SpringBoot 异步任务处理
SpringBoot配置异步任务
有些业务是不需要你同步去操作的, 例如: 适用于处理log、发送邮件、短信……等
我们不能因为短信没发出去而没有执行接下来的业务逻辑, 这个时候我们就应该去把这些耗时的任务弄成异步的
首先要在启动类里面增加如下注解
@EnableAsync
定义异步任务类并使用@Component标记组件被容器扫描,异步方法加上@Async
如果整个类的操作都是异步的话 @Async 可以给类加上, 要把异步任务封装到类里面,不能直接写到Controller
package com.cj.tool.comtool.controller;
import com.cj.tool.comtool.task.AsyncTask;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class TestTaskController {
@Autowired
private AsyncTask asyncTask;
// 直接调起异步任务。正常执行肯定是堵塞的
@GetMapping("/api/v1/test_task")
public long testTask() throws InterruptedException {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
asyncTask.task1();
asyncTask.task2();
asyncTask.task3();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Controller 执行时间" + (end - begin));
return end - begin;
}
}
// 直接调起异步任务。正常执行肯定是堵塞的
package com.cj.tool.comtool.task;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Async
public class AsyncTask {
public void task1() throws InterruptedException {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(1000);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("task1耗时:"+ (end - begin));
}
public void task2() throws InterruptedException {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(2000);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("task2耗时:"+ (end - begin));
}
public void task3() throws InterruptedException {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(3000);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("task3耗时:"+ (end - begin));
}
}
可以看到在AsyncTask里面都是有sleep的, 但是我们使用了异步
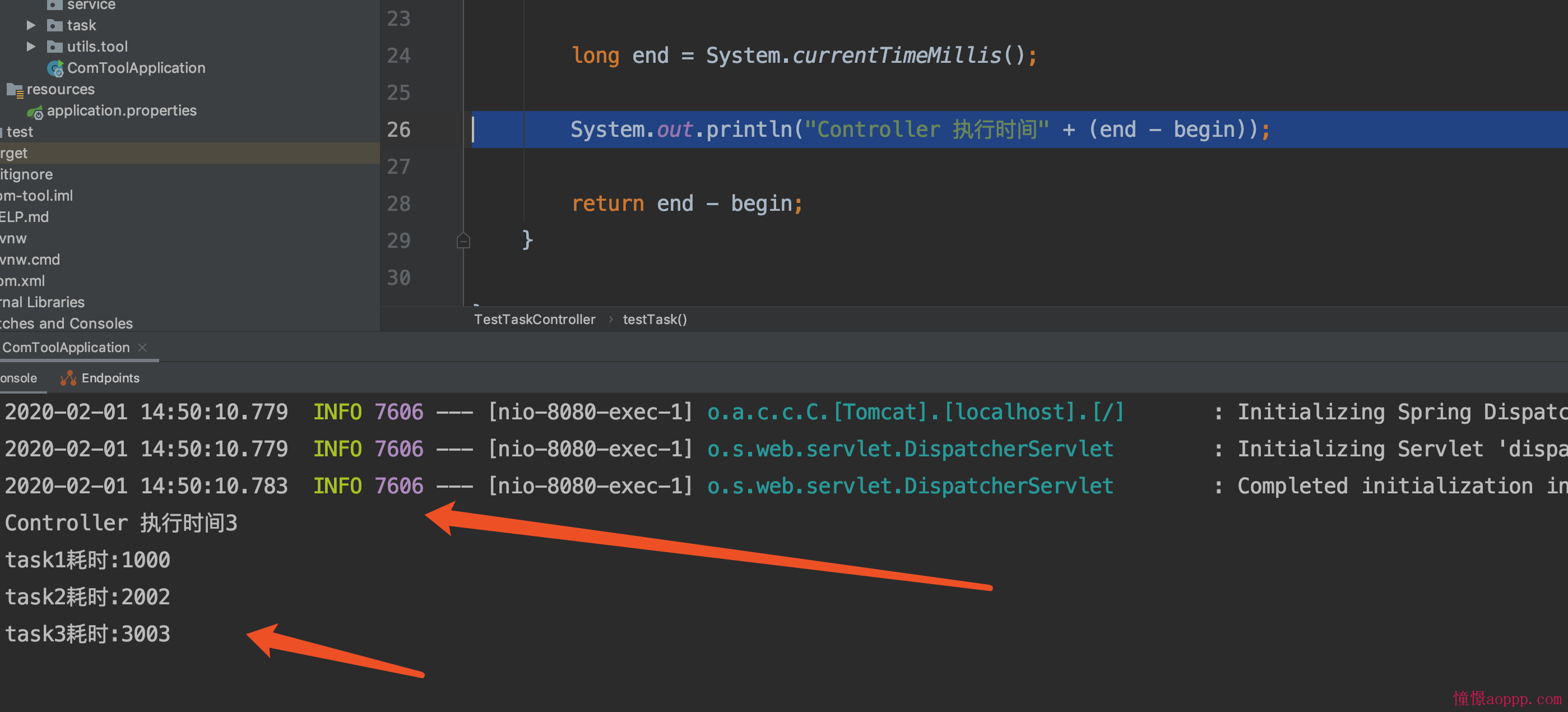
Controller执行时间 是先输出的, 我们的任务去开另外的线程执行, 这样大大增加了我们的程序效率, 在项目里面合适使用异步任务, 可以大大提高我们的QPS
获取异步返回数据
上面例子虽然解决了堵塞的问题, 但是有的时候我们希望获取异步任务的返回结果, 再进行后续工作。放心 这个也有方案
添加异步返回任务
public Future<String> task4() throws InterruptedException { long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); Thread.sleep(4000); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("task4耗时:"+ (end - begin)); return new AsyncResult<>("Task4的数据"); } public Future<Integer> task5() throws InterruptedException { long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); Thread.sleep(5000); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("task5耗时:"+ (end - begin)); return new AsyncResult<>(123); } public Future<String> task6() throws InterruptedException { long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); Thread.sleep(6000); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("task6耗时:"+ (end - begin)); return new AsyncResult<>("Task6的数据"); }
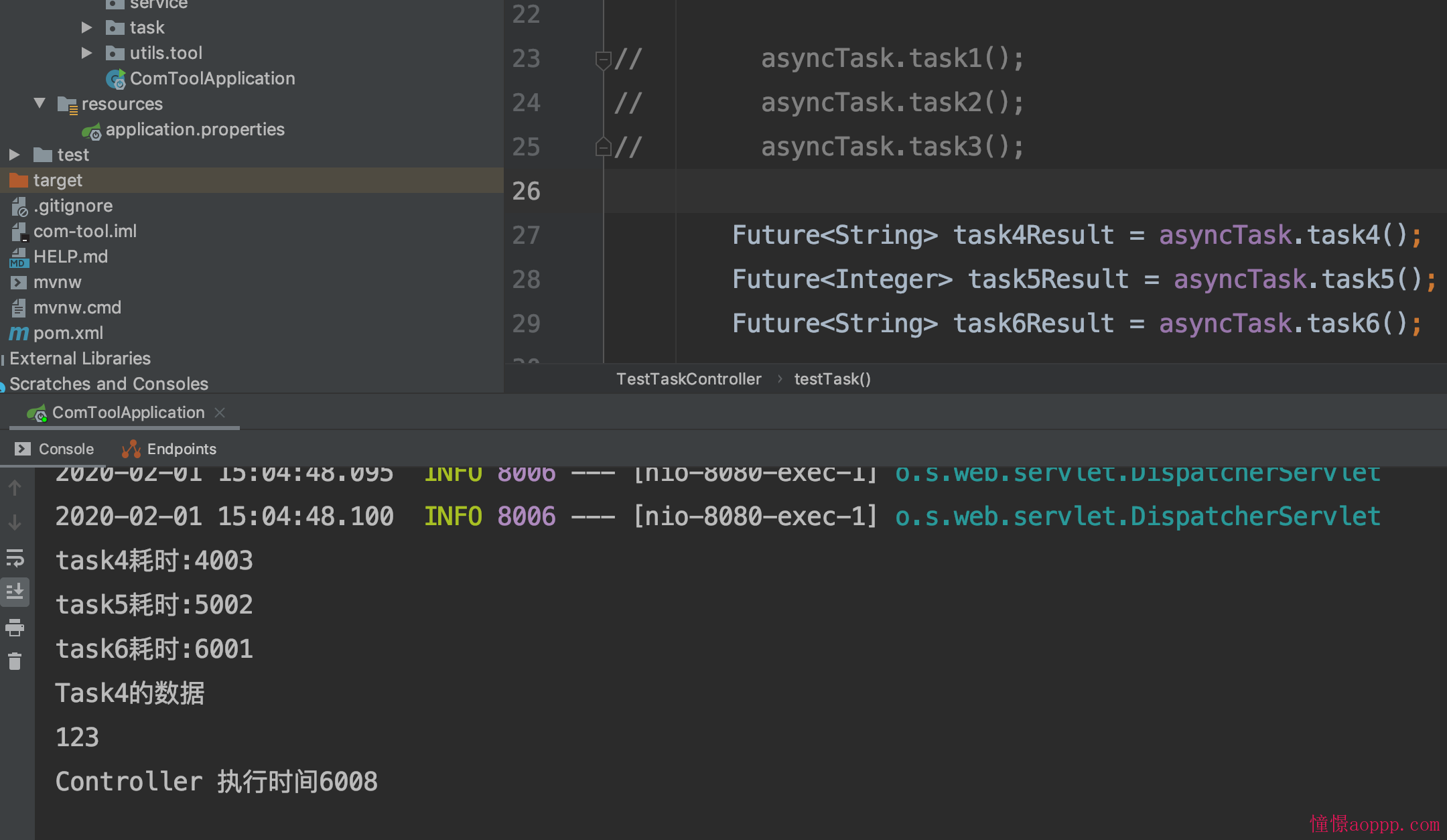
@GetMapping("/api/v1/test_task") public long testTask() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); // asyncTask.task1(); // asyncTask.task2(); // asyncTask.task3(); Future<String> task4Result = asyncTask.task4(); Future<Integer> task5Result = asyncTask.task5(); Future<String> task6Result = asyncTask.task6(); // 等每个任务执行完了就跳出 for (;;) { if (task4Result.isDone() && task5Result.isDone() && task6Result.isDone()) { break; } } // 获取返回结果 String task4res = task4Result.get(); int task5res = task5Result.get(); System.out.println(task4res); System.out.println(task5res); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("Controller 执行时间" + (end - begin)); return end - begin; }
说一下流程
1)增加Future<String> 返回结果需呀 new AsyncResult<String>("task执行完成");
2)如果需要拿到结果 需要判断全部的 task.isDone(), 然后再task.get() 获取返回数据
效果
可以看到 还是异步的, 最长耗时6000, 这样就可以应对不同的业务了, 如果是同步的话肯定需要 15000