.Net Core微服务入门全纪录(二)——Consul-服务注册与发现(上)
Tips:本篇已加入系列文章阅读目录,可点击查看更多相关文章。
前言
上一篇【.Net Core微服务入门全纪录(一)——项目搭建】讲到要做到服务的灵活伸缩,那么需要有一种机制来实现它,这个机制就是服务注册与发现。当然这也并不是必要的,如果你的服务实例很少,并且很稳定,那么就没有必要使用服务注册与发现。
服务注册与发现
- 服务注册:简单理解,就是有一个注册中心,我们的每个服务实例启动时,都去注册中心注册一下,告诉注册中心我的地址,端口等信息。同样的服务实例要删除时,去注册中心删除一下,注册中心负责维护这些服务实例的信息。
- 服务发现:既然注册中心维护了各个服务实例的信息,那么客户端通过注册中心就很容易发现服务的变化了。
有了服务注册与发现,客户端就不用再去配置各个服务实例的地址,改为从注册中心统一获取。
那注册中心又是怎么保证每个地址的可用状态呢,假如某个实例挂了怎么办呢?原则上挂掉的实例不应该被客户端获取到,所以就要提到:健康检查 。
- 健康检查:每个服务都需要提供一个用于健康检查的接口,该接口不具备业务功能。服务注册时把这个接口的地址也告诉注册中心,注册中心会定时调用这个接口来检测服务是否正常,如果不正常,则将它移除,这样就保证了服务的可用性。
常见注册中心有 Consul、ZooKeeper、etcd、Eureka。
Consul
Consul官网:https://www.consul.io/
Consul的主要功能有服务注册与发现、健康检查、K-V存储、多数据中心等。
- Consul安装:很简单,直接在官网下载解压即可。
- Consul运行:在consul.exe目录下打开命令行执行
consul.exe agent -dev - 浏览器访问:http://localhost:8500/
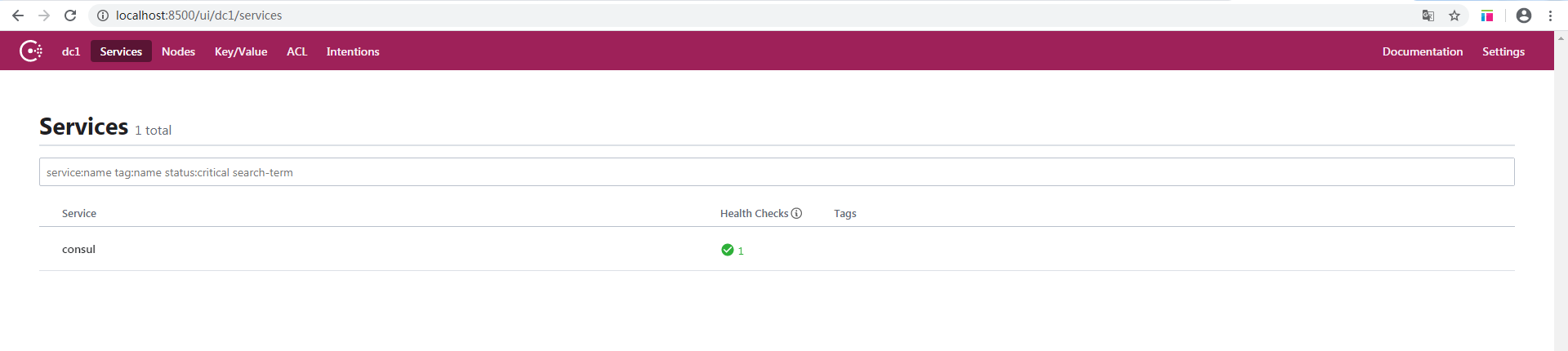
Consul已成功运行。
服务注册
-
首先Nuget安装一下Consul:

这个类库里封装了Consul的api操作,方便我们直接使用。当然自己去写http调用Consul的接口也不是不行。。。接口说明:https://www.consul.io/api-docs -
改造一下订单服务的代码:
ConsulHelper.cs:
public static class ConsulHelper
{
/// <summary>
/// 服务注册到consul
/// </summary>
/// <param name="app"></param>
/// <param name="lifetime"></param>
public static IApplicationBuilder RegisterConsul(this IApplicationBuilder app, IConfiguration configuration, IHostApplicationLifetime lifetime)
{
var consulClient = new ConsulClient(c =>
{
//consul地址
c.Address = new Uri(configuration["ConsulSetting:ConsulAddress"]);
});
var registration = new AgentServiceRegistration()
{
ID = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(),//服务实例唯一标识
Name = configuration["ConsulSetting:ServiceName"],//服务名
Address = configuration["ConsulSetting:ServiceIP"], //服务IP
Port = int.Parse(configuration["ConsulSetting:ServicePort"]),//服务端口 因为要运行多个实例,端口不能在appsettings.json里配置,在docker容器运行时传入
Check = new AgentServiceCheck()
{
DeregisterCriticalServiceAfter = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5),//服务启动多久后注册
Interval = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10),//健康检查时间间隔
HTTP = $"http://{configuration["ConsulSetting:ServiceIP"]}:{configuration["ConsulSetting:ServicePort"]}{configuration["ConsulSetting:ServiceHealthCheck"]}",//健康检查地址
Timeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5)//超时时间
}
};
//服务注册
consulClient.Agent.ServiceRegister(registration).Wait();
//应用程序终止时,取消注册
lifetime.ApplicationStopping.Register(() =>
{
consulClient.Agent.ServiceDeregister(registration.ID).Wait();
});
return app;
}
}
appsettings.json:
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Warning",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConsulSetting": {
"ServiceName": "OrderService",
"ServiceIP": "localhost",
"ServiceHealthCheck": "/healthcheck",
"ConsulAddress": "http://host.docker.internal:8500"//注意,docker容器内部无法使用localhost访问宿主机器,如果是控制台启动的话就用localhost
}
}
Startup.cs:
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllers();
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env, IHostApplicationLifetime lifetime)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllers();
});
//服务注册
app.RegisterConsul(Configuration, lifetime);
}
}
OrdersController.cs:
[Route("[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class OrdersController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly ILogger<OrdersController> _logger;
private readonly IConfiguration _configuration;
public OrdersController(ILogger<OrdersController> logger, IConfiguration configuration)
{
_logger = logger;
_configuration = configuration;
}
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult Get()
{
string result = $"【订单服务】{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")}——" +
$"{Request.HttpContext.Connection.LocalIpAddress}:{_configuration["ConsulSetting:ServicePort"]}";
return Ok(result);
}
}
HealthCheckController.cs:
[Route("[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class HealthCheckController : ControllerBase
{
/// <summary>
/// 健康检查接口
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult Get()
{
return Ok();
}
}
至此就完成了服务注册,取消注册,健康检查等功能的代码编写。
- 同样的改造一下产品服务,代码差不多一样,就不贴了。
运行服务
继续在docker中运行服务实例,不习惯docker的话用控制台启动也行。--ConsulSetting:ServicePort参数就是传入容器的端口信息。
docker build -t orderapi:1.0 -f ./Order.API/Dockerfile .
docker run -d -p 9060:80 --name orderservice orderapi:1.0 --ConsulSetting:ServicePort="9060"
docker run -d -p 9061:80 --name orderservice1 orderapi:1.0 --ConsulSetting:ServicePort="9061"
docker run -d -p 9062:80 --name orderservice2 orderapi:1.0 --ConsulSetting:ServicePort="9062"
docker build -t productapi:1.0 -f ./Product.API/Dockerfile .
docker run -d -p 9050:80 --name productservice productapi:1.0 --ConsulSetting:ServicePort="9050"
docker run -d -p 9051:80 --name productservice1 productapi:1.0 --ConsulSetting:ServicePort="9051"
docker run -d -p 9052:80 --name productservice2 productapi:1.0 --ConsulSetting:ServicePort="9052"
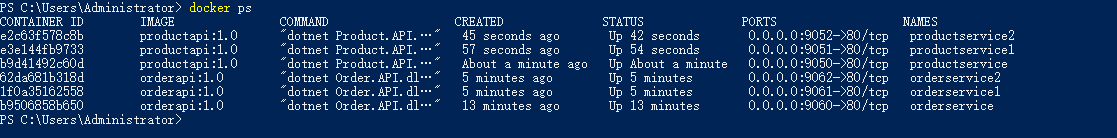
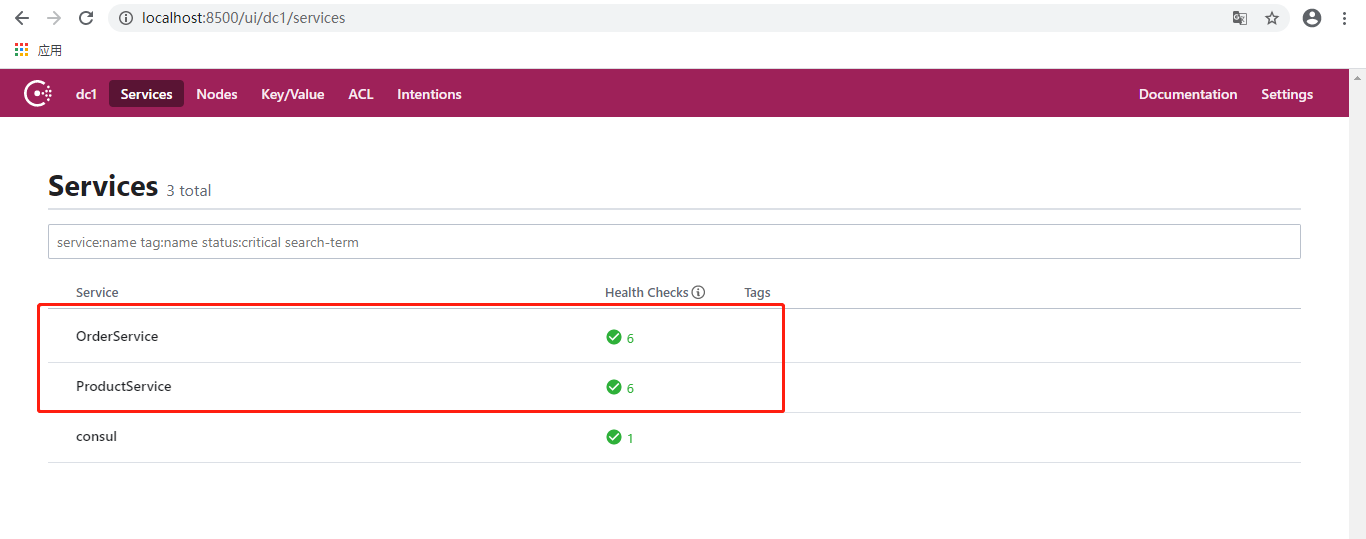
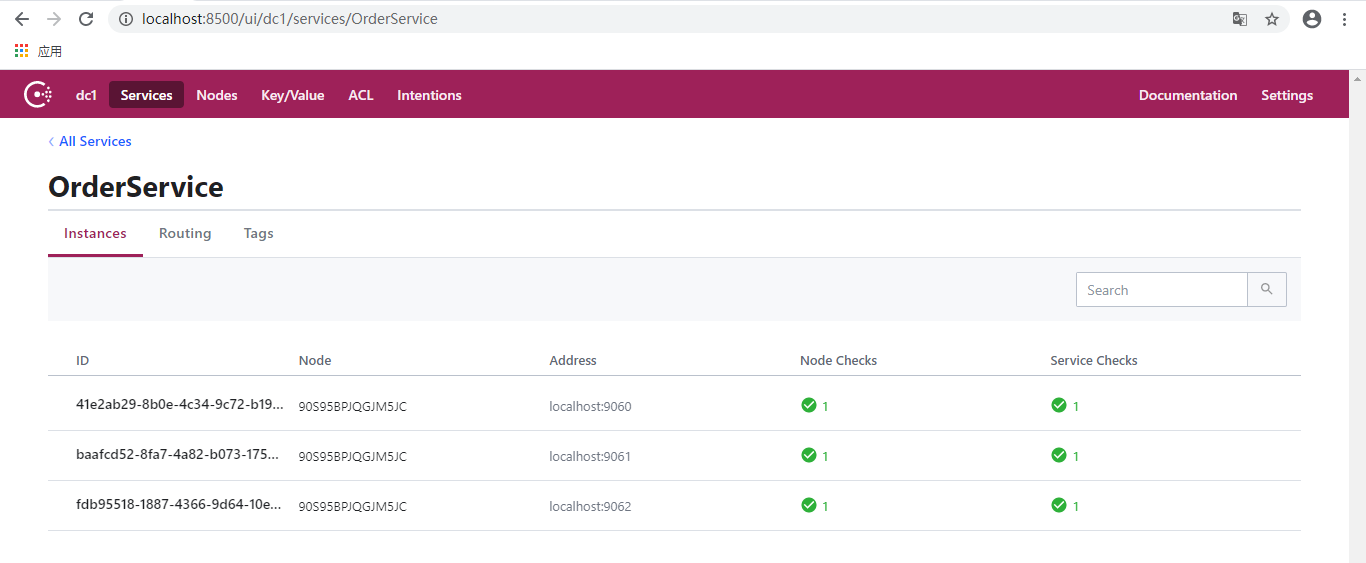
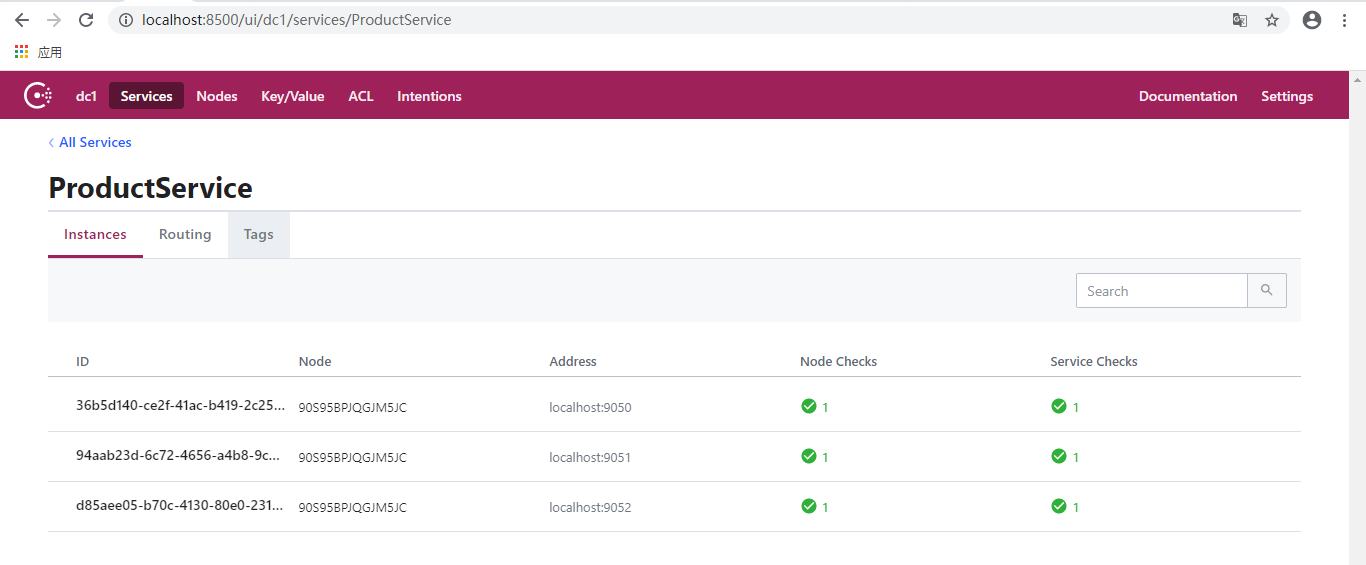
至此,6个服务器实例都已运行,并且成功注册到Consul。
随便停止2个服务:

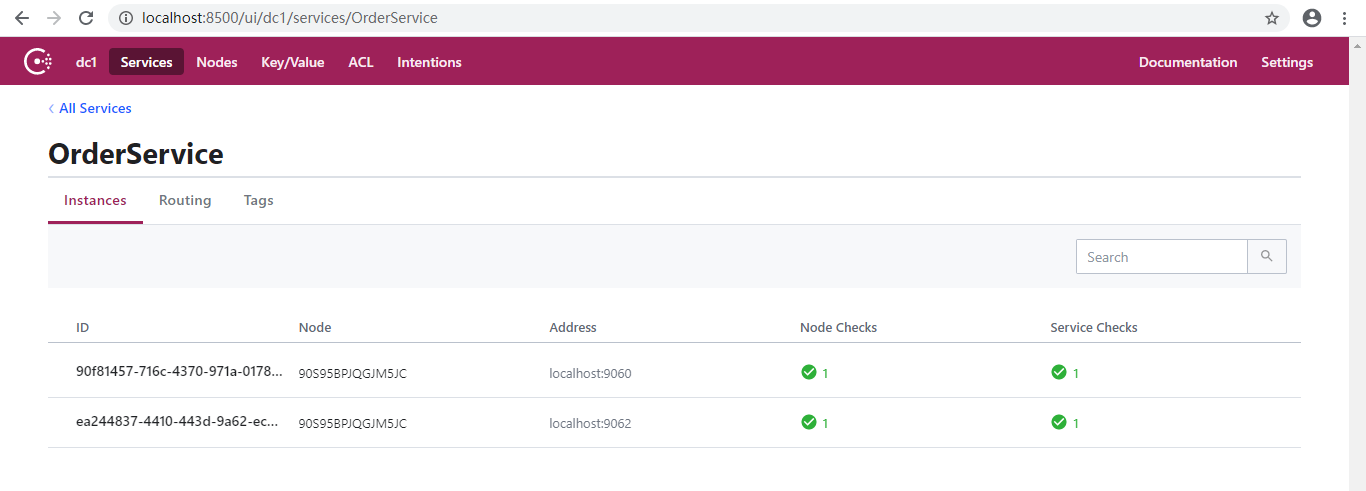
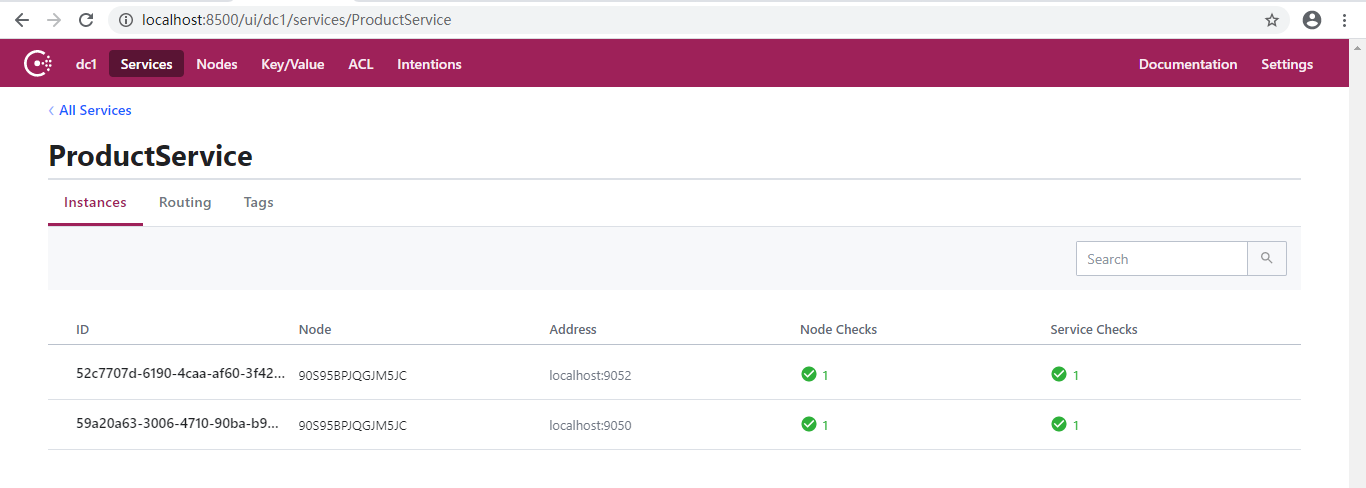
可以看到停止的服务已经在Consul中被移除。注意,这个是我们停止程序时主动调用Consul移除的。
//应用程序终止时,取消注册
lifetime.ApplicationStopping.Register(() =>
{
consulClient.Agent.ServiceDeregister(registration.ID).Wait();
});
当然程序发生异常,健康检查不能正确响应的话,Consul也会移除,有一点区别。
那么注册,发现,健康检查功能都完成了,下一步就该考虑客户端如何拿到这些服务实例的地址了。
代码放在:https://github.com/xiajingren/NetCoreMicroserviceDemo
未完待续...
——本文使用【Typora】+【EasyBlogImageForTypora】编辑
欢迎关注我的公众号,一起学习。
如果本文对您有所帮助,您可以点击右下方的【推荐】按钮支持一下;文中如有不妥之处,还望指正,非常感谢!!!

作者:xhznl
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/xhznl/
文章可以转载,但请注明出处





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· DeepSeek如何颠覆传统软件测试?测试工程师会被淘汰吗?
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端