本文转自:http://blog.csdn.net/sunkwei/article/details/6530343
/usr/local/include/libavutil/common.h
转载内容
今天尝试编写了一个基于 v4l2 的摄像头应用, 目前仅仅实现从摄像头捕捉视频, 然后本地回显.
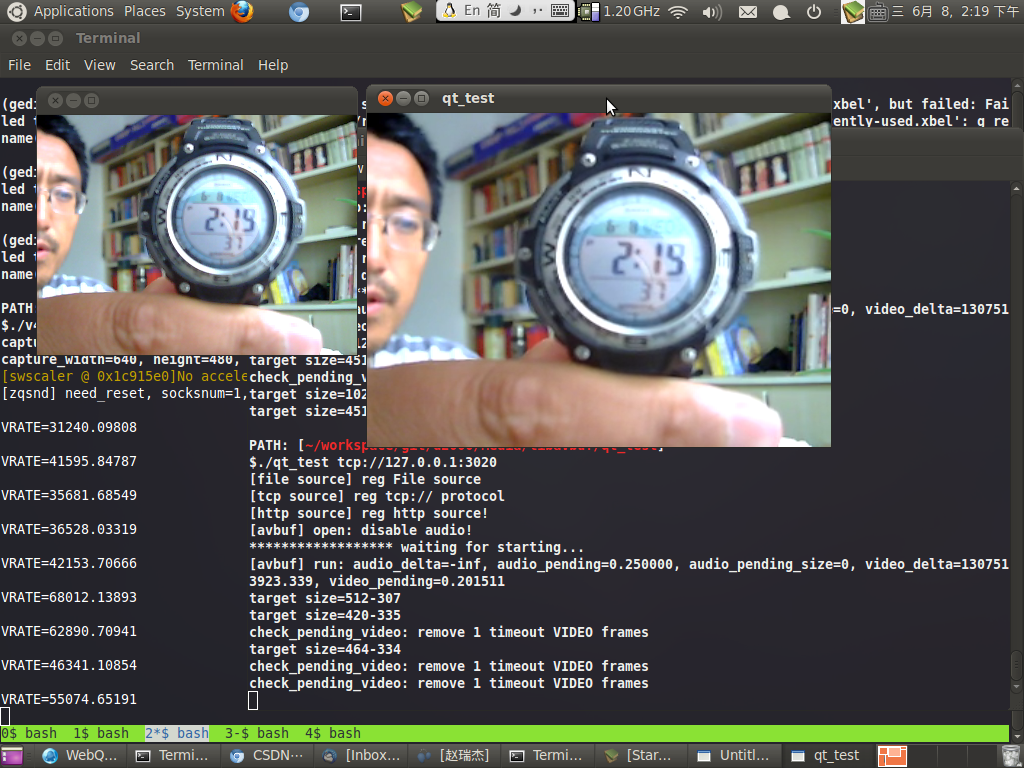
照例先上效果图, 其中左侧小点为预监窗口, 右侧为经过 x264 压缩, tcp 传输, libavcodec 解压, 再用 qt 显示的效果., 延迟很低很低 :)
主要就是以下几个知识点:
1. v4l2接口:
2. X11的本地回显:
3. 使用 libswscale 进行拉伸:
4. 使用 libx264 压缩:
1. v4l2接口: 大眼一看, 密密丫丫的 VIDIOC_XXXX, 其实静下心来, 也没多少, 很清晰, 大体流程如下:
capture_open(name)
open /dev/video0 // 打开设备
check driver caps // 检查一些 caps
VIDIOC_REQBUFS // 使用 streaming mode, mmap mode, 分配
VIDIOC_QUERYBUF // 获取分配的buf, 并且mmap到进程空间
mmap
VIDIOC_QBUF // buf 入列
VIDIOC_STREAMON // 开始
使用的数据结构
- struct Buffer
- {
- void *start;
- size_t length;
- };
- typedef struct Buffer Buffer;
- struct Ctx
- {
- int vid;
- int width, height; // 输出图像大小
- struct SwsContext *sws; // 用于转换
- int rows; // 用于 sws_scale()
- int bytesperrow; // 用于cp到 pic_src
- AVPicture pic_src, pic_target; // 用于 sws_scale
- Buffer bufs[2]; // 用于 mmap
- };
- typedef struct Ctx Ctx;
capture_open(...) 打开设备
- void *capture_open (const char *dev_name, int t_width, int t_height)
- {
- int id = open(dev_name, O_RDWR);
- if (id < 0) return 0;
- Ctx *ctx = new Ctx;
- ctx->vid = id;
- // to query caps
- v4l2_capability caps;
- ioctl(id, VIDIOC_QUERYCAP, &caps);
- if (caps.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_VIDEO_CAPTURE) {
- if (caps.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_READWRITE) {
- // TODO: ...
- }
- if (caps.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_STREAMING) {
- // 检查是否支持 MMAP, 还是 USERPTR
- v4l2_requestbuffers bufs;
- memset(&bufs, 0, sizeof(bufs));
- bufs.count = 2;
- bufs.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
- bufs.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
- if (ioctl(id, VIDIOC_REQBUFS, &bufs) < 0) {
- fprintf(stderr, "%s: don't support MEMORY_MMAP mode!/n", __func__);
- close(id);
- delete ctx;
- return 0;
- }
- fprintf(stderr, "%s: using MEMORY_MMAP mode, buf cnt=%d/n", __func__, bufs.count);
- // mmap
- for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
- v4l2_buffer buf;
- memset(&buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
- buf.type = bufs.type;
- buf.memory = bufs.memory;
- if (ioctl(id, VIDIOC_QUERYBUF, &buf) < 0) {
- fprintf(stderr, "%s: VIDIOC_QUERYBUF ERR/n", __func__);
- close(id);
- delete ctx;
- return 0;
- }
- ctx->bufs[i].length = buf.length;
- ctx->bufs[i].start = mmap(0, buf.length, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE,
- MAP_SHARED, id, buf.m.offset);
- }
- }
- else {
- fprintf(stderr, "%s: can't support read()/write() mode and streaming mode/n", __func__);
- close(id);
- delete ctx;
- return 0;
- }
- }
- else {
- fprintf(stderr, "%s: can't support video capture!/n", __func__);
- close(id);
- delete ctx;
- return 0;
- }
- int rc;
- // enum all support image fmt
- v4l2_fmtdesc fmt_desc;
- uint32_t index = 0;
- // 看起来, 不支持 plane fmt, 直接使用 yuyv 吧, 然后使用 libswscale 转换
- #if 0
- do {
- fmt_desc.index = index;
- fmt_desc.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
- rc = ioctl(id, VIDIOC_ENUM_FMT, &fmt_desc);
- if (rc >= 0) {
- fprintf(stderr, "/t support %s/n", fmt_desc.description);
- }
- index++;
- } while (rc >= 0);
- #endif // 0
- v4l2_format fmt;
- fmt.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
- rc = ioctl(id, VIDIOC_G_FMT, &fmt);
- if (rc < 0) {
- fprintf(stderr, "%s: can't VIDIOC_G_FMT.../n", __func__);
- return 0;
- }
- PixelFormat pixfmt = PIX_FMT_NONE;
- switch (fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat) {
- case V4L2_PIX_FMT_YUYV:
- pixfmt = PIX_FMT_YUYV422;
- break;
- }
- if (pixfmt == PIX_FMT_NONE) {
- fprintf(stderr, "%s: can't support %4s/n", __func__, (char*)&fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat);
- return 0;
- }
- // 构造转换器
- fprintf(stderr, "capture_width=%d, height=%d, stride=%d/n", fmt.fmt.pix.width, fmt.fmt.pix.height,
- fmt.fmt.pix.bytesperline);
- ctx->width = t_width;
- ctx->height = t_height;
- ctx->sws = sws_getContext(fmt.fmt.pix.width, fmt.fmt.pix.height, pixfmt,
- ctx->width, ctx->height, PIX_FMT_YUV420P, // PIX_FMT_YUV420P 对应 X264_CSP_I420
- SWS_FAST_BILINEAR, 0, 0, 0);
- ctx->rows = fmt.fmt.pix.height;
- ctx->bytesperrow = fmt.fmt.pix.bytesperline;
- avpicture_alloc(&ctx->pic_target, PIX_FMT_YUV420P, ctx->width, ctx->height);
- // queue buf
- for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(ctx->bufs)/sizeof(Buffer); i++) {
- v4l2_buffer buf;
- memset(&buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
- buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
- buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
- buf.index = i;
- if (ioctl(id, VIDIOC_QBUF, &buf) < 0) {
- fprintf(stderr, "%s: VIDIOC_QBUF err/n", __func__);
- exit(-1);
- }
- }
- int type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
- if (ioctl(id, VIDIOC_STREAMON, &type) < 0) {
- fprintf(stderr, "%s: VIDIOC_STREAMON err/n", __func__);
- exit(-1);
- }
- return ctx;
- }
capture_get_pic()
VIDIOC_DQBUF // 出列,
sws_scale // 格式转换/拉伸到 PIX_FMT_YUV420P, 准备方便压缩
VIDIOC_QBUF // 重新入列
capture_get_picture(...) 从摄像头得到一帧图片
- int capture_get_picture (void *id, Picture *pic)
- {
- // 获取, 转换
- Ctx *ctx = (Ctx*)id;
- v4l2_buffer buf;
- memset(&buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
- buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
- buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
- if (ioctl(ctx->vid, VIDIOC_DQBUF, &buf) < 0) {
- fprintf(stderr, "%s: VIDIOC_DQBUF err/n", __func__);
- return -1;
- }
- // _save_pic(ctx->bufs[buf.index].start, buf.length);
- // __asm("int $3");
- ctx->pic_src.data[0] = (unsigned char*)ctx->bufs[buf.index].start;
- ctx->pic_src.data[1] = ctx->pic_src.data[2] = ctx->pic_src.data[3] = 0;
- ctx->pic_src.linesize[0] = ctx->bytesperrow;
- ctx->pic_src.linesize[1] = ctx->pic_src.linesize[2] = ctx->pic_src.linesize[3] = 0;
- // sws_scale
- int rs = sws_scale(ctx->sws, ctx->pic_src.data, ctx->pic_src.linesize,
- 0, ctx->rows, ctx->pic_target.data, ctx->pic_target.linesize);
- // out
- for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
- pic->data[i] = ctx->pic_target.data[i];
- pic->stride[i] = ctx->pic_target.linesize[i];
- }
- // re queue buf
- if (ioctl(ctx->vid, VIDIOC_QBUF, &buf) < 0) {
- fprintf(stderr, "%s: VIDIOC_QBUF err/n", __func__);
- return -1;
- }
- return 1;
- }
2. X11 的本地回显: 采用 XShm, 效率还行
vs_open ()
XOpenDisplay()
XCreateSimpleWindow()
XCreateGC()
XMapWindow()
XShmCreateImage()
shmget()
shmat()
使用的数据结构
- struct Ctx
- {
- Display *display;
- int screen;
- Window window;
- GC gc;
- XVisualInfo vinfo;
- XImage *image;
- XShmSegmentInfo segment;
- SwsContext *sws;
- PixelFormat target_pixfmt;
- AVPicture pic_target;
- int v_width, v_height;
- int curr_width, curr_height;
- };
- typedef struct Ctx Ctx;
vs_open(...) 打开设备
- void *vs_open (int v_width, int v_height)
- {
- Ctx *ctx = new Ctx;
- ctx->v_width = v_width;
- ctx->v_height = v_height;
- // window
- ctx->display = XOpenDisplay(0);
- ctx->window = XCreateSimpleWindow(ctx->display, RootWindow(ctx->display, 0),
- 100, 100, v_width, v_height, 0, BlackPixel(ctx->display, 0),
- WhitePixel(ctx->display, 0));
- ctx->screen = 0;
- ctx->gc = XCreateGC(ctx->display, ctx->window, 0, 0);
- XMapWindow(ctx->display, ctx->window);
- // current screen pix fmt
- Window root;
- unsigned int cx, cy, border, depth;
- int x, y;
- XGetGeometry(ctx->display, ctx->window, &root, &x, &y, &cx, &cy, &border, &depth);
- // visual info
- XMatchVisualInfo(ctx->display, ctx->screen, depth, DirectColor, &ctx->vinfo);
- // image
- ctx->image = XShmCreateImage(ctx->display, ctx->vinfo.visual, depth, ZPixmap, 0,
- &ctx->segment, cx, cy);
- if (!ctx->image) {
- fprintf(stderr, "%s: can't XShmCreateImage !/n", __func__);
- exit(-1);
- }
- ctx->segment.shmid = shmget(IPC_PRIVATE,
- ctx->image->bytes_per_line * ctx->image->height,
- IPC_CREAT | 0777);
- if (ctx->segment.shmid < 0) {
- fprintf(stderr, "%s: shmget err/n", __func__);
- exit(-1);
- }
- ctx->segment.shmaddr = (char*)shmat(ctx->segment.shmid, 0, 0);
- if (ctx->segment.shmaddr == (char*)-1) {
- fprintf(stderr, "%s: shmat err/n", __func__);
- exit(-1);
- }
- ctx->image->data = ctx->segment.shmaddr;
- ctx->segment.readOnly = 0;
- XShmAttach(ctx->display, &ctx->segment);
- PixelFormat target_pix_fmt = PIX_FMT_NONE;
- switch (ctx->image->bits_per_pixel) {
- case 32:
- target_pix_fmt = PIX_FMT_RGB32;
- break;
- case 24:
- target_pix_fmt = PIX_FMT_RGB24;
- break;
- default:
- break;
- }
- if (target_pix_fmt == PIX_FMT_NONE) {
- fprintf(stderr, "%s: screen depth format err/n", __func__);
- delete ctx;
- return 0;
- }
- // sws
- ctx->target_pixfmt = target_pix_fmt;
- ctx->curr_width = cx;
- ctx->curr_height = cy;
- ctx->sws = sws_getContext(v_width, v_height, PIX_FMT_YUV420P,
- cx, cy, target_pix_fmt,
- SWS_FAST_BILINEAR, 0, 0, 0);
- avpicture_alloc(&ctx->pic_target, target_pix_fmt, cx, cy);
- XFlush(ctx->display);
- return ctx;
- }
vs_show()
sws_scale() // 拉伸到当前窗口大小, 转换格式
XShmPutImage() // 显示, 呵呵, 真的很简单
vs_show(...) 主要代码都是处理窗口变化的
- int vs_show (void *ctx, unsigned char *data[4], int stride[4])
- {
- // 首选检查 sws 是否有效, 根据当前窗口大小决定
- Ctx *c = (Ctx*)ctx;
- Window root;
- int x, y;
- unsigned int cx, cy, border, depth;
- XGetGeometry(c->display, c->window, &root, &x, &y, &cx, &cy, &border, &depth);
- if (cx != c->curr_width || cy != c->curr_height) {
- avpicture_free(&c->pic_target);
- sws_freeContext(c->sws);
- c->sws = sws_getContext(c->v_width, c->v_height, PIX_FMT_YUV420P,
- cx, cy, c->target_pixfmt,
- SWS_FAST_BILINEAR, 0, 0, 0);
- avpicture_alloc(&c->pic_target, c->target_pixfmt, cx, cy);
- c->curr_width = cx;
- c->curr_height = cy;
- // re create image
- XShmDetach(c->display, &c->segment);
- shmdt(c->segment.shmaddr);
- shmctl(c->segment.shmid, IPC_RMID, 0);
- XDestroyImage(c->image);
- c->image = XShmCreateImage(c->display, c->vinfo.visual, depth, ZPixmap, 0,
- &c->segment, cx, cy);
- c->segment.shmid = shmget(IPC_PRIVATE,
- c->image->bytes_per_line * c->image->height,
- IPC_CREAT | 0777);
- c->segment.shmaddr = (char*)shmat(c->segment.shmid, 0, 0);
- c->image->data = c->segment.shmaddr;
- c->segment.readOnly = 0;
- XShmAttach(c->display, &c->segment);
- }
- //
- sws_scale(c->sws, data, stride, 0, c->v_height, c->pic_target.data, c->pic_target.linesize);
- // cp to image
- unsigned char *p = c->pic_target.data[0], *q = (unsigned char*)c->image->data;
- int xx = MIN(c->image->bytes_per_line, c->pic_target.linesize[0]);
- for (int i = 0; i < c->curr_height; i++) {
- memcpy(q, p, xx);
- p += c->image->bytes_per_line;
- q += c->pic_target.linesize[0];
- }
- // 显示到 X 上
- XShmPutImage(c->display, c->window, c->gc, c->image, 0, 0, 0, 0, c->curr_width, c->curr_height, 1);
- return 1;
- }
3. libswscale: 用于picture格式/大小转换, 占用cpu挺高 :), 用起来很简单, 基本就是
sws = sws_getContext(....);
sws_scale(sws, ...)
4. libx264 压缩: 考虑主要用于互动, 所以使用 preset=fast, tune=zerolatency, 320x240, 10fps, 300kbps, jj实测延迟很低, 小于 100ms
使用的数据结构
- struct Ctx
- {
- x264_t *x264;
- x264_picture_t picture;
- x264_param_t param;
- void *output; // 用于保存编码后的完整帧
- int output_bufsize, output_datasize;
- int64_t pts; // 输入 pts
- int64_t (*get_pts)(struct Ctx *);
- int64_t info_pts, info_dts;
- int info_key_frame;
- int info_valid;
- };
vc_open(...) 设置必要的参数, 打开编码器
- void *vc_open (int width, int height)
- {
- Ctx *ctx = new Ctx;
- // 设置编码属性
- //x264_param_default(&ctx->param);
- x264_param_default_preset(&ctx->param, "fast", "zerolatency");
- ctx->param.i_width = width;
- ctx->param.i_height = height;
- ctx->param.b_repeat_headers = 1; // 重复SPS/PPS 放到关键帧前面
- ctx->param.b_cabac = 1;
- ctx->param.i_fps_num = 10;
- ctx->param.i_fps_den = 1;
- ctx->param.i_keyint_max = 30;
- ctx->param.i_keyint_min = 10;
- // rc
- ctx->param.rc.i_rc_method = X264_RC_CRF;
- ctx->param.rc.i_bitrate = 300;
- //ctx->param.rc.f_rate_tolerance = 0.1;
- //ctx->param.rc.i_vbv_max_bitrate = ctx->param.rc.i_bitrate * 1.3;
- //ctx->param.rc.f_rf_constant = 600;
- //ctx->param.rc.f_rf_constant_max = ctx->param.rc.f_rf_constant * 1.3;
- #ifdef DEBUG
- ctx->param.i_log_level = X264_LOG_WARNING;
- #else
- ctx->param.i_log_level = X264_LOG_NONE;
- #endif // release
- ctx->x264 = x264_encoder_open(&ctx->param);
- if (!ctx->x264) {
- fprintf(stderr, "%s: x264_encoder_open err/n", __func__);
- delete ctx;
- return 0;
- }
- x264_picture_init(&ctx->picture);
- ctx->picture.img.i_csp = X264_CSP_I420;
- ctx->picture.img.i_plane = 3;
- ctx->output = malloc(128*1024);
- ctx->output_bufsize = 128*1024;
- ctx->output_datasize = 0;
- ctx->get_pts = first_pts;
- ctx->info_valid = 0;
- return ctx;
- }
vc_compress(...) 压缩, 如果成功, 得到串流
- static int encode_nals (Ctx *c, x264_nal_t *nals, int nal_cnt)
- {
- char *pout = (char*)c->output;
- c->output_datasize = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < nal_cnt; i++) {
- if (c->output_datasize + nals[i].i_payload > c->output_bufsize) {
- // 扩展
- c->output_bufsize = (c->output_datasize+nals[i].i_payload+4095)/4096*4096;
- c->output = realloc(c->output, c->output_bufsize);
- }
- memcpy(pout+c->output_datasize, nals[i].p_payload, nals[i].i_payload);
- c->output_datasize += nals[i].i_payload;
- }
- return c->output_datasize;
- }
- int vc_compress (void *ctx, unsigned char *data[4], int stride[4], const void **out, int *len)
- {
- Ctx *c = (Ctx*)ctx;
- // 设置 picture 数据
- for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
- c->picture.img.plane[i] = data[i];
- c->picture.img.i_stride[i] = stride[i];
- }
- // encode
- x264_nal_t *nals;
- int nal_cnt;
- x264_picture_t pic_out;
- c->picture.i_pts = c->get_pts(c);
- #ifdef DEBUG_MORE
- static int64_t _last_pts = c->picture.i_pts;
- fprintf(stderr, "DBG: pts delta = %lld/n", c->picture.i_pts - _last_pts);
- _last_pts = c->picture.i_pts;
- #endif //
- x264_picture_t *pic = &c->picture;
- do {
- // 这里努力消耗掉 delayed frames ???
- // 实际使用 zerolatency preset 时, 效果足够好了
- int rc = x264_encoder_encode(c->x264, &nals, &nal_cnt, pic, &pic_out);
- if (rc < 0) return -1;
- encode_nals(c, nals, nal_cnt);
- } while (0);
- *out = c->output;
- *len = c->output_datasize;
- if (nal_cnt > 0) {
- c->info_valid = 1;
- c->info_key_frame = pic_out.b_keyframe;
- c->info_pts = pic_out.i_pts;
- c->info_dts = pic_out.i_dts;
- }
- else {
- fprintf(stderr, ".");
- return 0; // 继续
- }
- #ifdef DEBUG_MORE
- static size_t _seq = 0;
- fprintf(stderr, "#%lu: [%c] frame type=%d, size=%d/n", _seq,
- pic_out.b_keyframe ? '*' : '.',
- pic_out.i_type, c->output_datasize);
- _seq++;
- #endif // debug
- return 1;
- }
附上源码: 唉, 源码是不停更新的, csdn居然没有一个类似 git, svn 之类的仓库, 算了, 如果有人要, email吧.
main.cpp 主流程
capture.cpp, capture.h 获取 v4l2 的图像帧
vcompress.cpp vcompress.h 实现 x264 的压缩
vshow.cpp vsho.h 用 X11 显示实时图像
解压
解压之后直接make 如果报错出现UINT64_C未定义,在/usr/local/include/libavutil/common.h 或者是/usr/include/libavutil/common.h文件中添加
#ifndef INT64_C
#define INT64_C(c) (c ## LL)
#define UINT64_C(c) (c ## ULL)
#endif


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号