File I/O
File类
File类访问文件属性
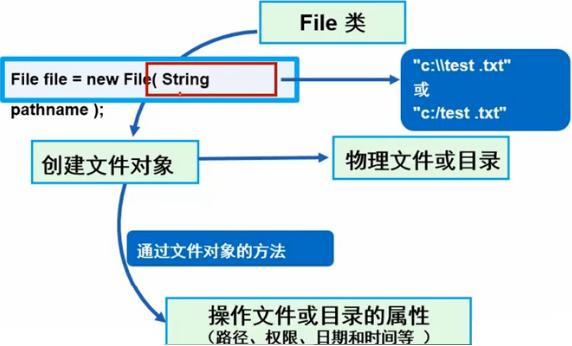
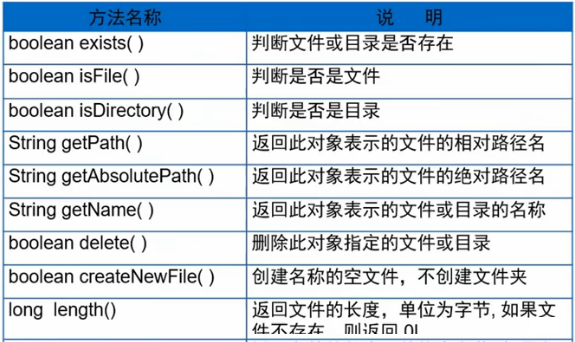
File类的常用方法
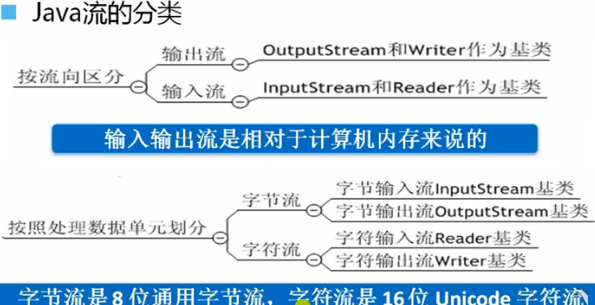
IO流
流
![]()
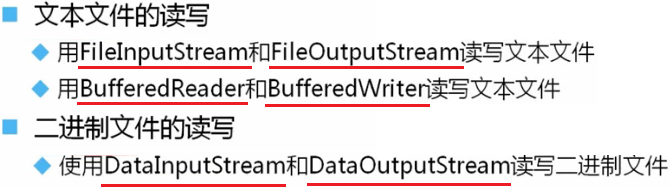
文件的读写
使用FileInputStream读文本文件



import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; public class TestFileInputStream { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1、创建字节输入流 InputStream fis = null; try { fis = new FileInputStream("d:/我的青春我做主.txt"); // 2、实现读取操作 // int data; // 存储读到的字节 // while ((data = fis.read()) != -1) { // System.out.print((char) data); // } byte[] words = new byte[1024]; int len; // 存储读入数组的长度 while ((len = fis.read(words)) != -1) { System.out.print(new String(words, 0, len)); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 3、关闭流 try { if (fis != null) { fis.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
使用FileOutputStream写文本文件



import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.OutputStream; public class TestFileOutputStream { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1、创建字节输出流 OutputStream fis = null; try { fis = new FileOutputStream(new File("d:/Hello.txt")); // 2、执行写操作 String str = "好好学习Java!"; // 要写出的字符串 byte[] words = str.getBytes(); // 将字符串转换为字节数组 fis.write(words); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("创建文件是出错!"); } finally { // 3、关闭流 if (fis != null) { try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
使用FileReader读取文件


import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Reader; public class TestFileReader { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1、创建字符流对象 Reader fr = null; StringBuffer sb = null; try { fr = new FileReader("d:/我的青春我做主.txt"); // 2、读取文本文件 // int word; // 接收读取到的字符 // while ((word = fr.read()) != -1) { // System.out.print((char) word); // } char[] words = new char[1024]; // 存储读取到的字符 sb = new StringBuffer(); int len = fr.read(words); // 读取到字符数组中 while (len != -1) { sb.append(words); len = fr.read(words); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 3、关闭流 if (fr != null) { try { fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } System.out.println(sb.toString()); } }
BufferedReader类

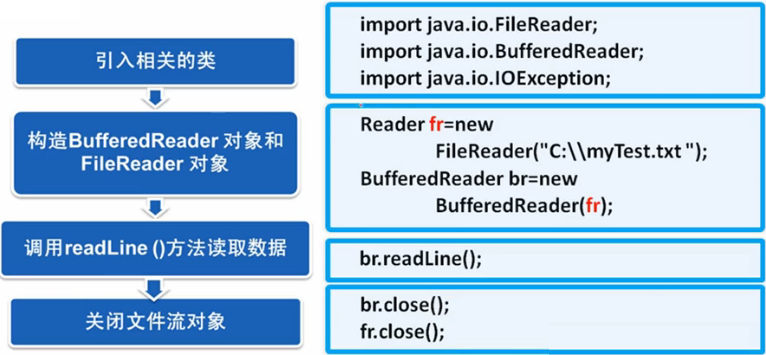

import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Reader; public class TestBufferedReader { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1、创建字符流对象 Reader fr = null; BufferedReader br = null; try { fr = new FileReader("d:/我的青春我做主.txt"); br = new BufferedReader(fr); // 2、读取文本文件 String line = null; // 接收读取到的信息 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println(line); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 3、关闭流 if (br != null) { try { br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (fr != null) { try { fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
使用FileWriter写文件


import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Writer; public class TestFileWriter { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1、创建流 Writer fw = null; try { fw = new FileWriter("d:/简介.txt"); // 2、写入信息 fw.write("我爱我的团队!"); fw.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 3、关闭流 if (fw != null) { try { fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
BufferedWriter类

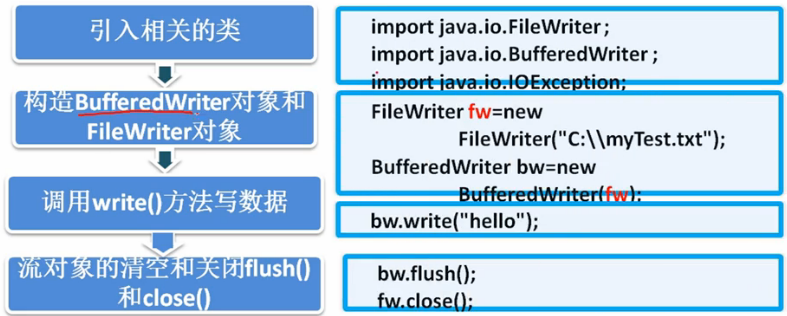

import java.io.BufferedWriter; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Writer; public class TestBufferedWriter { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1、创建流 Writer fw = null; BufferedWriter bw = null; try { fw = new FileWriter("d:/hello.txt"); bw = new BufferedWriter(fw); // 2、写入信息 bw.write("大家好!"); bw.newLine(); bw.write("我正在学习BufferedWriter。"); bw.newLine(); bw.write("请多指教!"); bw.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ // 3、关闭流 if (bw!=null) { try { bw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
读写二进制文件



import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class ReadAndWriteBinaryFile { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1、创建流 DataInputStream dis = null; DataOutputStream dos = null; try { dis = new DataInputStream( new FileInputStream("d:/StringDemo.class")); dos = new DataOutputStream( new FileOutputStream("d:/FileCopy.class")); // 2、实现读写操作 int temp; while ((temp = dis.read()) != -1) { dos.write(temp); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 3、关闭流 if (dis != null) { try { dis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (dos != null) { try { dos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
序列化
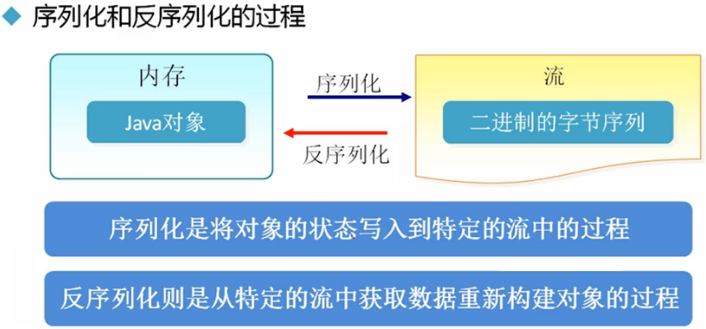
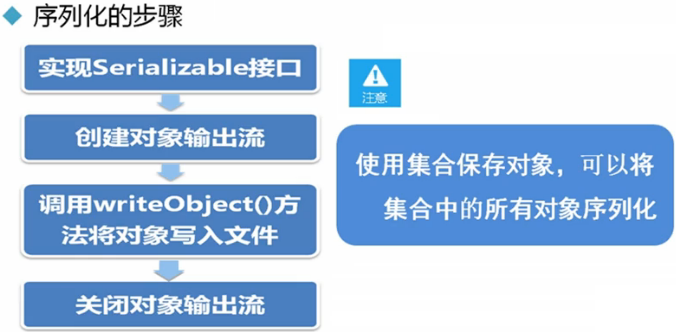

import java.io.Serializable; public class Student implements Serializable { private String name; private int age; private transient String gender; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age, String gender) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; this.gender = gender; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(String gender) { this.gender = gender; } }

import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; public class TestSerializable { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1、创建一个需要序列化的学生对象 Student stu = new Student("王宝宝", 18, "男"); // 2、创建一个对象输出流 OutputStream os = null; ObjectOutputStream oos = null; // 3、创建对象输入流 InputStream is = null; ObjectInputStream ois = null; try { os = new FileOutputStream("d:/student.bin"); oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os); oos.writeObject(stu); is = new FileInputStream("d:/student.bin"); ois = new ObjectInputStream(is); Student stu1 = (Student) ois.readObject(); System.out.println("学生姓名:" + stu1.getName() + ",年龄:" + stu1.getAge() + ",性别:" + stu1.getGender()); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (oos != null) { try { oos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (os != null) { try { os.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (ois != null) { try { ois.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (is != null) { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }



