人工智能-A*算法-八数码问题
一,A*算法设计思想
A*算法(A-star)是一种寻路算法,主要用于游戏、机器人等领域。
它的设计思想是将最短路径搜索问题转化为一个优化问题,通过计算每个节点的评分(f(n) = g(n) + h(n))来寻找最优路径。
以下是 A*算法的设计思想:
1. 引入启发式函数(h(n)):
A*算法使用一个启发式函数来估计从当前节点到目标节点的距离。
启发式函数越好,搜索速度越快。
通常情况下,启发式函数为曼哈顿距离(曼哈顿距离是指两点在网格上沿着网格线走的距离之和)。
2. 优先级队列:
A*算法使用一个优先级队列(开启列表)来存储待处理的节点。
队列中的节点按照评分(f(n))从高到低排列。
这样,每次迭代都可以优先处理评分最高的节点,从而保证搜索的速度和效率。
3. 扩展节点:
A*算法从当前节点开始,遍历其所有相邻节点。
对于每个相邻节点,检查它是否在关闭列表中(表示已经访问过),如果不在关闭列表中,则将其加入开启列表,并更新其父节点和评分。
4. 关闭列表:
A*算法使用一个关闭列表来记录已访问过的节点。
每次扩展节点时,都需要检查新节点是否在关闭列表中。
如果在,则忽略该节点,继续处理其他相邻节点。
5. 停止条件:
A*算法在找到目标节点或开启列表为空时停止搜索。
找到目标节点时,意味着找到了一条从起始节点到目标节点的最短路径。
6. 回溯法:
当开启列表为空时,搜索失败。
此时,可以使用回溯法(如 Dijkstra 算法)从起始节点开始,重新寻找一条路径。
这种情况下,A*算法退化为 Dijkstra 算法。
二,题目需求
应用启发式搜索算法A 解决以下八数码问题:
初始状态:
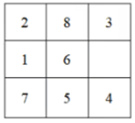
目标状态:

三,代码实现
完整代码,需要下载pygame库,直接使用,运行可以查看动画演示效果。
import heapq from copy import deepcopy import time import pygame # 定义启发式函数,使用当前状态与目标状态,棋子的错位数作为估价值 def heuristic(move_state, goal_state): err_num = 0 for i in range(3): for j in range(3): if move_state[i][j] != goal_state[i][j]: err_num += 1 return err_num # 根据当前状态,获取可移动方向 def get_moves(state, g): # 获取空缺位(或0值)坐标 x, y = None, None for i in range(3): for j in range(3): if state[i][j] == 0: x, y = i, j break moves = [] if x > 0: new_state = deepcopy(state) # 空位与它左侧1位交换,左侧数字右移 new_state[x][y], new_state[x - 1][y] = new_state[x - 1][y], new_state[x][y] moves.append((new_state, g + 1)) if x < 2: new_state = deepcopy(state) # 空位与它右侧1位交换,右侧数字左移 new_state[x][y], new_state[x + 1][y] = new_state[x + 1][y], new_state[x][y] moves.append((new_state, g + 1)) if y > 0: new_state = deepcopy(state) # 空位与它下面1位交换,下面数字上移 new_state[x][y], new_state[x][y - 1] = new_state[x][y - 1], new_state[x][y] moves.append((new_state, g + 1)) if y < 2: new_state = deepcopy(state) # 空位与它上面1位交换,上面数字下移 new_state[x][y], new_state[x][y + 1] = new_state[x][y + 1], new_state[x][y] moves.append((new_state, g + 1)) return moves # A星算法搜索 def a_star_search(initial_state, goal_state): f, g, h = 0, 0, 0 open_set = [(f, initial_state)] close_set = set() # 从哪里来字典,记录节点来源,当成父节点 come_from = {} while open_set: f, current_state = heapq.heappop(open_set) if current_state == goal_state: data = [] current_state = tuple(map(tuple, current_state)) # 从目标点向起点遍历路径 while current_state in come_from: # 将当前点的位置加入路径 data.append(current_state) # 将当前点设为从哪里来的节点,继续向上遍历 current_state = come_from[current_state] # 将起始点的位置也加入路径 data.append(tuple(map(tuple, initial_state))) # 将路径反转,因为我们是从目标向起点遍历的,所以需要反转得到真正的路径 return data[::-1] close_set.add(tuple(map(tuple, current_state))) for move, g in get_moves(current_state, g): if tuple(map(tuple, move)) not in close_set: come_from[tuple(map(tuple, move))] = tuple(map(tuple, current_state)) h = heuristic(move, goal_state) f = g + h heapq.heappush(open_set, (f, move)) return None # 打印网格地图 def grid_print(grid): for line in grid: print(line) # 定义网格矩阵长宽 map_size = (3, 3) # 定义屏幕一个格子大小 CELL_SIZE = 200 # 定义屏幕宽高大小 WIDTH, HEIGHT = map_size[0] * CELL_SIZE, map_size[1] * CELL_SIZE # 定义颜色 WHITE = (255, 255, 255) RED = (255, 0, 0) BLUE = (0, 0, 255) BLACK = (0, 0, 0) # 绘制主地图,棋盘数字 def draw_grid(pygame, screen, num_states): # 填充屏幕背景为白色 screen.fill(WHITE) for i in range(0, WIDTH, CELL_SIZE): pygame.draw.line(screen, BLACK, (i, 0), (i, HEIGHT)) for i in range(0, HEIGHT, CELL_SIZE): pygame.draw.line(screen, BLACK, (0, i), (WIDTH, i)) # 字体 font = pygame.font.Font(None, 48) for i in range(3): for j in range(3): # 数字值 num_text = str(num_states[j][i]) if num_text == '0': # 写数字 text = font.render(num_text, True, RED) else: # 写数字 text = font.render(num_text, True, BLUE) screen.blit(text, (i * CELL_SIZE + CELL_SIZE / 2, j * CELL_SIZE + CELL_SIZE / 2)) # 绘制A*算法找到的路径,动画演示 def draw_a_star_path(initial_state, goal_state): # 执行A*算法,寻找最优路径 path_states = a_star_search(initial_state, goal_state) print("绘制网格地图和最优路径:") # 返回搜索路径和Open、Close表的内容 i = 0 for path in path_states: grid_print(path) print(f"======={i}=======") i += 1 print("绘制A*算法找到的路径地图:") # 初始化 Pygame pygame.init() # 创建一个窗口(屏幕)对象 screen = pygame.display.set_mode((WIDTH, HEIGHT)) # 窗口描述 pygame.display.set_caption("A星算法-8数码问题-动画演示") # 循环刷新地图,显示最优路径 for num_states in path_states: # 绘制主地图,棋盘数字 draw_grid(pygame, screen, num_states) # 更新显示屏幕 pygame.display.flip() time.sleep(1) # 退出 Pygame pygame.quit() if __name__ == "__main__": # 八数码初始状态 initial_state = [ [2, 8, 3], [1, 6, 0], [7, 5, 4] ] # 八数码最终状态 goal_state = [ [1, 2, 3], [8, 0, 4], [7, 6, 5] ] # 绘制A*算法找到的路径,动画演示 draw_a_star_path(initial_state, goal_state)
四,运行动画效果
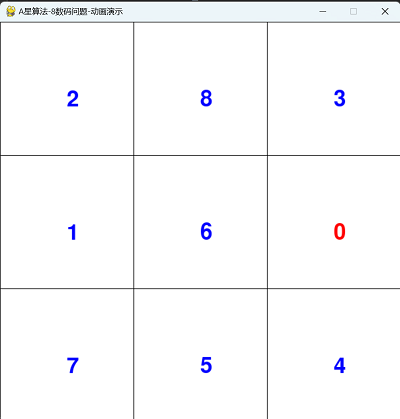
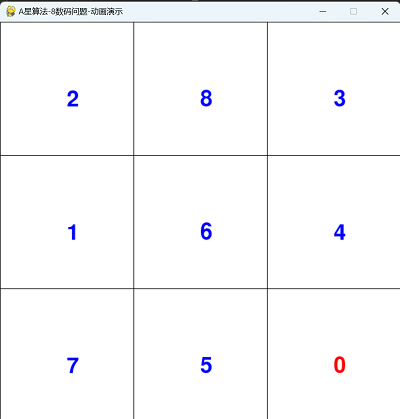

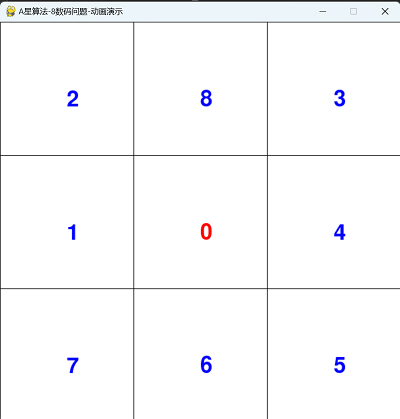
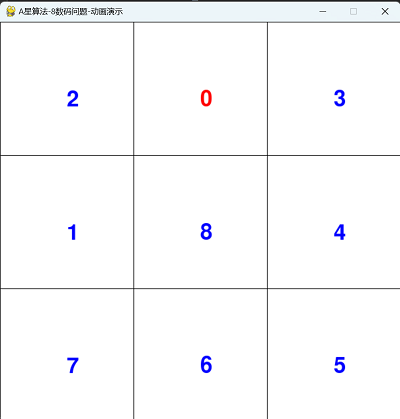
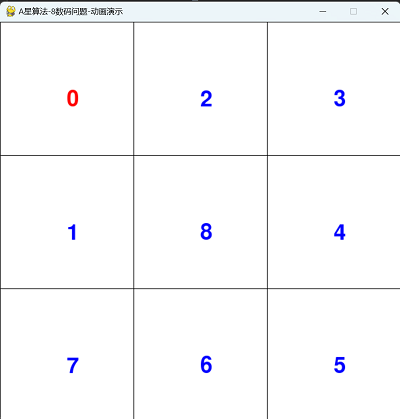
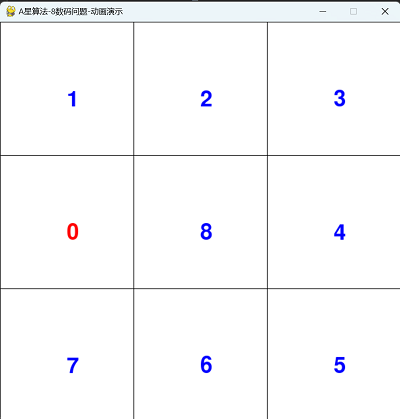
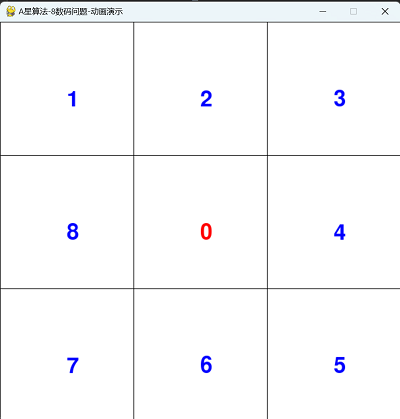
==========结束==========






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!