SpringMVC中就是HandlerExceptionResolver。具体来说,此组件的作用是根据异常设置ModelAndView,之后再交给render方法进行渲染。
ViewResolver
ViewResolver用来将String类型的视图名和Locale解析为View类型的视图。View是用来渲染页面的,也就是将程序返回的参数填入模板里,生成html(也可能是其它类型)文件。这里就有两个关键问题:使用哪个模板?用什么技术(规则)填入参数?这其实是ViewResolver主要要做的工作,ViewResolver需要找到渲染所用的模板和所用的技术(也就是视图的类型)进行渲染,具体的渲染过程则交由不同的视图自己完成。
RequestToViewNameTranslator
ViewName是根据ViewName查找View,但有的Handler处理完后并没有设置View也没有设置ViewName,这时就需要从request获取ViewName了,如何从request中获取ViewName就是RequestToViewNameTranslator要做的事情了。RequestToViewNameTranslator在Spring MVC容器里只可以配置一个,所以所有request到ViewName的转换规则都要在一个Translator里面全部实现。
LocaleResolver
解析视图需要两个参数:一是视图名,另一个是Locale。视图名是处理器返回的,Locale是从哪里来的?这就是LocaleResolver要做的事情。LocaleResolver用于从request解析出Locale,Locale就是zh-cn之类,表示一个区域,有了这个就可以对不同区域的用户显示不同的结果。SpringMVC主要有两个地方用到了Locale:一是ViewResolver视图解析的时候;二是用到国际化资源或者主题的时候。
ThemeResolver
用于解析主题。SpringMVC中一个主题对应一个properties文件,里面存放着跟当前主题相关的所有资源、如图片、css样式等。SpringMVC的主题也支持国际化,同一个主题不同区域也可以显示不同的风格。SpringMVC中跟主题相关的类有 ThemeResolver、ThemeSource和Theme。主题是通过一系列资源来具体体现的,要得到一个主题的资源,首先要得到资源的名称,这是ThemeResolver的工作。然后通过主题名称找到对应的主题(可以理解为一个配置)文件,这是ThemeSource的工作。最后从主题中获取资源就可以了。
MultipartResolver
用于处理上传请求。处理方法是将普通的request包装成MultipartHttpServletRequest,后者可以直接调用getFile方法获取File,如果上传多个文件,还可以调用getFileMap得到FileName->File结构的Map。此组件中一共有三个方法,作用分别是判断是不是上传请求,将request包装成MultipartHttpServletRequest、处理完后清理上传过程中产生的临时资源。
FlashMapManager
用来管理FlashMap的,FlashMap主要用在redirect中传递参数。
SpringMVC工程结构与代码
该项目最终的工程文件及目录如下:
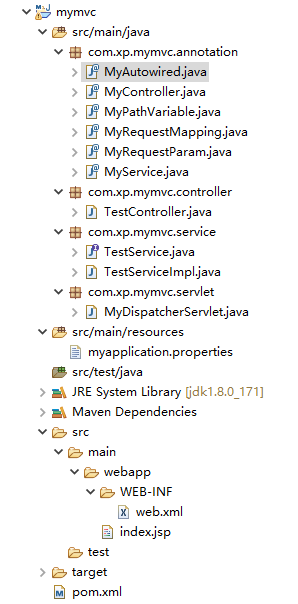
1、新建一个Maven项目,可以设置勾选自动生成web.xml,也可以自己手动添加,在pom.xml中导入javax.servlet-api,仅需要导入这一个包就可以啦。
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.xp</groupId> <artifactId>mymvc</artifactId> <packaging>war</packaging> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>mymvc Maven Webapp</name> <url>http://maven.apache.org</url> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>3.8.1</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>3.0.1</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <finalName>mymvc</finalName> </build> </project>
2、在生成的web.xml中配置一个MyDispatcherServlet,用于拦截符合“/”的请求,配置一个myapplication.properties文件,用于配置需要扫描的包名。
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN" "http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mymvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.xp.mymvc.servlet.MyDispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>myapplication.properties</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mymvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
在myapplication.properties文件中,配置为:
scanPackage=com.xp.mymvc
3、创建自己的注解@MyController,@MyService,@MyRequesMapping,@RequestParam,@MyAutowired,@MyPathVariable等。
package com.xp.mymvc.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; @Target(ElementType.FIELD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface MyAutowired { String value() default ""; } /*********************************************/ package com.xp.mymvc.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface MyController { String value() default ""; } /*********************************************/ package com.xp.mymvc.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; @Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface MyPathVariable { String value() default ""; } /*********************************************/ package com.xp.mymvc.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; @Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface MyRequestMapping { String value() default ""; } /*********************************************/ package com.xp.mymvc.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; @Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface MyRequestParam { String value() default ""; } /*********************************************/ package com.xp.mymvc.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface MyService { String value() default ""; }
4、创建MyDispatcherServlet这个类,继承HttpServlet,重写init()、doGet()、doPost(),以及实现自动注入、请求匹配等代码:
package com.xp.mymvc.servlet; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.net.URL; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.logging.Logger; import javax.servlet.ServletConfig; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import com.xp.mymvc.annotation.MyAutowired; import com.xp.mymvc.annotation.MyController; import com.xp.mymvc.annotation.MyRequestMapping; import com.xp.mymvc.annotation.MyService; /** * @author xp * MVC框架的请求分发中转 * 继承HttpServlet,重写init方法、doGet、doPost方法 */ public class MyDispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = -6972248998529463469L; private Logger log = Logger.getLogger("init"); private Properties properties = new Properties(); private List<String> classNames = new ArrayList<String>(); private Map<String, Object> ioc = new HashMap<String, Object>(); // handlerMapping的类型可以自定义为Handler private Map<String, Method> handlerMapping = new HashMap<String, Method>(); private Map<String, Object> controllerMap = new HashMap<String, Object>(); @Override public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException { super.init(); log.info("初始化MyDispatcherServlet"); /** 1.加载配置文件,填充properties字段;*/ doLoadConfig(config.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation")); /** 2.根据properties,初始化所有相关联的类,扫描用户设定的包下面所有的类 */ doScanner(properties.getProperty("scanPackage")); /** 3.拿到扫描到的类,通过反射机制,实例化,并且放到ioc容器中(k-v beanName-bean) beanName默认是首字母小写 */ doInstance(); /** 4.自动化注入依赖 */ doAutowired(); /** 5.初始化HandlerMapping(将url和method对应上) */ initHandlerMapping(); doAutowired2(); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // 注释掉父类实现,不然会报错:405 HTTP method GET is not supported by this URL // super.doPost(req, resp); log.info("执行MyDispatcherServlet的doPost()"); try { // 处理请求 doDispatch(req, resp); } catch (Exception e) { resp.getWriter().write("500!! Server Exception"); } } @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // 注释掉父类实现,不然会报错:405 HTTP method GET is not supported by this URL // super.doGet(req, resp); log.info("执行MyDispatcherServlet的doGet()"); try { // 处理请求 doDispatch(req, resp); } catch (Exception e) { resp.getWriter().write("500!! Server Exception"); } } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws Exception { if (handlerMapping.isEmpty()) { return; } String url = req.getRequestURI(); String contextPath = req.getContextPath(); url = url.replace(contextPath, "").replaceAll("/+", "/"); ArrayList<String> dimMatchArgsList = new ArrayList<String>(); HashMap<String, Object> dimMatchMap = dimMatch(handlerMapping, url);//模糊匹配,@MyPathVariable if (!dimMatchMap.isEmpty()) { url = dimMatchMap.get("url").toString(); dimMatchArgsList.addAll((List<String>) dimMatchMap.get("args")); } if (!this.handlerMapping.containsKey(url) ) { resp.getWriter().write("404 NOT FOUND!"); log.info("404 NOT FOUND!"); return; } Method method = this.handlerMapping.get(url); // 获取方法的参数列表 Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes(); // 获取请求的参数 Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = req.getParameterMap(); // 保存参数值 Object[] paramValues = new Object[parameterTypes.length]; // 方法的参数列表 for (int i = 0; i < parameterTypes.length; i++) { // 根据参数名称,做某些处理 String requestParam = parameterTypes[i].getSimpleName(); if (requestParam.equals("HttpServletRequest")) { // 参数类型已明确,这边强转类型 paramValues[i] = req; continue; } if (requestParam.equals("HttpServletResponse")) { paramValues[i] = resp; continue; } if (requestParam.equals("String")) { for (Map.Entry<String, String[]> param : parameterMap.entrySet()) { String value = Arrays.toString(param.getValue()).replaceAll("\\[|\\]", "").replaceAll(",\\s", ","); paramValues[i] = value; } } if (!dimMatchMap.isEmpty()) {//@MyPathVariable for (String args : dimMatchArgsList) { paramValues[i] = args; } } } // 利用反射机制来调用 try { // 第一个参数是method所对应的实例 在ioc容器中 method.invoke(this.controllerMap.get(url), paramValues); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 根据配置文件位置,读取配置文件中的配置信息,将其填充到properties字段 */ private void doLoadConfig(String location) { // 把web.xml中的contextConfigLocation对应value值的文件加载到流里面 InputStream resourceAsStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(location); try { // 用Properties文件加载文件里的内容 log.info("读取" + location + "里面的文件"); properties.load(resourceAsStream); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 关流 if (null != resourceAsStream) { try { resourceAsStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } /** * 将指定包下扫描得到的类,添加到classNames字段中 */ private void doScanner(String packageName) { URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/" + packageName.replaceAll("\\.", "/")); File dir = new File(url.getFile()); for (File file : dir.listFiles()) { if (file.isDirectory()) { // 递归读取包 doScanner(packageName + "." + file.getName()); } else { String className = packageName + "." + file.getName().replace(".class", ""); classNames.add(className); } } } /** * 将classNames中的类实例化,经key-value:类名(小写)-类对象放入ioc字段中 */ @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") private void doInstance() { if (classNames.isEmpty()) { return; } for (String className : classNames) { try { // 把类搞出来,反射来实例化(只有加@MyController需要实例化) Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className); if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent((Class<? extends Annotation>) MyController.class)) { ioc.put(toLowerFirstWord(clazz.getSimpleName()), clazz.newInstance()); } else if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent((Class<? extends Annotation>) MyService.class)) { MyService myService = clazz.getAnnotation(MyService.class); String beanName = myService.value(); if ("".equals(beanName.trim())) { beanName = toLowerFirstWord(clazz.getSimpleName()); } Object instance = clazz.newInstance(); ioc.put(beanName, instance); Class[] interfaces = clazz.getInterfaces(); for (Class<?> i : interfaces) { ioc.put(i.getName(), instance); } } else { continue; } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); continue; } } } /** * 自动化的依赖注入 */ private void doAutowired() { if (ioc.isEmpty()) { return; } for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : ioc.entrySet()) { // 包括私有的方法,在spring中没有隐私,@MyAutowired可以注入public、private字段 Field[] fields = entry.getValue().getClass().getDeclaredFields(); for (Field field : fields) { if (!field.isAnnotationPresent((Class<? extends Annotation>) MyAutowired.class)) { continue; } MyAutowired autowired = field.getAnnotation(MyAutowired.class); String beanName = autowired.value().trim(); if ("".equals(beanName)) { beanName = field.getType().getName(); } field.setAccessible(true); try { field.set(entry.getValue(), ioc.get(beanName)); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); continue; } } } } private void doAutowired2() { if (controllerMap.isEmpty()) { return; } for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : controllerMap.entrySet()) { // 包括私有的方法,在spring中没有隐私,@MyAutowired可以注入public、private字段 Field[] fields = entry.getValue().getClass().getDeclaredFields(); for (Field field : fields) { if (!field.isAnnotationPresent(MyAutowired.class)) { continue; } MyAutowired autowired = field.getAnnotation(MyAutowired.class); String beanName = autowired.value().trim(); if ("".equals(beanName)) { beanName = field.getType().getName(); } field.setAccessible(true); try { field.set(entry.getValue(), ioc.get(beanName)); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); continue; } } } } /** * 初始化HandlerMapping(将url和method对应上) */ private void initHandlerMapping() { if (ioc.isEmpty()) { return; } try { for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : ioc.entrySet()) { Class<? extends Object> clazz = entry.getValue().getClass(); if (!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyController.class)) { continue; } // 拼url时,是controller头的url拼上方法上的url String baseUrl = ""; if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent((Class<? extends Annotation>) MyRequestMapping.class)) { MyRequestMapping annotation = clazz.getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class); baseUrl = annotation.value(); } Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods(); for (Method method : methods) { if (!method.isAnnotationPresent(MyRequestMapping.class)) { continue; } MyRequestMapping annotation = method.getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class); String url = annotation.value(); url = (baseUrl + "/" + url).replaceAll("/+", "/"); handlerMapping.put(url, method); controllerMap.put(url, clazz.newInstance()); System.out.println(url + "," + method); } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 将字符串中的首字母小写 */ private String toLowerFirstWord(String name) { char[] charArray = name.toCharArray(); charArray[0] += 32; return String.valueOf(charArray); } /** * 模糊匹配,适用@MyPathVariable,很low * @param handlerMapping2 * @param url * @return */ private HashMap<String, Object> dimMatch(Map<String, Method> handlerMapping, String url) { HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); List<String> argsList = new ArrayList<String>(); String[] urlSplits = url.split("/"); for (String key : handlerMapping.keySet()) { if (key.contains("{") && key.contains("}")) { String[] splits = key.split("/"); if (urlSplits.length==splits.length) {//匹配上了 map.put("url", key); for (int i = 0; i < splits.length; i++) { if(splits[i].contains("{") && splits[i].contains("}")) { argsList.add(urlSplits[i]);//拿到参数 } } map.put("args", argsList); } } } return map; } }
5、新建TestService接口及其实现类TestServiceImpl,可以将TestService注入到后面的Controller中使用。
package com.xp.mymvc.service; public interface TestService { void printParam(String param); }
package com.xp.mymvc.service;
@MyService public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService{ public void printParam(String param) { System.out.println("接收到的参数为: "+param); } }
6、然后使用自己的@MyController等注解实现一个Controller类
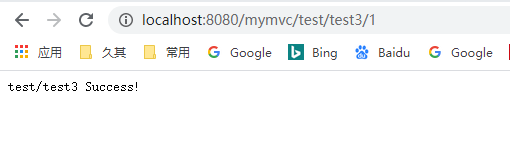
package com.xp.mymvc.controller; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import com.xp.mymvc.annotation.MyAutowired; import com.xp.mymvc.annotation.MyController; import com.xp.mymvc.annotation.MyPathVariable; import com.xp.mymvc.annotation.MyRequestMapping; import com.xp.mymvc.annotation.MyRequestParam; import com.xp.mymvc.service.TestService; @MyController @MyRequestMapping("/test") public class TestController { @MyAutowired public TestService testService; @MyRequestMapping("/test1") public void myTest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @MyRequestParam("param") String param) { try { testService.printParam(param); response.getWriter().print("test/test1 Success!"); System.err.println("test1/test1 Success!"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @MyRequestMapping("/test2") public void myTest2(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { try { response.getWriter().print("test/test2 Success!"); System.err.println("test1/test2 Success!"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @MyRequestMapping("/test3/{id}") public void myTest3(@MyPathVariable String id, HttpServletResponse response) { try { response.getWriter().print("test/test3 Success!"); System.err.println("test1/test3 Success!"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
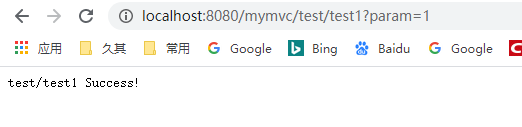
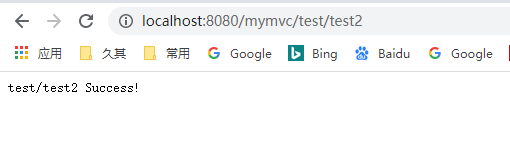
7、测试







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· C#/.NET/.NET Core技术前沿周刊 | 第 29 期(2025年3.1-3.9)