List集合源码解读
一:总述:
主要讲解3个集合
1.ArrayList:
底层是数组,线程不安全;
2.LinkedList:
底层是链表,线程不安全;
3.Vector
底层数据结构是数组。线程安全;
二:ArrayList解析
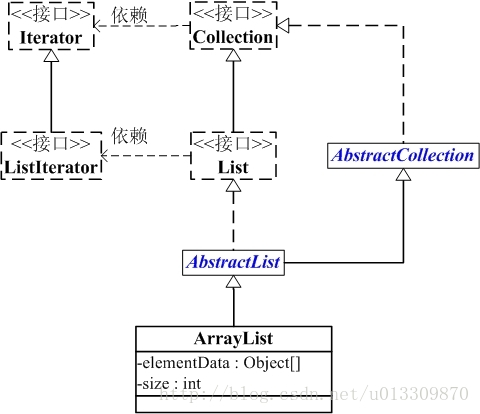
首先,我们来看一下ArrayList的属性:
/**
* Default initial capacity.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;//初始化容量值
/** * Shared empty array instance used for empty instances. */ private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};//指定ArrayList的容量为0时,返回该空数组 /** * Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We * distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when * first element is added. */ private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};//与上个属性的区别是:该数组是默认返回的,而上个属性是指定容量为0时返回 /** * The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored. * The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any * empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA * will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added. */ transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access//第一次保存元素时,数组将会扩容 /** * The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains). * * @serial */ private int size;//ArrayList的实际大小
根据上面我们可以清晰的发现:ArrayList底层其实就是一个数组,ArrayList中有扩容这么一个概念,正因为它扩容,所以它能够实现“动态”增长
2.2构造方法
/** * Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity * is negative */
//指定初始化长度initCapacity public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity > 0) { this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); } } /** * Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten. */
//否则返回的是:DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA public ArrayList() { this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } /** * Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified * collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's * iterator. * * @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null */ public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { elementData = c.toArray(); if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) { // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); } else { // replace with empty array. this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } }
2.3 Add()方法
源码如下:
/** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * * @param e element to be appended to this list * @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) */ public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! elementData[size++] = e; return true; } /** * Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this * list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and * any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices). * * @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted * @param element element to be inserted * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public void add(int index, E element) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index); elementData[index] = element; size++; }
2.3.1 Add(E e)
步骤:
- 检查是否需要扩容
- 插入元素
首先,我们来看看这个方法:
public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! elementData[size++] = e; return true; }
该方法很短,我们可以根据方法名就猜到他是干了什么:
- 确认list容量,尝试容量加1,看看有无必要
- 添加元素
接下来我们来看看这个小容量(+1)是否满足我们的需求:
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
//想要得到的最小的容量 if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } //确定明确的容量 ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); }
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { modCount++; //如果最小容量比数组长度大,则用用grow扩容 // overflow-conscious code if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); }
接下来看grow是如何扩容的
/** * Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the * number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument. * * @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity */ private void grow(int minCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);//扩容1.5倍 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);//扩容完后调用copyOf方法把原数组的值存入新数组 }
再来看是怎么把原数组的值放入新数组
/** * Copies the specified array, truncating or padding with nulls (if necessary) * so the copy has the specified length. For all indices that are * valid in both the original array and the copy, the two arrays will * contain identical values. For any indices that are valid in the * copy but not the original, the copy will contain <tt>null</tt>. * Such indices will exist if and only if the specified length * is greater than that of the original array. * The resulting array is of the class <tt>newType</tt>. * * @param <U> the class of the objects in the original array * @param <T> the class of the objects in the returned array * @param original the array to be copied * @param newLength the length of the copy to be returned * @param newType the class of the copy to be returned * @return a copy of the original array, truncated or padded with nulls * to obtain the specified length * @throws NegativeArraySizeException if <tt>newLength</tt> is negative * @throws NullPointerException if <tt>original</tt> is null * @throws ArrayStoreException if an element copied from * <tt>original</tt> is not of a runtime type that can be stored in * an array of class <tt>newType</tt> * @since 1.6 */ public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class) ? (T[]) new Object[newLength] : (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength); System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0, Math.min(original.length, newLength)); return copy; }
到目前为止,我们就可以知道add(E e)的基本实现了:
- 首先去检查一下数组的容量是否足够
- 足够:直接添加
- 不足够:扩容
- 扩容到原来的1.5倍
- 第一次扩容后,如果容量还是小于minCapacity,就将容量扩充为minCapacity。
2.3.2:add(int index, E element)
步骤:
- 检查角标
- 空间检查,如果有需要进行扩容
- 插入元素
我们来看看插入的实现:
/** * Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this * list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and * any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices). * * @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted * @param element element to be inserted * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public void add(int index, E element) { rangeCheckForAdd(index);//检查是否越界 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!//扩容 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index);//调用arraycopy进行插入 elementData[index] = element; size++; }
注:arraycopy是用c++来编写的
2.4:get()
- 检查角标
- 返回元素
/** * Returns the element at the specified position in this list. * * @param index index of the element to return * @return the element at the specified position in this list * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E get(int index) { rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); }
// 检查角标 private void rangeCheck(int index) { if (index >= size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } // 返回元素 E elementData(int index) { return (E) elementData[index]; }
2.5:set()方法
步骤:
- 检查角标
- 替代元素
- 返回旧值
/** * Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with * the specified element. * * @param index index of the element to replace * @param element element to be stored at the specified position * @return the element previously at the specified position * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E set(int index, E element) { rangeCheck(index); //将值进行替代,返回旧值 E oldValue = elementData(index); elementData[index] = element; return oldValue; }
2.6:remove()方法
步骤:
- 检查角标
- 删除元素
- 计算出需要移动的个数,并移动
- 设置为null,让Gc回收
/** * Removes the element at the specified position in this list. * Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their * indices). * * @param index the index of the element to be removed * @return the element that was removed from the list * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E remove(int index) { rangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index);
//左移的个数
int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue; }
2.7:总述
- ArrayList是基于动态数组实现的,在增删时候,需要数组的拷贝复制(使用的是System.arrayCopy()效率最高的数组拷贝方法)。
- ArrayList的默认初始化容量是10,每次扩容时候增加原先容量的一半,也就是变为原来的1.5倍
- 删除元素时不会减少容量,若希望减少容量则调用trimToSize()
- 它不是线程安全的。它能存放null值。
三:Vector与ArrayList的区别
1.Vector底层也是数组,与ArrayList最大的区别就是:同步(线程安全),Vector的每个方法都是同步的 (相对效率较低)
2.在要求非同步的情况下,我们一般都是使用ArrayList来替代Vector的了,如果想要ArrayList实现同步,可以使用Collections的方法:List list =Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList(...));,就可以实现同步了
3.ArrayList是以1.5倍扩容,Vector是以2倍扩容
以上的结论可以在源码中得到验证
四:LinkedList解析
此处放一张全家桶
LinkedList底层是双向链表
private static class Node<E> { E item; Node<E> next; Node<E> prev; Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } }
4.1:构造方法
/** * Constructs an empty list. */ public LinkedList() { } /** * Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified * collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's * iterator. * * @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null */ public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { this(); addAll(c); }
4.2: add()方法
public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; } //往链表的最后添加元素 void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); last = newNode; if (l == null) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
4.3:remove()方法
/** * Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list, * if it is present. If this list does not contain the element, it is * unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index * {@code i} such that * <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt> * (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list * contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list * changed as a result of the call). * * @param o element to be removed from this list, if present * @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element */ public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) {
//删除元素 unlink(x); return true; } } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
//判断元素是否存在里面 if (o.equals(x.item)) { unlink(x); return true; } } } return false; }
/** * Unlinks non-null node x. */ E unlink(Node<E> x) { // assert x != null; final E element = x.item; final Node<E> next = x.next; final Node<E> prev = x.prev; if (prev == null) { first = next; } else { prev.next = next; x.prev = null; } if (next == null) { last = prev; } else { next.prev = prev; x.next = null; } x.item = null; size--; modCount++; return element; }
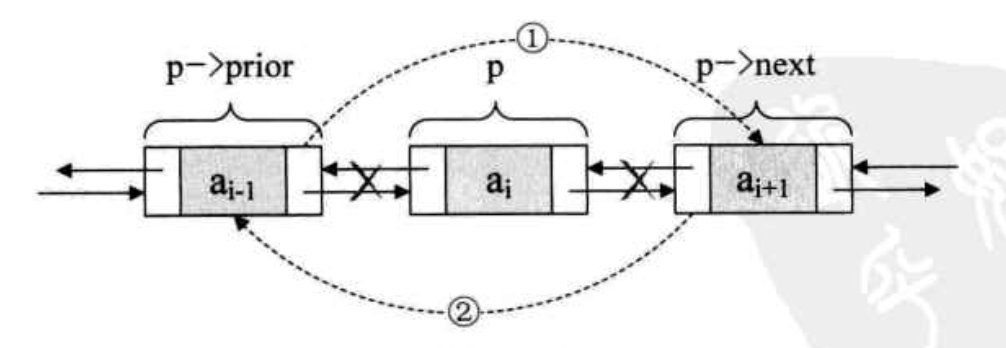
4.4:get()方法
public E get(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return node(index).item; }
node()方法
/** * Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index. */ Node<E> node(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); //下标小于长度的一半,从头部开始遍历 if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x;
//否则从尾部开始遍历 } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }
4.5:set方法
set方法和get方法其实差不多,根据下标来判断是从头遍历还是从尾遍历
public E set(int index, E element) { checkElementIndex(index); Node<E> x = node(index); E oldVal = x.item; x.item = element; return oldVal; }
具体请参考源码
五:总结
ArrayList:
- 底层实现是数组
- ArrayList的默认初始化容量是10,每次扩容时候增加原先容量的一半,也就是变为原来的1.5倍
- 在增删时候,需要数组的拷贝复制(C++实现)
LinkedList:
- 底层实现是双向链表[双向链表方便实现往前遍历]
Vector:
- 底层是数组,现在已少用,被ArrayList替代,原因有两个:
- Vector所有方法都是同步,有性能损失。
- Vector初始length是10 超过length时 以100%比率增长,相比于ArrayList更多消耗内存。
总的来说:查询多用ArrayList,增删多用LinkedList。
ArrayList增删慢不是绝对的(在数量大的情况下,已测试):
- 如果增加元素一直是使用
add()(增加到末尾)的话,那是ArrayList要快 - 一直删除末尾的元素也是ArrayList要快【不用复制移动位置】
- 至于如果删除的是中间的位置的话,还是ArrayList要快!
但一般来说:增删多还是用LinkedList,因为上面的情况是极端的~

