如何使用 vscode 搭建 Django Restful API 开发环境 All In One
如何使用 vscode 搭建 Django Restful API 开发环境 All In One
vscode + Django (
Python)
demos
DRF
https://www.django-rest-framework.org
https://github.com/encode/django-rest-framework
Django REST framework is a powerful and flexible toolkit for building Web APIs.

settings.py module:
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
# Use Django's standard `django.contrib.auth` permissions,
# or allow read-only access for unauthenticated users.
'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.permissions.DjangoModelPermissionsOrAnonReadOnly'
]
}
urls.py module:
from django.urls import path, include
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
from rest_framework import routers, serializers, viewsets
# Serializers define the API representation.
class UserSerializer(serializers.HyperlinkedModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = User
fields = ['url', 'username', 'email', 'is_staff']
# ViewSets define the view behavior.
class UserViewSet(viewsets.ModelViewSet):
queryset = User.objects.all()
serializer_class = UserSerializer
# Routers provide an easy way of automatically determining the URL conf.
router = routers.DefaultRouter()
router.register(r'users', UserViewSet)
# Wire up our API using automatic URL routing.
# Additionally, we include login URLs for the browsable API.
urlpatterns = [
path('', include(router.urls)),
path('api-auth/', include('rest_framework.urls', namespace='rest_framework'))
]
(🐞 反爬虫测试!打击盗版⚠️)如果你看到这个信息, 说明这是一篇剽窃的文章,请访问 https://www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms/ 查看原创文章!
Quickstart
# Create the project directory
$ mkdir tutorial
$ cd tutorial
# Create a virtual environment to isolate our package dependencies locally
$ python3 -m venv env
# On Windows use `env\Scripts\activate`
$ source env/bin/activate
# Install Django and Django REST framework into the virtual environment
$ pip install django
$ pip install djangorestframework
# Set up a new project with a single application
# Note the trailing `.` character
$ django-admin startproject tutorial .
$ cd tutorial
$ django-admin startapp quickstart
$ cd ..
$ pwd
<some path>/tutorial
$ find .
.
./tutorial
./tutorial/asgi.py
./tutorial/__init__.py
./tutorial/quickstart
./tutorial/quickstart/migrations
./tutorial/quickstart/migrations/__init__.py
./tutorial/quickstart/models.py
./tutorial/quickstart/__init__.py
./tutorial/quickstart/apps.py
./tutorial/quickstart/admin.py
./tutorial/quickstart/tests.py
./tutorial/quickstart/views.py
./tutorial/settings.py
./tutorial/urls.py
./tutorial/wsgi.py
./env
./env/...
./manage.py
$ python manage.py migrate
$ python manage.py createsuperuser --username admin --email admin@example.com
tutorial/quickstart/serializers.py
from django.contrib.auth.models import Group, User
from rest_framework import serializers
class UserSerializer(serializers.HyperlinkedModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = User
fields = ['url', 'username', 'email', 'groups']
class GroupSerializer(serializers.HyperlinkedModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Group
fields = ['url', 'name']
tutorial/quickstart/views.py
from django.contrib.auth.models import Group, User
from rest_framework import permissions, viewsets
from tutorial.quickstart.serializers import GroupSerializer, UserSerializer
class UserViewSet(viewsets.ModelViewSet):
"""
API endpoint that allows users to be viewed or edited.
"""
queryset = User.objects.all().order_by('-date_joined')
serializer_class = UserSerializer
permission_classes = [permissions.IsAuthenticated]
class GroupViewSet(viewsets.ModelViewSet):
"""
API endpoint that allows groups to be viewed or edited.
"""
queryset = Group.objects.all()
serializer_class = GroupSerializer
permission_classes = [permissions.IsAuthenticated]
tutorial/urls.py
from django.urls import include, path
from rest_framework import routers
from tutorial.quickstart import views
router = routers.DefaultRouter()
router.register(r'users', views.UserViewSet)
router.register(r'groups', views.GroupViewSet)
# Wire up our API using automatic URL routing.
# Additionally, we include login URLs for the browsable API.
urlpatterns = [
path('', include(router.urls)),
path('api-auth/', include('rest_framework.urls', namespace='rest_framework'))
]
urlpatterns += router.urls
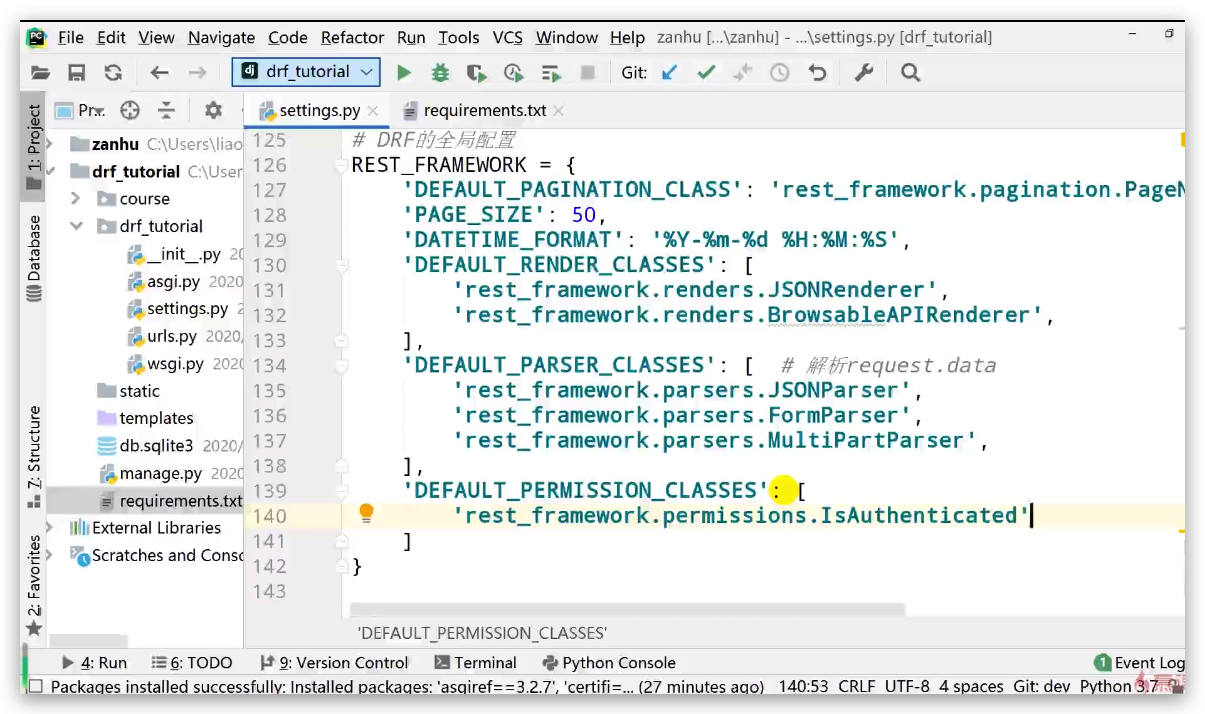
tutorial/settings.py
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS': 'rest_framework.pagination.PageNumberPagination',
'PAGE_SIZE': 10
}
INSTALLED_APPS = [
# ...
'rest_framework',
]
$ python manage.py runserver
# curl
bash: curl -u admin -H 'Accept: application/json; indent=4' http://127.0.0.1:8000/users/
Enter host password for user 'admin':
{
"count": 1,
"next": null,
"previous": null,
"results": [
{
"url": "http://127.0.0.1:8000/users/1/",
"username": "admin",
"email": "admin@example.com",
"groups": []
}
]
}
bash: http -a admin http://127.0.0.1:8000/users/
http: password for admin@127.0.0.1:8000::
$HTTP/1.1 200 OK
...
{
"count": 1,
"next": null,
"previous": null,
"results": [
{
"email": "admin@example.com",
"groups": [],
"url": "http://127.0.0.1:8000/users/1/",
"username": "admin"
}
]
}
https://httpie.io/docs#installation
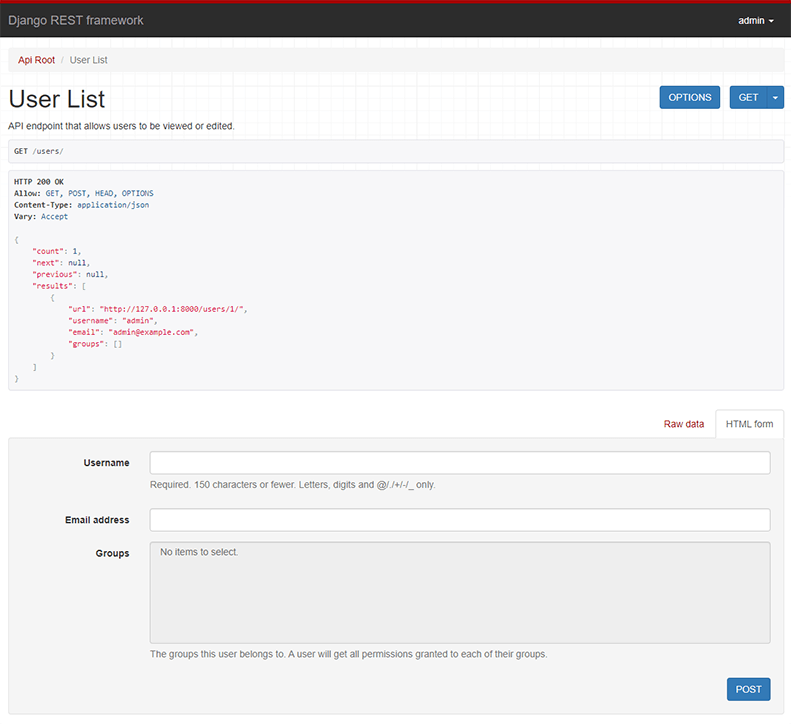
https://www.django-rest-framework.org/tutorial/quickstart/
The Browsable API
https://www.django-rest-framework.org/topics/browsable-api/#the-browsable-api
# BrowsableAPIRenderer
refs
https://www.imooc.com/video/22363
©xgqfrms 2012-2021
www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms 发布文章使用:只允许注册用户才可以访问!
原创文章,版权所有©️xgqfrms, 禁止转载 🈲️,侵权必究⚠️!
本文首发于博客园,作者:xgqfrms,原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms/p/18042454
未经授权禁止转载,违者必究!


