2017-2018-2 20155203《网络对抗技术》Exp4 恶意代码分析
1. 实践过程记录
1. 使用Windows计划任务schtasks监控系统运行
Windows计划任务schtasks监控系统:
- 在C盘建立一个netstatlog.bat文件,用来将记录的联网结果格式化输出到netstatlog.txt文件中:
date /t >> c:\netstatlog.txt
time /t >> c:\netstatlog.txt
netstat -bn >> c:\netstatlog.txt

-
创建任务:
schtasks /create /TN netstat /sc MINUTE /MO 5 /TR "c:\netstatlog.bat"
指令创建一个每隔五分钟记录计算机联网情况的任务; -
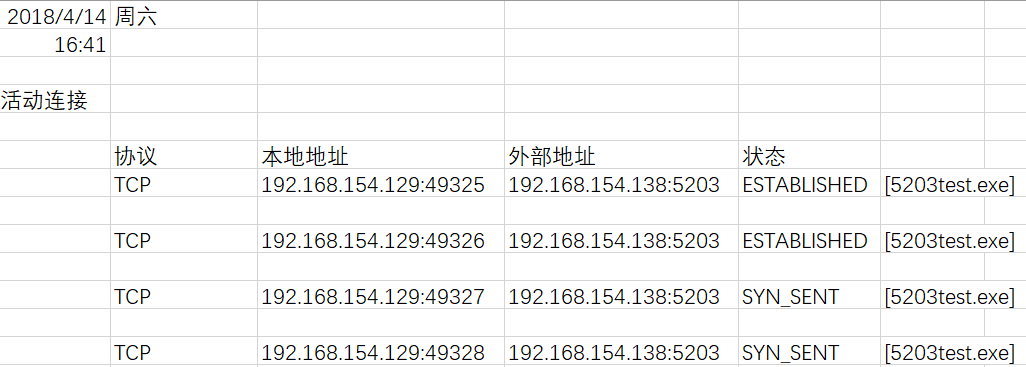
查看netstatlog.txt中的记录:
2. 使用Sysmon工具监控系统运行
- 配置文件如下:
<Sysmon schemaversion="7.01">
<!-- Capture all hashes -->
<HashAlgorithms>*</HashAlgorithms>
<EventFiltering>
<!-- Log all drivers except if the signature -->
<!-- contains Microsoft or Windows -->
<DriverLoad onmatch="exclude">
<Signature condition="contains">Microsoft</Signature>
<Signature condition="contains">Windows</Signature>
</DriverLoad>
<ProcessCreate onmatch="exclude" >
<TargetFilename condition="end with">.tmp</TargetFilename>
<TargetFilename condition="end with">.exe</TargetFilename>
</ProcessCreate>
<!-- Log network connection if the destination port equal 443 -->
<!-- or 80, and process isn't InternetExplorer -->
<!--NetworkConnect onmatch="include">
<DestinationPort>443</DestinationPort>
<DestinationPort>80</DestinationPort >
</NetworkConnect -->
<FileCreateTime onmatch="exclude" >
<Image condition="end with">chrome.exe</Image>
</FileCreateTime>
<ImageLoad onmatch="include">
<Signed condition="is">false</Signed>
</ImageLoad>
<!-- Log access rights for lsass.exe or winlogon.exe is not PROCESS_QUERY_INFORMATION -->
<ProcessAccess onmatch="exclude">
<GrantedAccess condition="is">0x1400</GrantedAccess>
</ProcessAccess>
<ProcessAccess onmatch="include">
<TargetImage condition="end with">lsass.exe</TargetImage>
<TargetImage condition="end with">winlogon.exe</TargetImage>
</ProcessAccess>
<FileCreateTime onmatch="exclude">
<Image condition="end with">chrome.exe</Image>
</FileCreateTime>
<NetworkConnect onmatch="exclude">
<Image condition="end with">chrome.exe</Image>
</NetworkConnect>
<NetworkConnect onmatch="include">
<DestinationPort condition="is">80</DestinationPort>
<DestinationPort condition="is">443</DestinationPort>
</NetworkConnect>
<CreateRemoteThread onmatch="include">
<TargetImage condition="end with">explorer.exe</TargetImage>
<TargetImage condition="end with">svchost.exe</TargetImage>
<TargetImage condition="end with">winlogon.exe</TargetImage>
<SourceImage condition="end with">powershell.exe</SourceImage>
</CreateRemoteThread>
</EventFiltering>
</Sysmon>
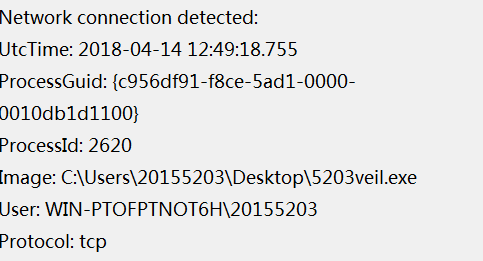
直接在时间查看器中查找恶意软件名称,可以看到有关恶意软件的信息有名称,时间,使用协议,源和目的ip

3. 使用在线沙盘分析恶意软件
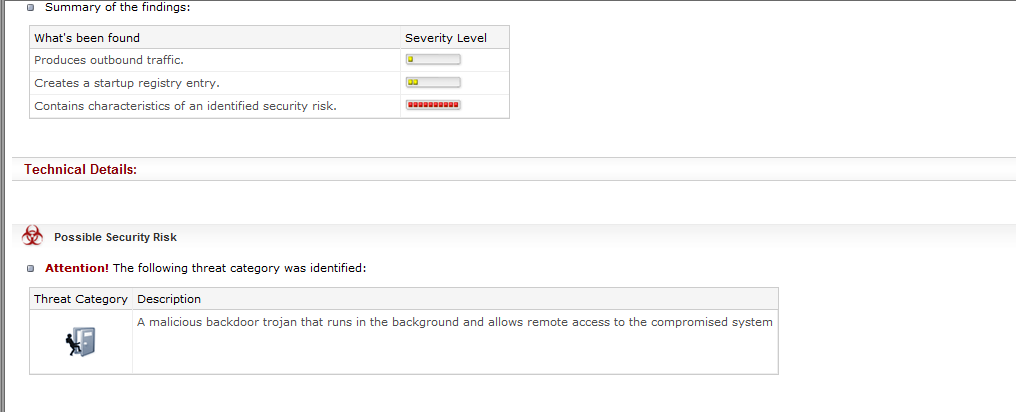
- Threat Expert:可以根据恶意程序的特征分析出用途:后门,还可以分析ip地址
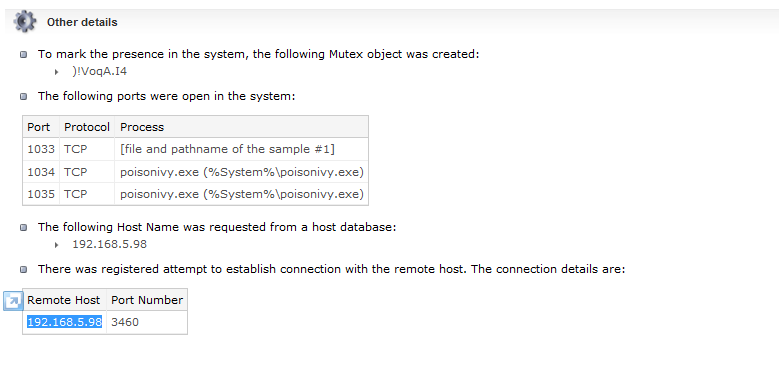

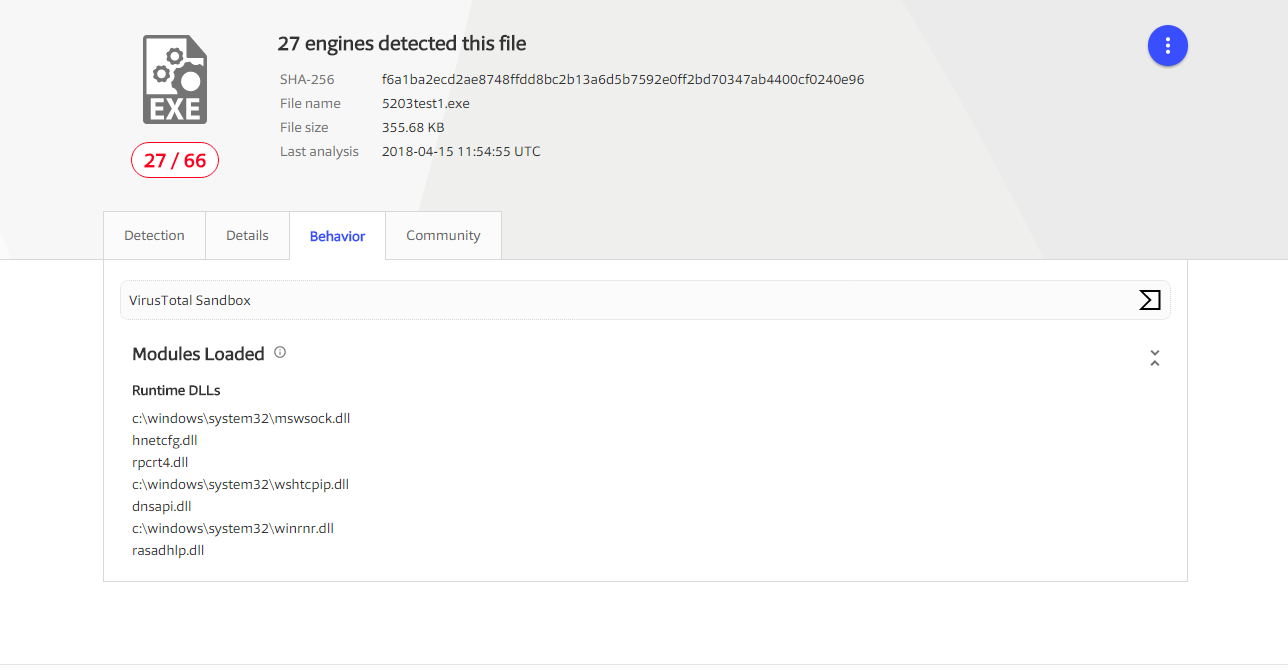
- VirusTotal:
可以总结分析恶意程序的行为,并标注产生的时间
4. 使用systracer工具分析恶意软件
启用回连后会修改注册表
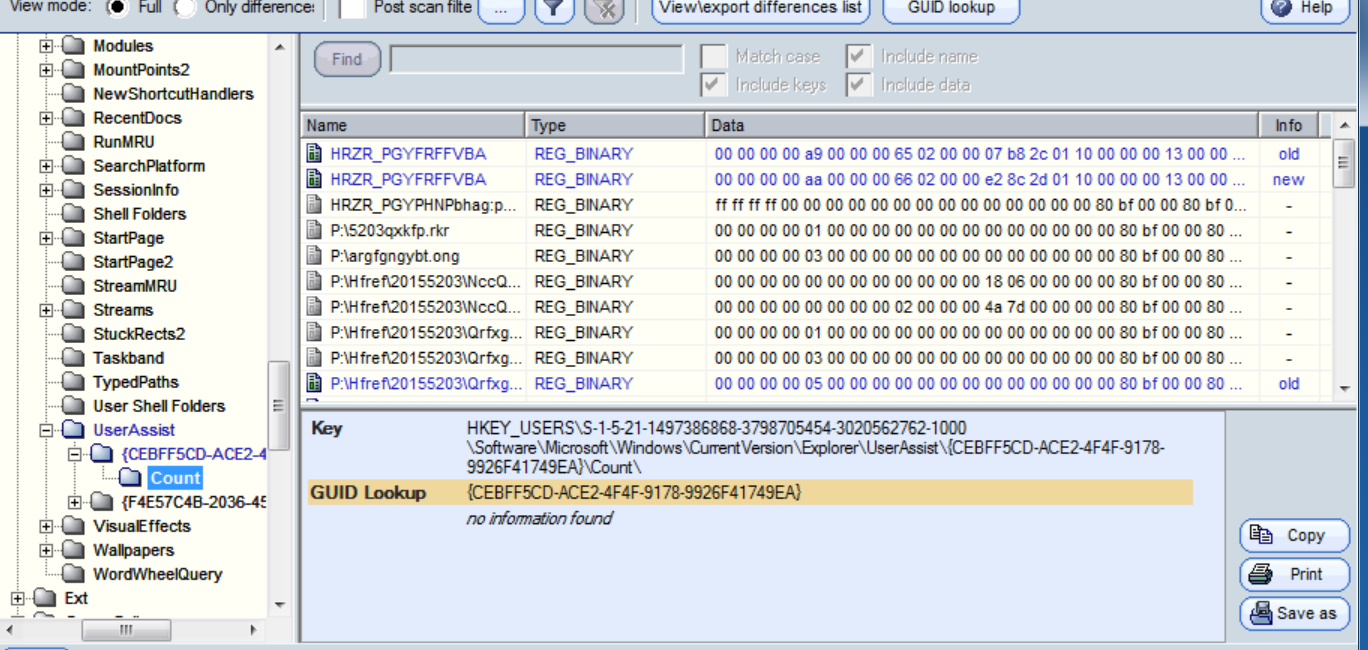
根据观察发现,在使用回连后门程序进行音频,摄像头和屏幕捕捉的时候会反复出现下图这个HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Enum注册表的修改
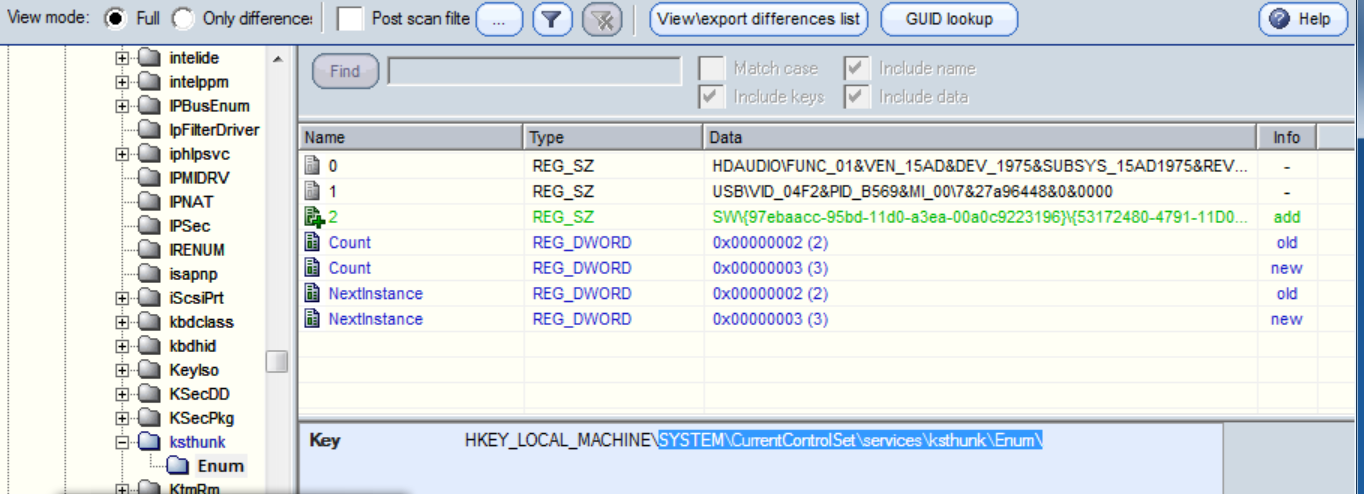
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Enum注册表树包含了系统的设备信息。即插即用(PnP)管理器为每个设备创建了一个名为HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Enum\Enumerator\deviceID的子键(Subkey)。这些键值下面的每一项都是目前系统中存在的每个设备实例的子键。这些被称作设备的硬件键值(或设备键值)的子键,拥有一些如设备描述,硬件ID,兼容ID和资源需求等信息。
枚举树被保留给操作系统组件使用,它们的排列也会随之改变。驱动程序和用户模式的设备安装组件必须使用系统提供的函数,比如IoGetDeviceProperty和SetupDiGetDeviceRegistryProperty,从这个树上获取信息。驱动程序和Windows应用程序不能直接访问该树,因此进程对这个注册树的改动应该引起注意。当你调试驱动程序时,你可以直接使用注册表编辑器(regedit)查看这个树。
5. 使用Process Explorer分析恶意软件
可以分析到使用的通信协议,线程号及线程调用的dll文件从而了解恶意软件的作用,使用的环境参数。可以直接使用这个工具进行virustotal检查,右键点击进程就可以看到
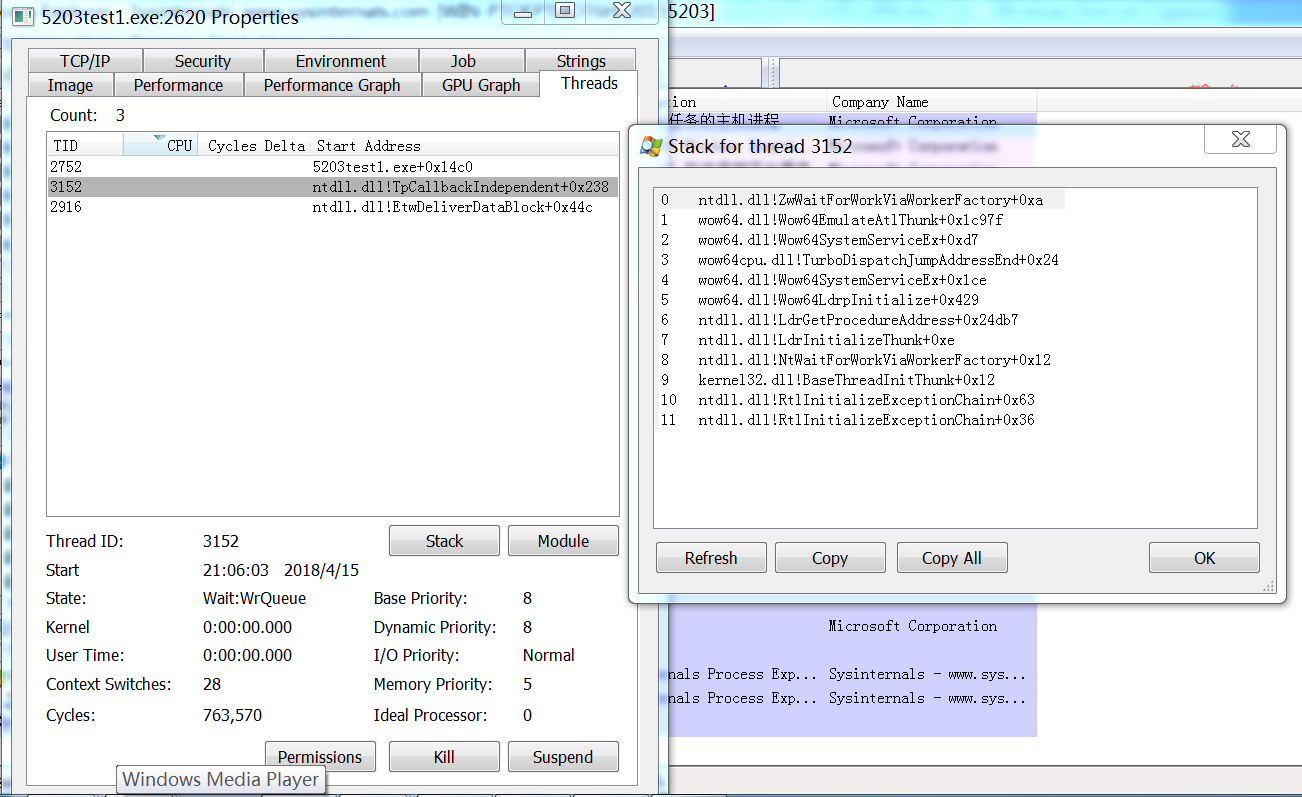
WSOCK32.dll和WS2_32.dll,是用来创建套接字的dll库
ntdll.dll是NT操作系统重要的模块。
ntdll.dll是Windows系统从ring3到ring0的入口。位于Kernel32.dll和user32.dll中的所有win32 API 最终都是调用ntdll.dll中的函数实现的。ntdll.dll中的函数使用SYSENTRY进入ring0,函数的实现实体在ring0中。
为什么会使用到核心的dll,说明这个程序确实有问题
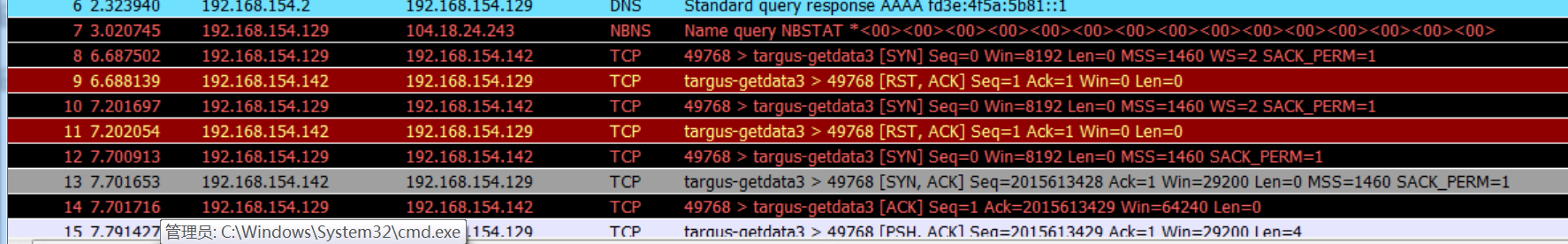
6. 使用wireshark分析恶意软件回连情况
观察到建立连接的过程
反复发送rst再建立连接,这样的通信行为很可疑。
2. 实验总结与体会
这次实验认识到了很多平时注意不到的恶意软件的特征,同时也可以理解很多杀毒软件识别恶意软件的模式。
3. 思考的问题
(1)如果在工作中怀疑一台主机上有恶意代码,但只是猜想,所有想监控下系统一天天的到底在干些什么。请设计下你想监控的操作有哪些,用什么方法来监控。
监控占用内存有多大,是否调用cmd.exe等敏感程序,是否调用核心dll,是否更改普通程序不能接触的注册表,重点观察没有明显用处的小程序,对其MD5或SHA1摘要值做检查。
(2)如果已经确定是某个程序或进程有问题,你有什么工具可以进一步得到它的哪些信息。
可以在线上扫描,或直接在进程分析器中对其行为进行分析。





