scala
https://www.scala-lang.org/
http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.6.3/
java、scala 基于jvm
concise
adj. 简明的,简洁的
The Scala Programming Language
Scala combines object-oriented and functional programming in one concise, high-level language. Scala's static types help avoid bugs in complex applications, and its JVM and JavaScript runtimes let you build high-performance systems with easy access to huge ecosystems of libraries.
scala 面向对象、面向函数。 scala可以在方法中传入方法
seamless
adj. 无缝的;无缝合线的;无伤痕的
scala
var 变量, val:常量(val便于回收)
C:\Users\Administrator>scala
Welcome to Scala 2.12.8 (Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM, Java 1.8.0_201).
Type in expressions for evaluation. Or try :help.
scala> var a =100
a: Int = 100
scala> print(a)
100
scala> val a = 100
a: Int = 100
scala> val = 1000
<console>:1: error: illegal start of simple pattern
val = 1000
^
scala> var b = 1
b: Int = 1
scala> b =3
b: Int = 3
scala>
traits
英 美 [tret]
n. 特性,特质,性格(trait的复数)
scala 既可以单继承,多继承,接口定义变量
方法与函数 指的是方法
高阶函数:方法中的参数可以使方法。
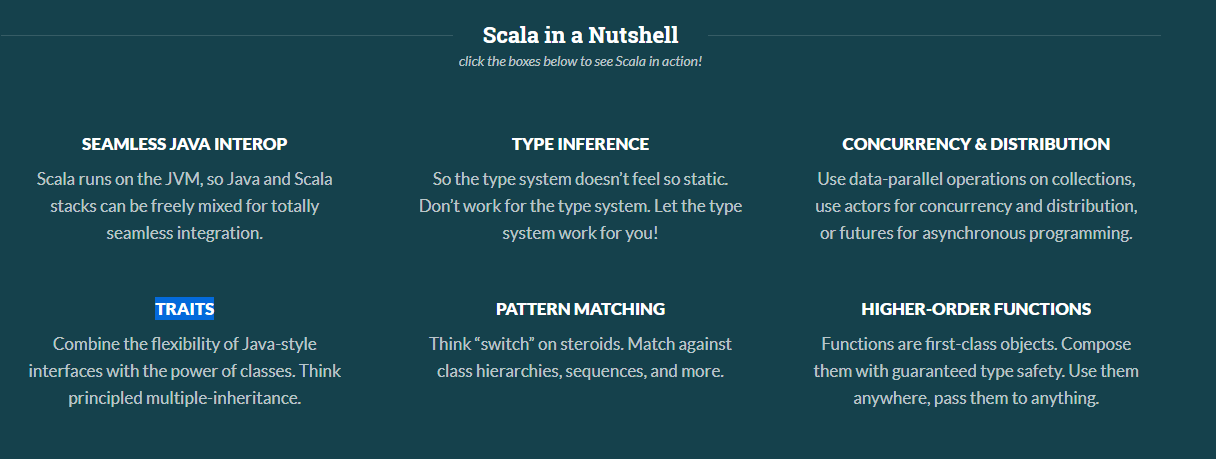

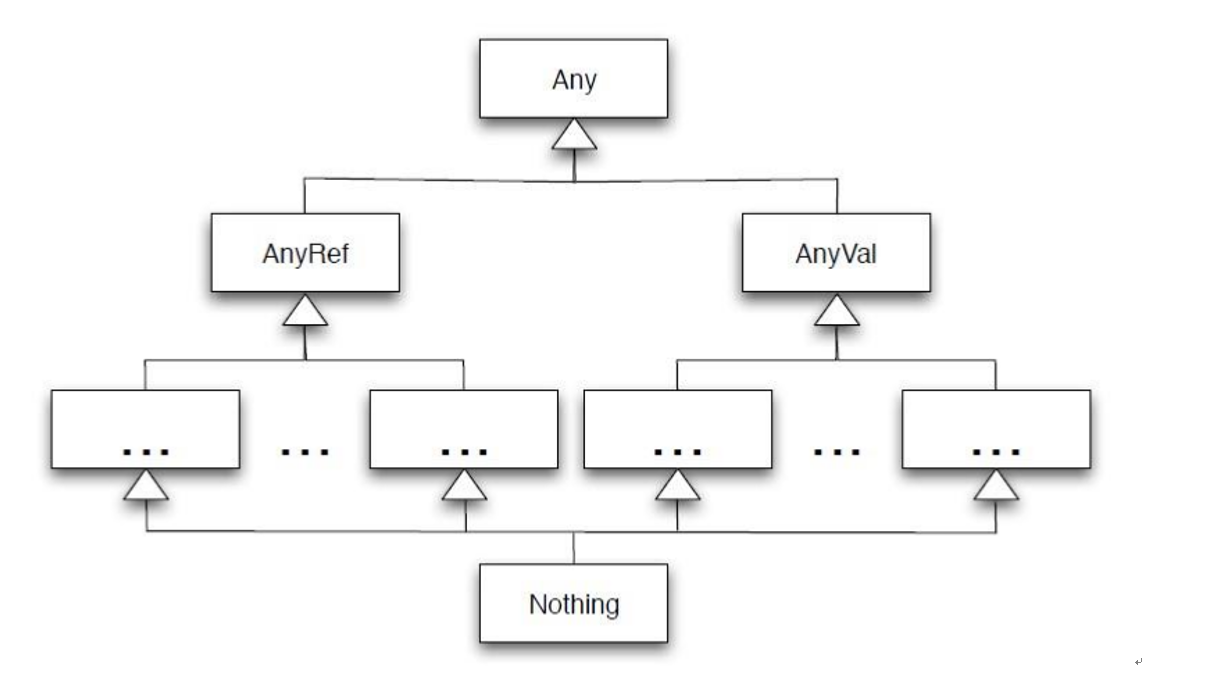
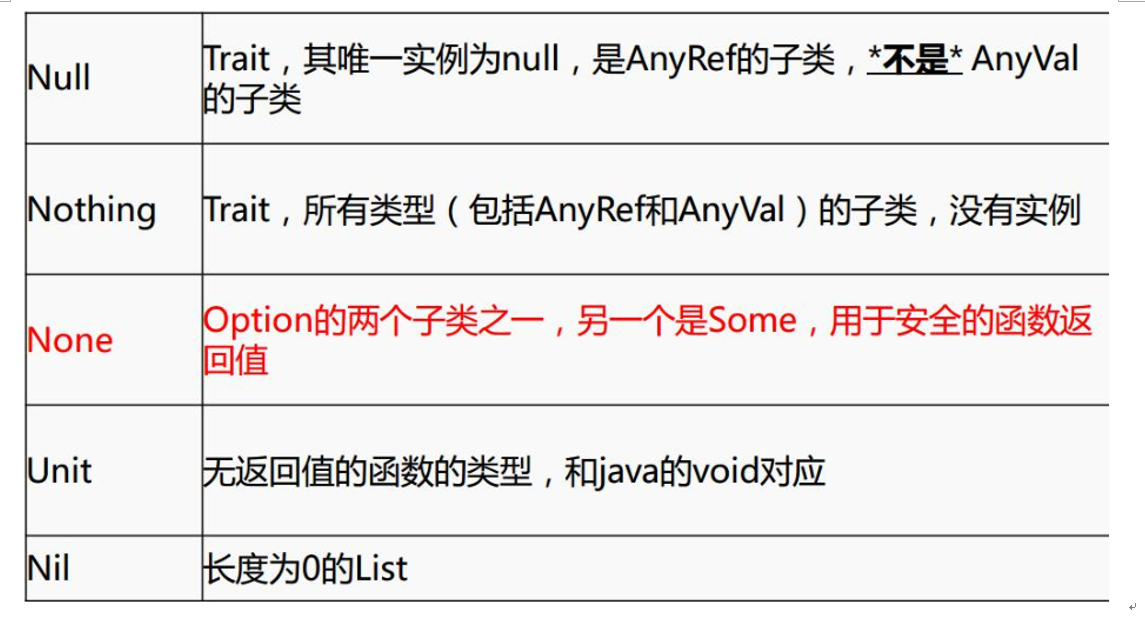
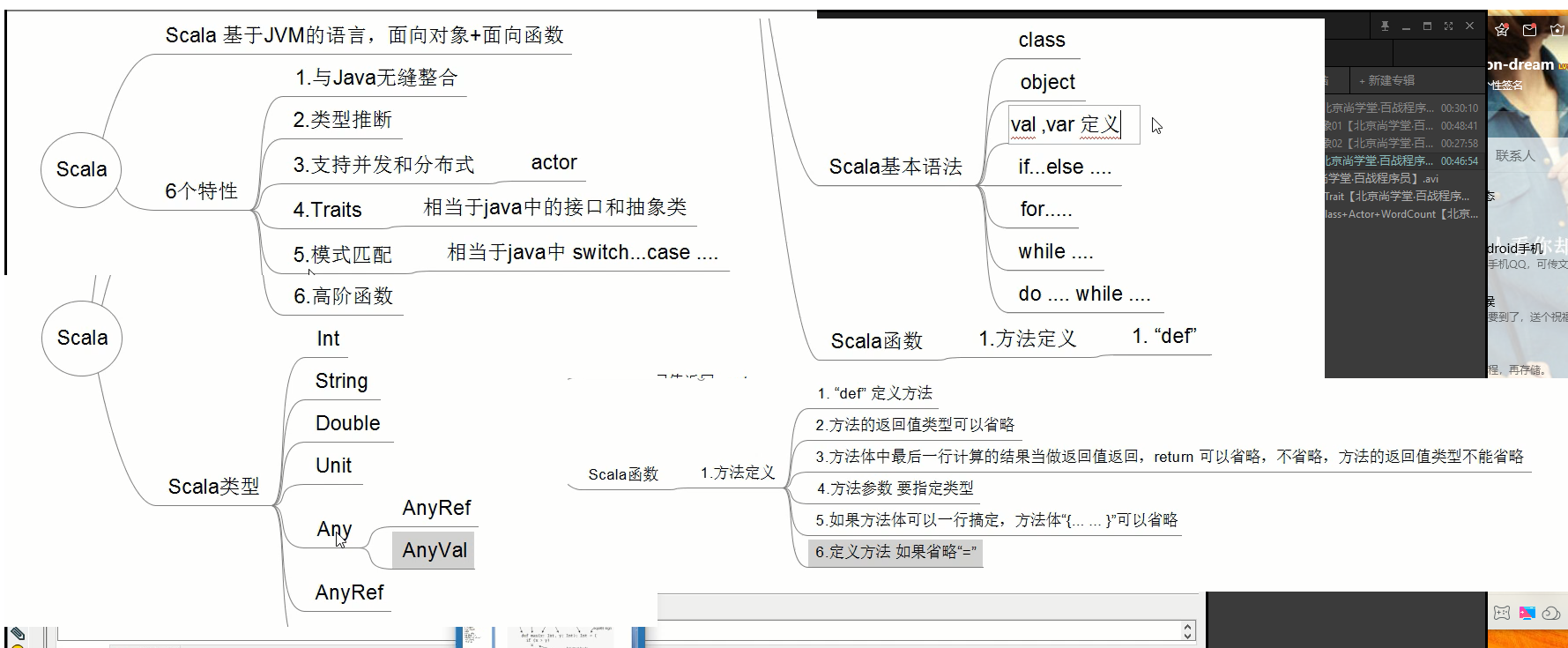
Scala介绍 1.Spark中使用的是Sacla2.10。 2.Scala官网6个特征。 1).Java和scala可以混编 2).类型推测(自动推测类型) 3).并发和分布式(Actor) 4).特质,特征(类似java中interfaces 和 abstract结合) 5).模式匹配(类似java switch) 6).高阶函数 Scala安装使用 1. windows安装,配置环境变量 官网下载scala2.10:http://www.scala-lang.org/download/2.10.4.html 下载好后安装。双击msi包安装,记住安装的路径。 配置环境变量(和配置jdk一样) 新建SCALA_HOME

window安装scala环境,并且配置环境变量。 eclispe配置环境: plugins idea配置环境 plugin install 选择相应的jdk版本。eclipse选择java path compile scala jdk 版本。
2. eclipse 配置scala插件 下载插件(一定要对应eclipse版本下载) http://scala-ide.org/download/prev-stable.html
1 打开cmd,输入:scala - version 看是否显示版本号,确定是否安装成功 2. eclipse 配置scala插件 下载插件(一定要对应eclipse版本下载) http://scala-ide.org/download/prev-stable.html 将features和plugins两个文件夹拷贝到eclipse安装目录中的” dropins/scala”目录下。进入dropins,新建scala文件夹,将两个文件夹拷贝到“dropins/scala”下 3. scala ide 下载网址:http://scala-ide.org/download/sdk.html 4. idea 中配置scala插件 打开idea,close项目后,点击Configure->Plugins
选用scala ide :实质上是eclipse的scala插件版。

package com.bjsxt.scala
/**
* 1.scala中定义在object中的变量,方法都是静态的。object 交对象,相当于java中的单例对象,object可以传参,Trait不可以传参
* 2.scala中一行代码后可以写“;" 也可以不写,会有分号推断机制,多行代码写在一行要用分号隔开
* 3.定义变量用var,定义常量用val; a:Int 是变量的类型,可写可不写。不写会自动推断。
* 4.scala中变量、类、对象、方法 命名建议服务驼峰命名法。
* 5 class 是scala中的类;类可以传参数, 必须给参数指定类型;传参就默认有了带参数的构造
* 6 当new 一个class时,类中方法不会执行,其他都执行。同一个包下,class不能重名
* 7.scala中如果一个class名称和object的名称一致,那么这个class叫做这个object的伴生类,这个object叫做这个class的半生对象,他们之间可以互相访问私有变量。
*/
class Person(xname:String,xage:Int){
private val name = xname
var age = xage
var gender = 'm'
println("*******************")
/**
* 重写构造
*/
def this(yname:String,yage:Int,ygender:Char){
this(yname,yage)
this.gender = ygender
}
def showHello()={
// println("hello world" + Lesson_ObjAndClass.score)
println("hello world")
}
}
//object Lesson_ObjAndClass {
object Person {
val score = 200
println("=================")
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
/**
* 变量,常量
*/
// var a:Int = 100;
// a = 900
// println(a)
// val a = 100 ## 常量不可改变
// a=200
// var p = new Person("smith",18)
// p.age = 100
// print(p.name)
// print(p.age)
// var p1 = new Person("smith",18,'f')
// p1.age = 100
// println(p1.age)
// p1.showHello()
// var p1 = new Person("smith",18)
// println(p1.name)
// val a = 100
// if(a<50){
// println("a小于50")
// }else if(a >=50 && a <= 100){
// println("50--a--100")
// }else{
// println("其他")
// }
// println(1 to 10) // Range(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)
// println(1 until 10)//Range(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9)
/**
* for
* 1 to 10 这种表示是scala中的操作符操作
*
*/
// println(1.to(10,3)) // 步长3 //Range(1, 4, 7, 10)
// println(1.until(10,3)) // 步长3 //Range(1, 4, 7, 10)
// for(i <- 1 to 10){ // i 是val的
// println(i)
// }
// for(i <- 1 to 10){ // i 是val的
// for(j <- 1 to 10){ // i 是val的
// println("i=" + ";j=" + j)
// }
// }
// for(i <- 1 to 10;j <- 1 to 10){ // i 是val的
// println("i=" + ";j=" + j)
// }
// for(i <- 1 to 9;j <- 1 to 10){ // i 是val的
// if(i > j){
// print(i + "*" + j +"=" + i*j + "\t")
// }
// if(i == j){
// println()
// }
// }
// for(i <- 1 to 100 if(i%2==0) if (i ==98)){
// println( i)
// }
val result = for(i <- 1 to 100 if(i%10==0)) yield i
// println(result)// Vector(10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100)
// result.foreach ( (x:Int) => {
// println(x)
// })
// result.foreach ( x => {
// println(x)
// })
// result.foreach (println(_))
result.foreach (println)
}
}
package com.bjsxt.scala
import java.util.Date
object Lesson_Fun2 {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
/**
* 1.方法定义
* 1.方法定义用def,函数的参数 要写类型,不写类型不可以。
* 2.函数的返回值类型可以不写,会自动推断
* 3.scala会将函数体中最后一行计算的结果当做返回值返回
* 4.可以写“return”,写了return要显式的声明方法体的放回类型。
* 5.定义方法时,如果不写“=”,那么无论方法体中最后一行计算的结果返回是什么,都会被丢弃,返回Unit
*/
// def max(x:Int,y:Int):Int={
// if(x >y){
// x
// }else{
// y
// }
// }
//
// println(max(10,11))
// def max(x:Int,y:Int) = if(x>y) x else y
// println(max(100,2))
// def max(x:Int,y:Int):Int={ // 返回类型
// if(x >y){
// x
// }else{
// y
// }
// }
// def max(x:Int,y:Int){ // 返回Unit ()
// if(x >y){
// x
// }else{
// y
// }
// }
/**
* 2.递归函数 , 要指定函数的返回值类型,因为fun(num-1)不能自动推断
*/
// def fun(num:Int):Int = {
// if(num == 1){
// num
// }else{
// num * fun(num-1)
// }
// }
// println(fun(5))
/**
* 3.参数有默认值的函数
*/
// def fun(a:Int=2,b:Int=3) = {
// a+b
// }
//
//// println(fun(1,9))
// println(fun())
// println(fun(100)) // 替换a
// println(fun(b=101))
/**
* 4 可变长参数的函数
*/
// def fun(eles:String*) = {
//// println(eles)
//// for(e<-eles){
//// println(e)
//// }
//// eles.foreach ( s => {println(s)} )
//// eles.foreach (println(_))
// eles.foreach (println)
// }
// fun("a")
// fun("a","b","c")
/**
* 5.匿名函数
*/
// val fun = (a:Int,b:Int)=>{
//// println("hello world" + a + "~"+ b)
// a+b
// }
// println(fun(2,7))
/**
* 6 嵌套函数
*
*/
// def fun(a:Int) ={
// def fun1(num:Int):Int={
// if(num ==1 ){
// 1
// }else{
// num*fun1(num-1)
// }
// }
// fun1(a)
// }
//
// println(fun(5));
/**
* 7 偏应用函数
*/
// def showLog(date:Date,log:String) ={
// println("date is " + date + ", log is " + log)
// }
//
// val date = new Date()
//// showLog(date,"a")
//// showLog(date,"b")
//// showLog(date,"c")
//
// val fun = showLog(date:Date,_:String) // 与不变化的参数,变化的参数
// fun("aaa")
// fun("bbb")
// fun("ccc")
/**
* 8.高阶函数
* 1.函数的参数时函数
* 2.函数的返回值是函数 -- 需要显示的声明函数的返回类型
* 3.函数的参数和返回值都是函数
*
*/
// def fun(a:Int,b:Int):Int = {
// a + b
// }
// def fun1(s:String,f:(Int,Int)=>Int) = {
// // 对应集群中逻辑被传入,但是集群不知道逻辑是什么,只要给数据,
// val rt = f(100,200)
// s + "~" + rt
// }
// 1.函数的参数是函数
// println(fun1("hello",fun)) // fun 是函数,不是fun(1,2)
// 传入逻辑,拿到集群的数据按传入的逻辑处理。(至于怎么处理就是传入逻辑的事情了)
// def fun1(f:(Int,Int)=>Int,s:String):String= {
// // 对应集群中逻辑被传入,但是集群不知道逻辑是什么,只要给数据,
// val rt = f(100,200)
// s + "~" + rt
// }
// val result = fun1((a:Int,b:Int) => { a * b },"hello")
// println(result)
// 函数的返回是函数
// def fun(a:Int,b:Int):(String,String) =>String = {
// val rt = a*b
// def fun1(s:String,s1:String)={
// s + "@" +s1 + rt
// }
// fun1
// }
//
// println(fun(10,20)("hello","world")) // hello@world200
//
// 函数的参数和返回值都是函数
// def fun(f:(Int,Int)=>Int):(String,String) =>String = {
// val rt = f(10,100)
// def fun1(s:String,s1:String)={
// s + "@" +s1 + "$" + rt
// }
// fun1
// }
//
// val rr = fun( (a,b)=>{a + b})("hello","world") // hello@world$110
// println(rr)
/**
* 9 柯里化函数,是高阶函数的简化版
*/
def fun(a:Int,b:Int)(c:Int,d:Int) = {
a + b + c +d
}
println(fun(1,2)(3,4))
}
}
lat
n. 平地;公寓;平面
adj. 平的;单调的;不景气的;干脆的;平坦的;扁平的;浅的
vi. 逐渐变平;[音乐]以降调唱(或奏)
tuple
英 [tjʊpəl; ˈtʌpəl] 美 [ˈtjʊpəl; ˈtʌpəl]
n. [计] 元组,重数
package com.bjsxt.scala
object Lesson_String {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// val s= "bjsxt"
// val s1 = "BJSXT"
//
// println(s.equals(s1))
// println(s.equalsIgnoreCase(s1))
val builder = new StringBuilder
builder.+('a')
builder.++=("hello")
builder.append(true)
println(builder)
}
}
package com.bjsxt.scala
object Lesson_Collections {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
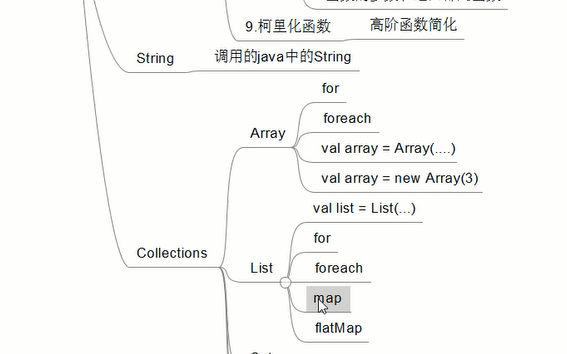
/**
* Array
*/
// val arr = Array(1,2,3,4,"hello",'c')
// val arr = Array[Int](1,2,3,4)
// arr.foreach(println)
// for(e<- arr){
// println(e)
// }
// val arr = new Array[String](3) // new 3 表示长度
// arr(0) = "a"
// arr(1) = "b"
// arr(2) = "c"
/**
* List
*/
// val list = List[Int](1,2,3,4,3)
// list.foreach(println)
// for(e<- list){
// println(e)
// }
/**
* map 输入输出 一对一;
* flatmap 一对多
*/
val list = List("hello world","hello bjsxt", "hello scala")
// val rt:List[Array[String]] = list.map(s =>{ // B 表示不为空;函数。// U 表示可以为Unit,或函数
// s.split(" ")
// })
// rt.foreach(arr=>{
// println("************")
// arr.foreach(println)
// })
// var rt2:List[String] = list.flatMap { s => {
// s.split(" ")
// }
// }
// rt2.foreach(println)
// val rt = list.filter(line =>{
// !line.equals("hello world") // false 被留下,true被过滤
// })
// rt.foreach(println) // hello world
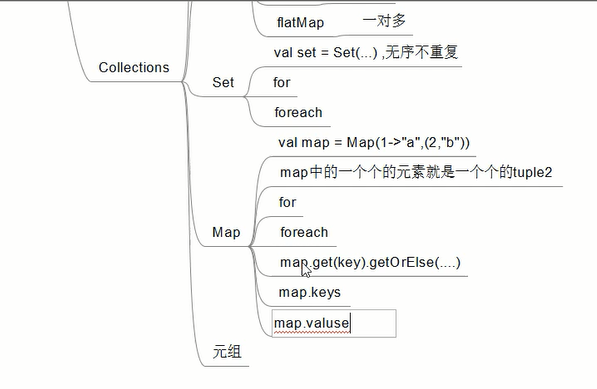
/**
* set 无序不重复
*/
// val set = Set[Int](1,2,3,4,5)
// set.foreach(println)
/**
* map
*/
// val map = Map(1->"a",2->"b",(3,"c"),(3,"d"))
// map.foreach(println)
// 取值
// val v:Option[String] = map.get(2)
// println(v) // Some(b)
// val v = map.get(2).get //String
// println(v) // Some(b)
// val v = map.get(12).getOrElse("xxx") //None.get
// println(v) // Some(b)
// val keys:Iterable[Int] = map.keys
// keys.foreach(println)
// val vs = map.values
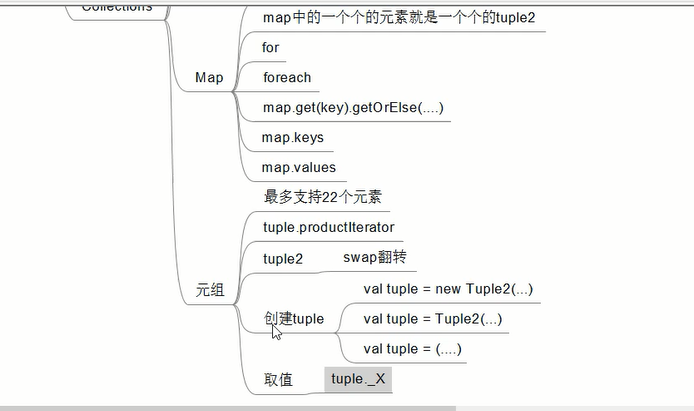
/**
* tuple 元组
* 最多支持22个元素
*/
// val tuple5 = new Tuple5(1,'c',3,4,"hello")
// val tuple1 = new Tuple1("hello")
// val tuple2 = new Tuple2("hello",10)
// val tuple3 = new Tuple3(1,2,3)
//
// // 最多22个元素
// val tuple = new Tuple22(1,2,2,3,"hello", 3,34,3,3,3, 3,2,23,3,3, 4,4,4,3,2, 2,3)
//
// val tuple6 = (1,2,3,4,5,6)
//
// val iter:Iterator[Any] = tuple.productIterator
//// iter.foreach(println)
// while(iter.hasNext){
// println(iter.next())
// }
/**
* map中每个元素就是一个二元组
*/
// val map = Map(1->"a",2->"b",(3,"c"),(3,"d"))
val tuple2 = new Tuple2("hello",10)
println(tuple2.swap) // (10,hello) 只有tuple2有此方法
// val Tuple4 = new Tuple4(1,2,3.5,"world")
// println(Tuple4._3)
}
}
package com.bjsxt.scala
/**
* trait接口的特质特性;第一个关键字用extends,之后用with
*/
trait Speak{
def speak(name:String)={
println(name + " is speaking....")
}
}
trait Listen{
def listen(name:String)={
println(name + " is listening....")
}
}
class Person1() extends Speak with Listen{
}
object Trait01 {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val p = new Person1()
p.speak("wangcai")
p.listen("xiaoqaing")
}
}
package com.bjsxt.scala
/**
* trait 方法实现,不实现
*/
trait IsEquale{
def isEqu(p:Any):Boolean
def isNotEqu(p:Any):Boolean = {
!isEqu(p)
}
}
class Point(xx:Int, xy:Int) extends IsEquale {
val x = xx
val y = xy
def isEqu(p: Any): Boolean = {
p.isInstanceOf[Point] && p.asInstanceOf[Point].x == this.x
// p.isInstanceOf[Point] && p.asInstanceOf[Point].y == this.x
}
}
object Trait02 {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val p1 = new Point(1,2)
val p2 = new Point(1,3)
println(p1.isEqu(p2)) // true
println(p1.isNotEqu(p2)) //
}
}
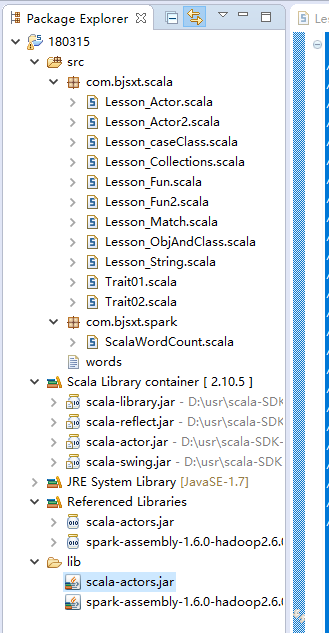
########## 需要导入lib/scala-actors.jar包
package com.bjsxt.scala
import scala.actors.Actor
/**
* Actor是通信模型,Spark底层代码就是scala编写,spark底层节点之间的通信就是Akka,Akka 是通信模型,Akka底层就是Actor实现的
* Actor 相当于我们理解的线程。Thread
*
*/
class MyActor extends Actor {
def act(): Unit = {
while(true){
receive{
case s:String => println("value is " + s)
case _=>{
println("default...")
}
}
}
}
}
object Lesson_Actor {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val actor = new MyActor()
actor.start()
// actor ! "hello"
actor ! "100"
}
}
package com.bjsxt.scala
import scala.actors.Actor
case class Message(actor:Actor,msg:String)
class MyActor1 extends Actor {
def act(): Unit = {
while(true){
receive{
case message:Message =>{
if(message.msg.equals("hello")){
println("hello")
message.actor ! "hi~"
}else if(message.msg.equals("could we have a date?")){
println("could we have a date?")
message.actor !"yes!"
}else if(message.msg.equals("ok ~")){
println("ok ~")
println("Let's go")
}
}
}
}
}
}
class MyActor2(actor:Actor) extends Actor {
actor ! Message(this,"hello")
def act(): Unit = {
while(true){
receive{
case s:String =>{
if(s.equals("hi~")){
println("hi~")
actor ! Message(this,"could we have a date?")
}else if(s.equals("yes!")){
println("yes!")
actor ! Message(this,"ok ~")
}
}
}
}
}
}
object Lesson_Actor2 {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val actor1 = new MyActor1()
val actor2 = new MyActor2(actor1)
actor1.start()
actor2.start()
}
}
使用scala 编写 wordcount
src/words 文件
lib/scala-actors.jar,spark-assembly-1.6.0-hadoop2.6.0.jar
hello spark
hello bjsxt
hello spark
hello spark
hello java
hello java
package com.bjsxt.spark
import org.apache.spark.SparkConf
import org.apache.spark.SparkContext
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
object ScalaWordCount {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// val conf = new SparkConf()
//
// conf.setMaster("local").setAppName("ScalaWordCount")
//
// val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
//
//
// val lines: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("src/words") // 一行行读取的
//
// val words:RDD[String] = lines.flatMap(line =>{
// line.split(" ")
// })
//
// val pairWords:RDD[(String, Int)] = words.map(word =>{
// new Tuple2(word,1)
// })
//
// /**
// * reduceByKey 先分组,后对每一组内的kye对应的value去聚合
// */
// val result = pairWords.reduceByKey((v1:Int,v2:Int) => { v1 + v2 })
//
// result.foreach(tuple =>{println(tuple)})
//
// sc.stop()
// 简化版
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("ScalaWordCount")
new SparkContext(conf).textFile("src/words").flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_,1)).reduceByKey(_ + _).foreach(println(_))
}
}