继承Thread类创建多线程
1. 继承Thread类创建多线程
需要去继承Thread类,重写Thread类的Run方法,然后调用start()方法启动线程,启动线程后执行的是run方法。
样例:TestThread类,继承了Thread类,重写Thread类的Run方法,getName() 方法是样Thread类的方法,如下所示:
package basic;
public class TestThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=1; i<=3; i++) {
System.out.println(this.getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
使用start()方法调用run()方法,setName()方法给线程命名,测试代码如下所示。
package basic;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
TestThread testThread = new TestThread();
TestThread testThread1 = new TestThread();
testThread.setName("testThread");
testThread1.setName("threadThread1");
testThread.start();
testThread1.start();
}
}
运行截图如下所示,注意:运行情况是固定不变的。
2. 继承Thread类是怎样实现的多线程
为什么重写run() 方法之后,再调用start() 方法就可以实现多线程,我尝试去读一下源码,如有错误请指出:
start 方法,使该线程开始执行;Java虚拟机调用该线程的<code>run</code>方法,结果是两个线程同时运行,当前线程(调用<code>start</code>方法的线程)和另一个线程(执行其<code>run</code>方法的线程)
多次启动线程是不合法的。特别是,线程完成后可能不会重新启动。重新启动会报错:Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalThreadStateException,如下图所示
start()方法如下所示:;
/**
* Causes this thread to begin execution; the Java Virtual Machine
* calls the <code>run</code> method of this thread.
* <p>
* The result is that two threads are running concurrently: the
* current thread (which returns from the call to the
* <code>start</code> method) and the other thread (which executes its
* <code>run</code> method).
* <p>
* It is never legal to start a thread more than once.
* In particular, a thread may not be restarted once it has completed
* execution.
*
* @exception IllegalThreadStateException if the thread was already
* started.
* @see #run()
* @see #stop()
*/
public synchronized void start() {
/**
* This method is not invoked for the main method thread or "system"
* group threads created/set up by the VM. Any new functionality added
* to this method in the future may have to also be added to the VM.
*
* A zero status value corresponds to state "NEW".
*/
if (threadStatus != 0)
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
/* Notify the group that this thread is about to be started
* so that it can be added to the group's list of threads
* and the group's unstarted count can be decremented. */
group.add(this);
boolean started = false;
try {
start0();
started = true;
} finally {
try {
if (!started) {
group.threadStartFailed(this);
}
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
/* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then
it will be passed up the call stack */
}
}
}
threadStatus,Java线程状态,默认指示线程尚未启动。
/*
* Java thread status for tools, default indicates thread 'not yet started'
*/
private volatile int threadStatus;
group,线程所在的组。
/* The group of this thread */
private ThreadGroup group;
start0()方法启动线程,start0是一个本地方法,native关键字说明其修饰的方法是一个原生态方法,方法对应的实现不是在当前文件,而是在用其他语言(如C和C++)实现的文件中,Java的底层是使用C++实现的。
private native void start0();
3. 实现Runnable接口创建多线程
实现Runnable接口,重写run方法,然后将这个实现类当做参数传给Thread类,例如:Thread dog = new Thread(runn,"小狗"),创建了一个线程,这里的runn是实现Runnable接口的类,“小狗”是线程的名字。
实现Runnable接口创建多线程和继承Thread类创建多线程相比,实现Runnable接口还可以继承其他类,因为Java中一个类只能继承一个类。
一个小实例,TestRunnable.java:
package basic;
public class TestRunnable implements Runnable{
// 实现 Runnable接口 中的run()方法
@Override
public void run() {
int times = 5;
for(int i=0; i<times; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
}
catch(InterruptedException ie){
ie.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
TestRunnable runn = new TestRunnable();
// 创建线程
Thread dog = new Thread(runn,"小狗");
Thread cat = new Thread(runn,"小猫");
// 启动线程
dog.start();
cat.start();
}
}
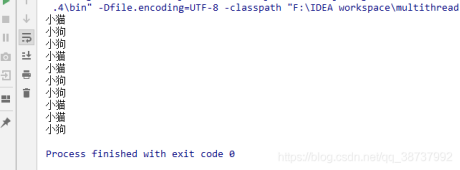
运行截图如下所示,注意:运行结果不是一成不变的。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号