使用Spring Cloud Stream 驱动 RabbitMQ 代码示例
1、Spring Cloud Stream 官方文档
官方配置文档参考:
Spring Cloud Stream Reference Documentation
Spring Cloud Stream RabbitMQ Binder Reference Guide
说明:
在网上查找了许多关于 SpringCloudStream 的中文配置文档,但多数文档更新不及时。而且 SpringCLoudStream 最近的版本在使用上变化较大,老版本的资料已经失去了参考价值。
官方文档虽然是英文的,对多数国内的开发人员阅读会有些吃力,但好在资料都是最新的,而且现在的翻译软件这么方便,国内的多数开发人员也是有一些英文的阅读基础的,建议还是参考官方文档来测试。
特别说明:
文档中的配置说明中,基本上都是 驼峰命名,但我们在实际的使用过程中,在 yaml 配置文件中,都是使用 - 来分割使用。
比如:文档中的 配置名为 acknowledgeMode
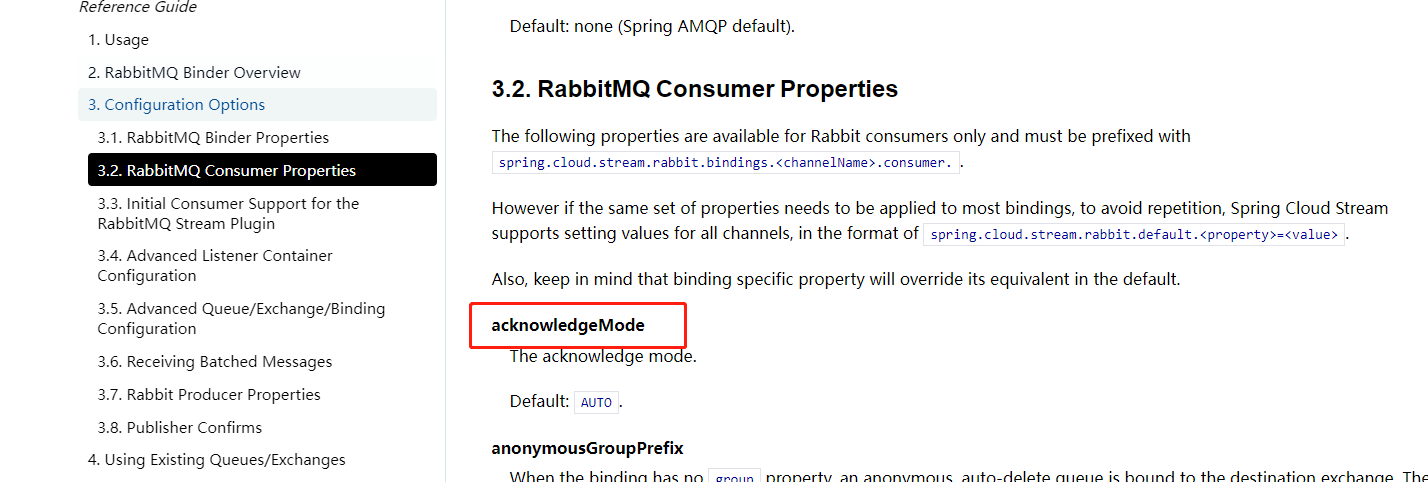
但在 yaml 中 acknowledge-mode

2、示例代码
2.1 application.yml
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 5672
username: admin
password: admin
virtual-host: /
cloud:
stream:
binders:
# 配置 Binder
defaultRabbit:
type: rabbit
environment:
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 127.0.0.1
default:
binder: defaultRabbit
consumer:
max-attempts: 1 # 重试次数, 设置为 1 即不重试
bindings:
flowEndConsumer-in-0:
group: queue # queue
destination: dap-oa.flowEnd # exchange
flowEndProducer-out-0:
destination: dap-oa.flowEnd
rabbit:
# default:
# acknowledge-mode: manual # manual 手动确认
# dlq-ttl: 5000
bindings:
flowEndConsumer-in-0:
consumer:
binding-routing-key: flowEnd # 路由键
exchange-type: topic # 交换机类型
# dlq-ttl: 5000 # 消息过期时间
# acknowledge-mode: manual # manual 手动确认 默认为 auto 自动确认
flowEndProducer-out-0:
producer:
exchange-type: topic
routing-key-expression: headers.routingKey # 根据 headers 中的 routingKey 参数,来确认路由到哪个 queue , "routingKey" 可自己命名
function:
definition: flowEndProducer;flowEndConsumer # 生产者和消费者必须在此配置,是能被自动识别
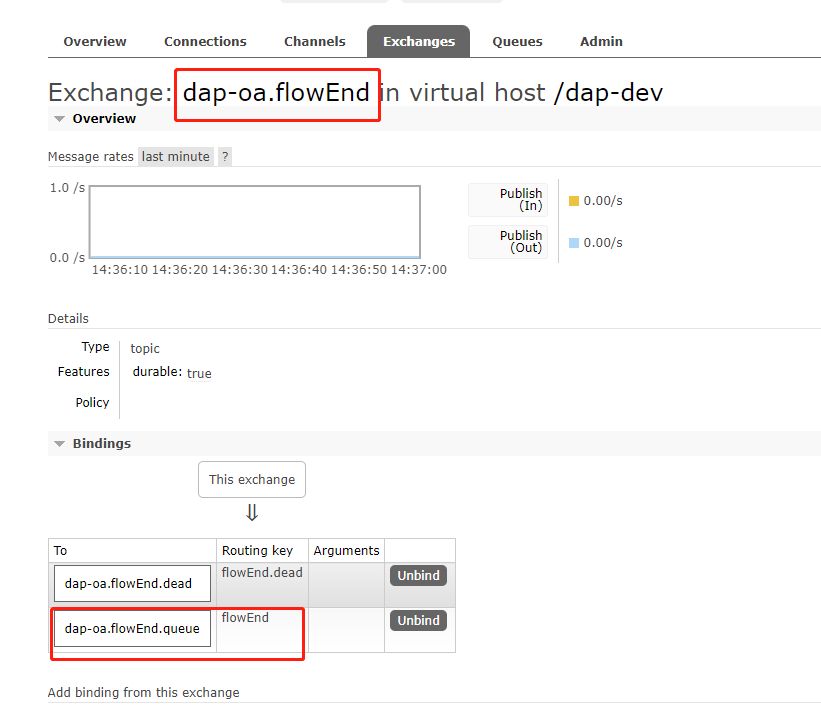
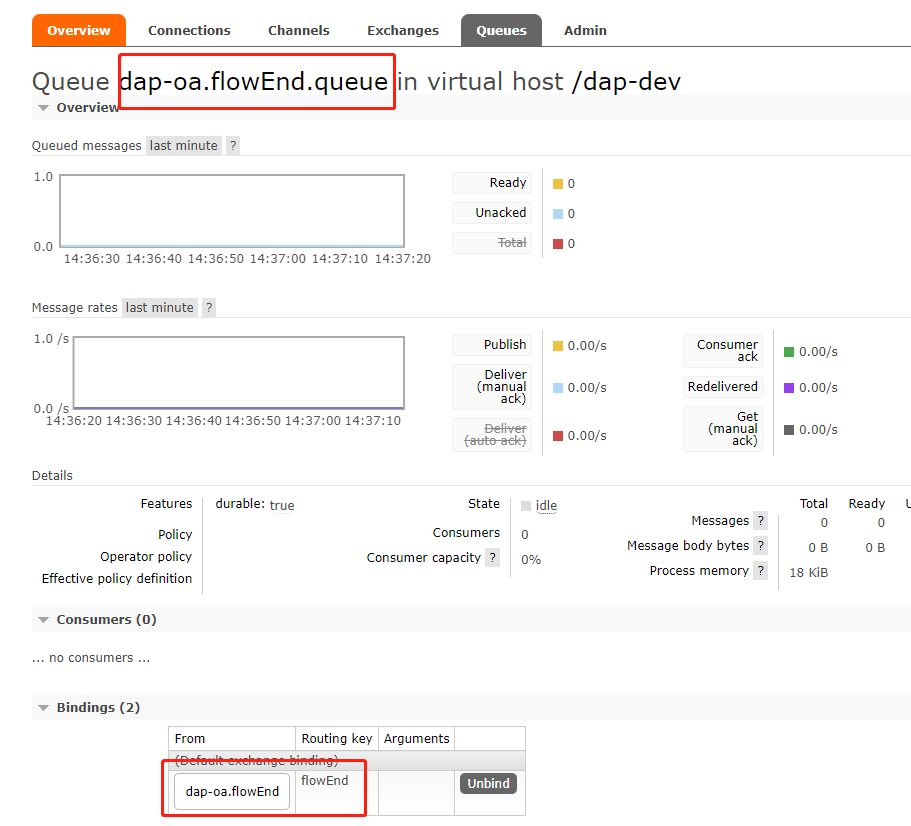
此配置内容,会在 rabbitMQ 中生成:
- exchange : dap-oa.flowEnd
- queue : dap-oa.flowEnd.queue
- dap-oa.flowEnd.queue 与 dap-oa.flowEnd 绑定的路由键:flowEnd
交换机 exchange:
队列 queue:
2.2 生产者
方式一:
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class ProducerDemo {
@Bean
public Supplier<Message<String>> flowEndProducer() {
return new Supplier<Message<String>>() {
@Override
public Message<MsgData> get() {
return MessageBuilder.withPayload("测试内容")
.setHeader("routingKey", "flowEnd") // 路由
.build();
}
};
}
}
方式二:
// 直接通过 StreamBridge 调用
private final StreamBridge streamBridge;
public void send() {
streamBridge.send(RabbitConstant.FLOW_END_PRODUCER,
MessageBuilder.withPayload("测试内容")
.setHeader("routingKey", "flowEnd")
.build());
}
2.2 消费者
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class ConsumerDemo {
@Bean
public Consumer<Message<String>> flowEndConsumer() {
return message -> {
System.out.println("******************");
System.out.println("At flowEndConsumer");
System.out.println("******************");
System.out.println("Received message " + message.getPayload());
Channel channel = message.getHeaders().get(AmqpHeaders.CHANNEL, Channel.class);
Long deliveryTag = message.getHeaders().get(AmqpHeaders.DELIVERY_TAG, Long.class);
log.info("******************");
log.info("channel:{}", channel);
log.info("deliveryTag:{}", deliveryTag);
};
}
}



