HashSet源码解读
一:先看其实现了哪些接口和继承了哪些类
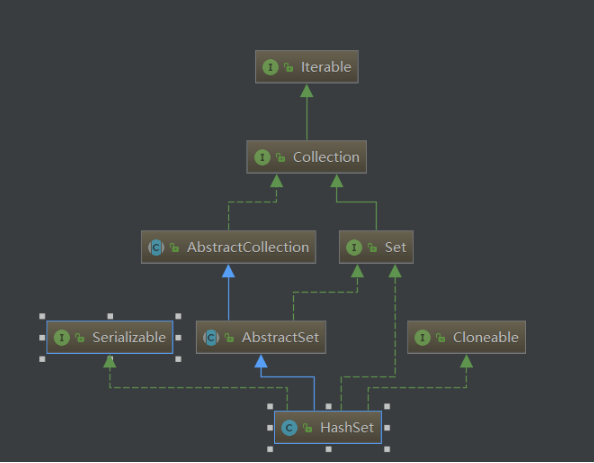
1.实现了Serializable接口,表明它支持序列化。
2.实现了Cloneable接口,表明它支持克隆,可以调用超类的clone()方法进行浅拷贝。
3.继承了AbstractSet抽象类,和ArrayList和LinkedList一样,在他们的抽象父类中,都提供了equals()方法和hashCode()方法。它们自身并不实现这两个方法
4.从JDK源码可以看出,底层并没有使用我们常规认为的利用hashcode()方法求的值进行比较,而是通过调用AbstractCollection的containsAll()方法,如果他们中元素完全相同(与顺序无关),则他们的equals()方法的比较结果就为true。
/** * Compares the specified object with this set for equality. Returns * <tt>true</tt> if the given object is also a set, the two sets have * the same size, and every member of the given set is contained in * this set. This ensures that the <tt>equals</tt> method works * properly across different implementations of the <tt>Set</tt> * interface.<p> * * This implementation first checks if the specified object is this * set; if so it returns <tt>true</tt>. Then, it checks if the * specified object is a set whose size is identical to the size of * this set; if not, it returns false. If so, it returns * <tt>containsAll((Collection) o)</tt>. * * @param o object to be compared for equality with this set * @return <tt>true</tt> if the specified object is equal to this set */ public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) return true; if (!(o instanceof Set)) return false; Collection<?> c = (Collection<?>) o;
//保证个数相等 if (c.size() != size()) return false; try {
//调用了AbstractCollection的方法。 return containsAll(c); } catch (ClassCastException unused) { return false; } catch (NullPointerException unused) { return false; } }
public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) { //只需要逐个判断集合是否包含其中的元素。 for (Object e : c) if (!contains(e)) return false; return true; }
4.实现了Set接口。
二:HashSet概述
1.HashSet是通过HashMap的键来存值,HashMap里面的所有值都为null;
2.学习这个之前先看HashMap;附上网址https://www.cnblogs.com/xhlwjy/p/11246618.html
三:HashSet的属性
private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;//用HashMap的Key来存值 // Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();//用于填充HashMap的value
四:构造方法
/** * Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has * default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75). */
//这个是初始化一个HashMap
public HashSet() { map = new HashMap<>(); } /** * Constructs a new set containing the elements in the specified * collection. The <tt>HashMap</tt> is created with default load factor * (0.75) and an initial capacity sufficient to contain the elements in * the specified collection. * * @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this set * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null */
//初始化HashMap,把c集合中的所有元素添加到map中
public HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c) { map = new HashMap<>(Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) + 1, 16)); addAll(c); } /** * Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has * the specified initial capacity and the specified load factor. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hash map * @param loadFactor the load factor of the hash map * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is less * than zero, or if the load factor is nonpositive */
//初始化HashMap的容量和加载因子 public HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor); } /** * Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has * the specified initial capacity and default load factor (0.75). * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hash table * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is less * than zero */
//初始化HashMap的容量
public HashSet(int initialCapacity) { map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity); } /** * Constructs a new, empty linked hash set. (This package private * constructor is only used by LinkedHashSet.) The backing * HashMap instance is a LinkedHashMap with the specified initial * capacity and the specified load factor. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hash map * @param loadFactor the load factor of the hash map * @param dummy ignored (distinguishes this * constructor from other int, float constructor.) * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is less * than zero, or if the load factor is nonpositive */
//这个初始化使用的是LinkedHashMap
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) { map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor); }
五:添加新元素
//底层仍然利用了HashMap键进行了元素的添加。 //在HashMap的put()方法中,该方法的返回值是对应HashMap中键值对中的值,而值总是PRESENT, //该PRESENT一直都是private static final Object PRESENT = new Object(); //PRESENT只是初始化了,并不能改变,所以PRESENT的值一直为null。 //所以只要插入成功了,put()方法返回的值总是null。 public boolean add(E e) { return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null; }
public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); }
这段代码就不分析了,与HashMap的插入差不多,可以先去看HashMap
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length; if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else { Node<K,V> e; K k; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p; else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); else { for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; }
六:删除一个元素
//该方法底层实现了仍然使用了map的remove()方法。 //map的remove()方法的返回的是被删除键对应的值。(在HashSet的底层HashMap中的所有键值对的值都是PRESENT) public boolean remove(Object o) { return map.remove(o)==PRESENT; }
之后的代码就不粘贴出来了,自己可以去源码里面看
七:清空方法
public void clear() { map.clear(); }
八:克隆方法
底层仍然使用了Object的clone()方法,得到的Object对象,并把它强制转化为HashSet<E>,然后把它的底层的HashMap也克隆一份(调用的HashMap的clone()方法),并把它赋值给newSet,最后返回newSet即可。
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object clone() {
try {
HashSet<E> newSet = (HashSet<E>) super.clone();
newSet.map = (HashMap<E, Object>) map.clone();
return newSet;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
九:是否包含某个元素
底层使用了HashMap的containsKey()
public boolean contains(Object o) { return map.containsKey(o); }
十:判读是不是空
调用HashMap的方法
public boolean isEmpty() { return map.isEmpty(); }
十一:统计HashSet中包含元素的个数
public int size() { return map.size(); }
十二:生成迭代器
public Iterator<E> iterator() { return map.keySet().iterator(); }
十三:序列化
/** * Save the state of this <tt>HashSet</tt> instance to a stream (that is, * serialize it). * * @serialData The capacity of the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance * (int), and its load factor (float) are emitted, followed by * the size of the set (the number of elements it contains) * (int), followed by all of its elements (each an Object) in * no particular order. */ private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws java.io.IOException { // Write out any hidden serialization magic s.defaultWriteObject(); // Write out HashMap capacity and load factor
//容量写入流 s.writeInt(map.capacity());
//加载因子写入流 s.writeFloat(map.loadFactor()); // Write out size
//存放的数量写入流 s.writeInt(map.size()); // Write out all elements in the proper order.
//把每个元素写入流 for (E e : map.keySet()) s.writeObject(e); }
十四:反序列化
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { // Read in any hidden serialization magic s.defaultReadObject(); // Read capacity and verify non-negative. int capacity = s.readInt(); if (capacity < 0) { throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal capacity: " + capacity); } // Read load factor and verify positive and non NaN. float loadFactor = s.readFloat(); if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) { throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); } // Read size and verify non-negative. int size = s.readInt(); if (size < 0) { throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal size: " + size); } // Set the capacity according to the size and load factor ensuring that // the HashMap is at least 25% full but clamping to maximum capacity. capacity = (int) Math.min(size * Math.min(1 / loadFactor, 4.0f), HashMap.MAXIMUM_CAPACITY); //HashMap中构建哈希桶数组是在第一个元素被添加的时候才构建,所以在构建之前检查它, // 调用HashMap.tableSizeFor来计算实际分配的大小, // 检查Map.Entry []类,因为它是最接近的公共类型实际创建的内容。 SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess() .checkArray(s, Map.Entry[].class,HashMap.tableSizeFor(capacity)); //创建HashMap。 map = (((HashSet<?>)this) instanceof LinkedHashSet ? new LinkedHashMap<E,Object>(capacity, loadFactor) : new HashMap<E,Object>(capacity, loadFactor)); // 按写入流中的顺序再把元素依次读取出来放到map中。 for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) s.readObject(); map.put(e, PRESENT); } }

