RPi.GPIO API All In One
RPi.GPIO API All In One
Python & Raspberry Pi
# RPi.GPIO 0.7.1 / Released: Feb 6, 2022
$ pip install RPi.GPIO
$ pip3 install RPi.GPIO
https://pypi.org/project/RPi.GPIO/
https://sourceforge.net/projects/raspberry-gpio-python/
API docs
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
GPIO.setmode
GPIO.BCM
GPIO.setup
GPIO.OUT
GPIO.PWM
https://sourceforge.net/p/raspberry-gpio-python/wiki/Examples/
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD)
func = GPIO.gpio_function(pin)
# will return a value from:
GPIO.IN, GPIO.OUT, GPIO.SPI, GPIO.I2C, GPIO.HARD_PWM, GPIO.SERIAL, GPIO.UNKNOWN
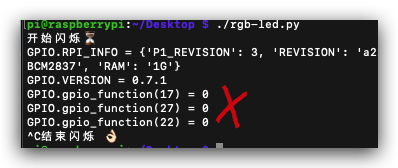
P17_value = GPIO.gpio_function(17)
P27_value = GPIO.gpio_function(27)
P22_value = GPIO.gpio_function(22)
print('GPIO.gpio_function(17) =', P17_value)
print('GPIO.gpio_function(27) =', P27_value)
print('GPIO.gpio_function(22) =', P22_value)
https://sourceforge.net/p/raspberry-gpio-python/wiki/Checking function of GPIO channels/
https://sourceforge.net/p/raspberry-gpio-python/wiki/Inputs/
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD)
GPIO.setup(12, GPIO.OUT)
# To set an output high:
GPIO.output(12, GPIO.HIGH)
# or
GPIO.output(12, 1)
# or
GPIO.output(12, True)
# To set an output low:
GPIO.output(12, GPIO.LOW)
# or
GPIO.output(12, 0)
# or
GPIO.output(12, False)
https://sourceforge.net/p/raspberry-gpio-python/wiki/Outputs/
# To discover information about your RPi:
GPIO.RPI_INFO
# To discover the Raspberry Pi board revision:
GPIO.RPI_INFO['P1_REVISION']
# GPIO.RPI_REVISION (deprecated)
# To discover the version of RPi.GPIO:
GPIO.VERSION
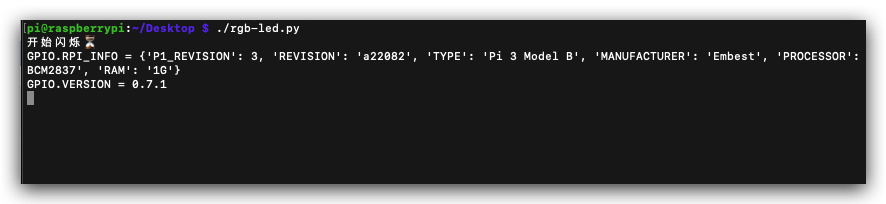
print('GPIO.RPI_INFO =', GPIO.RPI_INFO)
print('GPIO.VERSION =', GPIO.VERSION)
"""
GPIO.RPI_INFO = {'P1_REVISION': 3, 'REVISION': 'a22082', 'TYPE': 'Pi 3 Model B', 'MANUFACTURER': 'Embest', 'PROCESSOR': 'BCM2837', 'RAM': '1G'}
GPIO.VERSION = 0.7.1
"""
cleanup
GPIO.cleanup()
# It is possible that don't want to clean up every channel leaving some set up when your program exits.
# You can clean up individual channels, a list or a tuple of channels:
GPIO.cleanup(channel)
GPIO.cleanup( (channel1, channel2) )
GPIO.cleanup( [channel1, channel2] )
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
# choose BCM numbering scheme.
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
# red / green / blue
# GPIO.setup(17, GPIO.OUT)
# GPIO.setup(27, GPIO.OUT)
# GPIO.setup(22, GPIO.OUT)
# GPIO.setup list
LEDs = [17, 27, 22]
GPIO.setup(LEDs, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(LEDs, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(LEDs, GPIO.OUT)
https://sourceforge.net/p/raspberry-gpio-python/wiki/BasicUsage/
import time
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD)
GPIO.setup(12, GPIO.OUT)
p = GPIO.PWM(12, 50) # channel=12 frequency=50Hz
p.start(0)
try:
while 1:
for dc in range(0, 101, 5):
p.ChangeDutyCycle(dc)
time.sleep(0.1)
for dc in range(100, -1, -5):
p.ChangeDutyCycle(dc)
time.sleep(0.1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
p.stop()
GPIO.cleanup()
https://sourceforge.net/p/raspberry-gpio-python/wiki/PWM/
demos
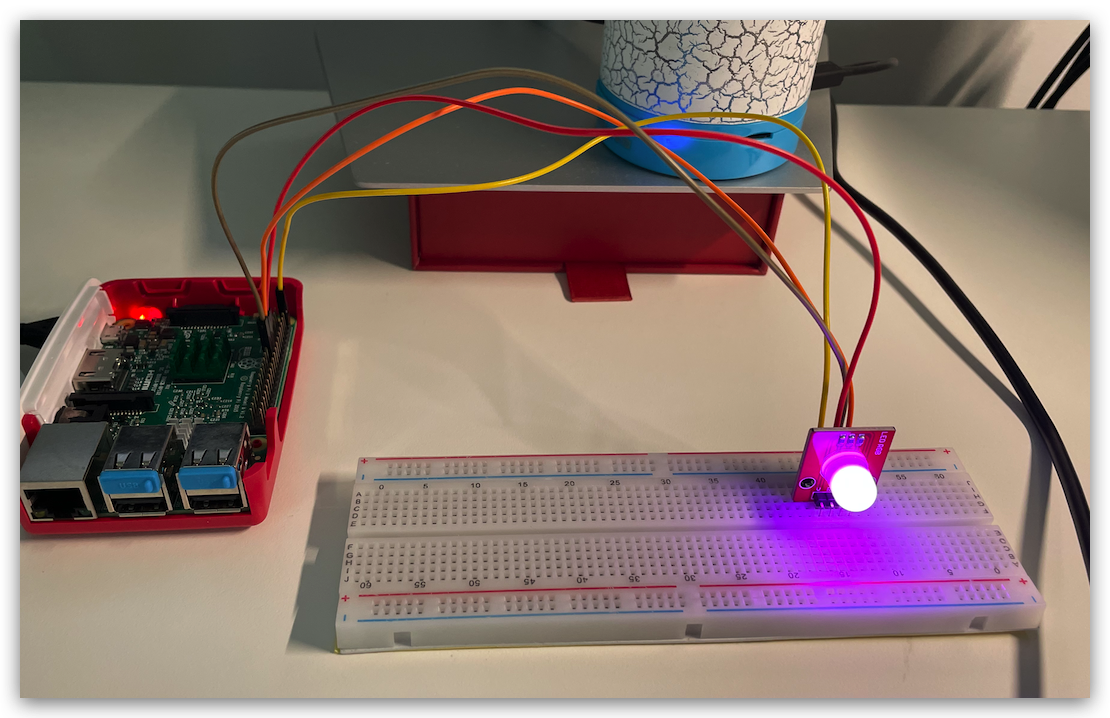
Keyes
RGB LED140C05
V 针脚需要接共阳极的 5V

#!/usr/bin/env python3
# coding: utf8
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
# choose BCM numbering scheme.
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
# red / green / blue
GPIO.setup(17, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(27, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(22, GPIO.OUT)
# hz = input('Please define the frequency in Herz(recommended:75): ')
# reddc = input('Please define the red LED Duty Cycle: ')
# greendc = input('Please define the green LED Duty Cycle: ')
# bluedc = input('Please define the blue LED Duty Cycle: ')
# hz = 1000
# hz = 800000
hz = 75
red = GPIO.PWM(17, hz)
green = GPIO.PWM(27, hz)
blue = GPIO.PWM(22, hz)
print('开始闪烁⏳')
try:
while True:
# red.start((reddc/2.55))
# green.start((greendc/2.55))
# blue.start((bluedc/2.55))
red.start((0/2.55))
green.start((255/2.55))
blue.start((0/2.55))
# ❌ ValueError: dutycycle must have a value from 0.0 to 100.0
except KeyboardInterrupt:
red.stop()
green.stop()
blue.stop()
# clean up GPIO on CTRL+C exit
GPIO.cleanup()
print('结束闪烁 👌🏻')
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# coding: utf8
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
# choose BCM numbering scheme.
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
# red / green / blue
# GPIO.setup(17, GPIO.OUT)
# GPIO.setup(27, GPIO.OUT)
# GPIO.setup(22, GPIO.OUT)
# GPIO.setup list
LEDs = [17, 27, 22]
GPIO.setup(LEDs, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(LEDs, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(LEDs, GPIO.OUT)
# hz = input('Please define the frequency in Herz(recommended:75): ')
# reddc = input('Please define the red LED Duty Cycle: ')
# greendc = input('Please define the green LED Duty Cycle: ')
# bluedc = input('Please define the blue LED Duty Cycle: ')
# hz = 1000
# hz = 800000
hz = 75
red = GPIO.PWM(17, hz)
green = GPIO.PWM(27, hz)
blue = GPIO.PWM(22, hz)
print('开始闪烁⏳')
print('GPIO.RPI_INFO =', GPIO.RPI_INFO)
print('GPIO.VERSION =', GPIO.VERSION)
P17_value = GPIO.gpio_function(17)
P27_value = GPIO.gpio_function(27)
P22_value = GPIO.gpio_function(22)
print('GPIO.gpio_function(17) =', P17_value)
print('GPIO.gpio_function(27) =', P27_value)
print('GPIO.gpio_function(22) =', P22_value)
try:
# while True:
# # red.start((reddc/2.55))
# # green.start((greendc/2.55))
# # blue.start((bluedc/2.55))
# red.start((0/2.55))
# green.start((255/2.55))
# blue.start((0/2.55))
# # ❌ ValueError: dutycycle must have a value from 0.0 to 100.0
for r in range(255):
for g in range(255):
for b in range(255):
red.start((r/2.55))
green.start((g/2.55))
blue.start((b/2.55))
except KeyboardInterrupt:
red.stop()
green.stop()
blue.stop()
# clean up GPIO on CTRL+C exit
GPIO.cleanup()
print('结束闪烁 👌🏻')
solution
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# coding: utf8
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
from time import sleep
# choose BCM numbering scheme.
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
# red / green / blue
# GPIO.setup(17, GPIO.OUT)
# GPIO.setup(27, GPIO.OUT)
# GPIO.setup(22, GPIO.OUT)
# GPIO.setup list
LEDs = [17, 22, 27]
GPIO.setup(LEDs, GPIO.OUT)
# LED Duty Cycle / LED 占空比
# hz = input('Please define the frequency in Herz(recommended:75): ')
# reddc = input('Please define the red LED Duty Cycle: ')
# greendc = input('Please define the green LED Duty Cycle: ')
# bluedc = input('Please define the blue LED Duty Cycle: ')
# hz = 1000
# hz = 800000
# hz = 75
hz = 60
# RBG => GPIO 17, 27, 22 真实引脚接线对应关系
# rgb => 输出颜色顺序 `绿红蓝` ❌
# red = GPIO.PWM(17, hz)
# blue = GPIO.PWM(27, hz)
# green = GPIO.PWM(22, hz)
# BGR => 蓝绿红 ✅, 但是与 RBG 逻辑上完全不符合呀 💩
blue = GPIO.PWM(17, hz)
green = GPIO.PWM(27, hz)
red = GPIO.PWM(22, hz)
print('开始闪烁⏳')
print('GPIO.RPI_INFO =', GPIO.RPI_INFO)
print('GPIO.VERSION =', GPIO.VERSION)
print('clean up GPIO on CTRL+C exit 🎉')
def init():
for color in ["r", "g", "b"]:
if(color == "r"):
red.start((100.0))
green.start((0.0))
blue.start((0.0))
elif(color == "g"):
red.start((0.0))
green.start((100.0))
blue.start((0.0))
else:
red.start((0.0))
green.start((0.0))
blue.start((100.0))
sleep(3)
# sleep(1)
init()
def clear():
red.stop()
green.stop()
blue.stop()
GPIO.cleanup()
try:
while True:
for r in range(11):
for g in range(11):
for b in range(11):
red.start((r * 10.0))
green.start((g * 10.0))
blue.start((b * 10.0))
# print('✅ RGB =', r*10.0, g* 10.0, b*10.0)
# ValueError: dutycycle must have a value from 0.0 to 100.0
sleep(0.01)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
# clear()
print('结束闪烁 ❌')
finally:
clear()
print('结束闪烁 👌🏻')
(🐞 反爬虫测试!打击盗版⚠️)如果你看到这个信息, 说明这是一篇剽窃的文章,请访问 https://www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms/ 查看原创文章!
Raspberry Pi 3B
fix low voltage error
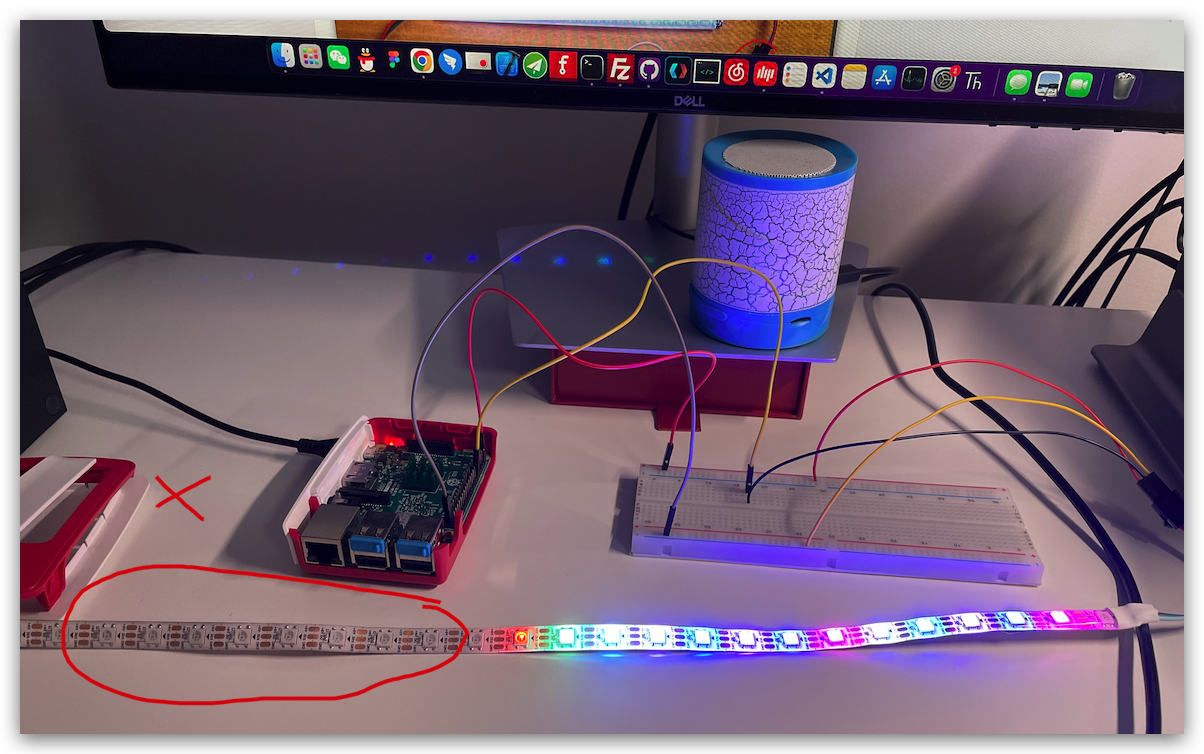
$ sudo vim /boot/config.txt
# disable audio (snd_bcm2835)
# dtparam=audio=on
$ sudo reboot
https://tutorials-raspberrypi.com/connect-control-raspberry-pi-ws2812-rgb-led-strips/
https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit_CircuitPython_NeoPixel/issues/151
https://github.com/xgqfrms/Raspberry-Pi
https://github.com/xgqfrms/Raspberry-Pi/commit/e6cdaf1f9b7394e7dc37d6022fe1cdf6aac23472
refs
https://www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms/p/17397022.html#5176673
https://www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms/p/17397440.html
https://ozeki.hu/p_3047-how-to-setup-a-rgb-led-on-raspberry-pi.html
https://s761111.gitbook.io/raspi-sensor/ba-wan-san-se-ledpwm-hu-xi
©xgqfrms 2012-2021
www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms 发布文章使用:只允许注册用户才可以访问!
原创文章,版权所有©️xgqfrms, 禁止转载 🈲️,侵权必究⚠️!
本文首发于博客园,作者:xgqfrms,原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms/p/17397440.html
未经授权禁止转载,违者必究!


