Linux shell script programming All In One
Linux shell script programming All In One
shell 脚本编程

Linux 系统中登录 shell 的时候,会从下面的 5 个启动文件里读取命令;
# 系统级,所有登录用户都会先启动这个文件
$ cat /etc/profile
# 用户级,按照Linux 发行版中实际存在的文件个数,依次进行启动
$ cat $HOME/.bash_profile
$ cat $HOME/.bashrc
$ cat $HOME/.bash_login
$ cat $HOME/.profile
.sh => Bourne shell => bash
.csh => c shell
https://www.gnu.org/software/bash/manual/bash.pdf
Linux 进程信号量
process signal

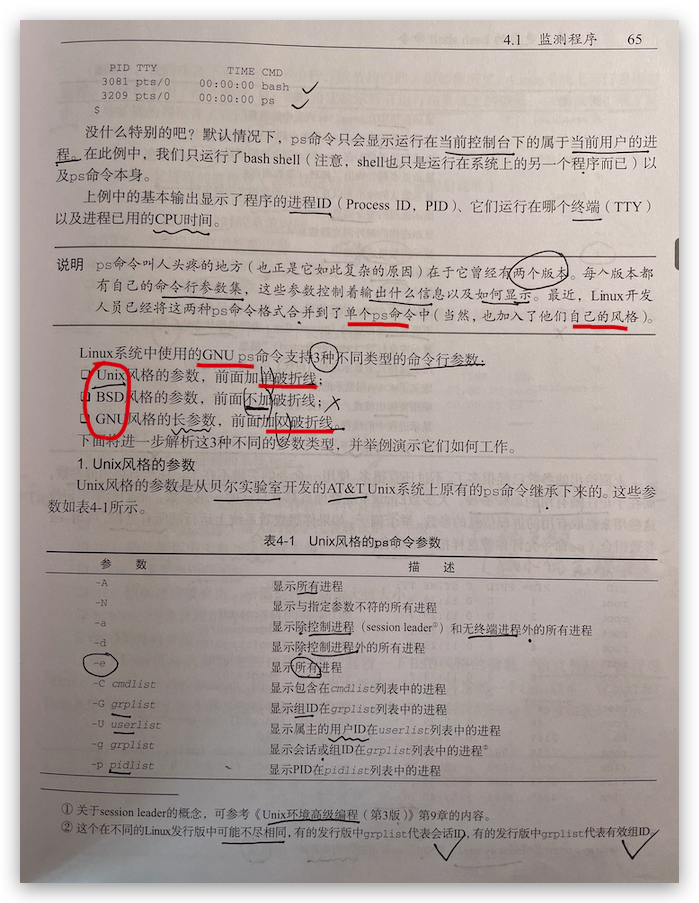
Linux shell commands argument styles
Linux shell 命令行参数风格
Unix 风格, AT&T,-单破折号
BSD 风格, 加州大学伯克利分校, 没有破折号
GNU 风格, -- 双破折号
Unix
BSD
GNU
shell types
shell 类型 / shell 种类
# $ which shell
$ which bash
$ which sh
$ which zsh
| 系统 | 截图 |
|---|---|
| Raspberry Pi | 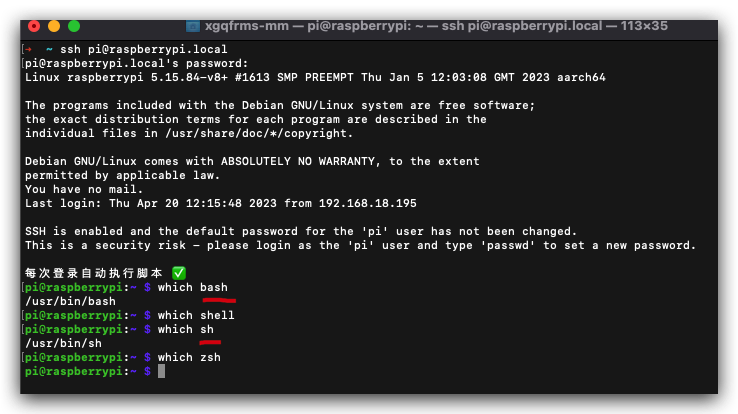 |
| macOS | 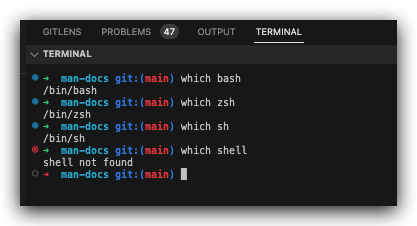 |
启动文件
- 系统的 shell 启动配置文件
/etc/profile
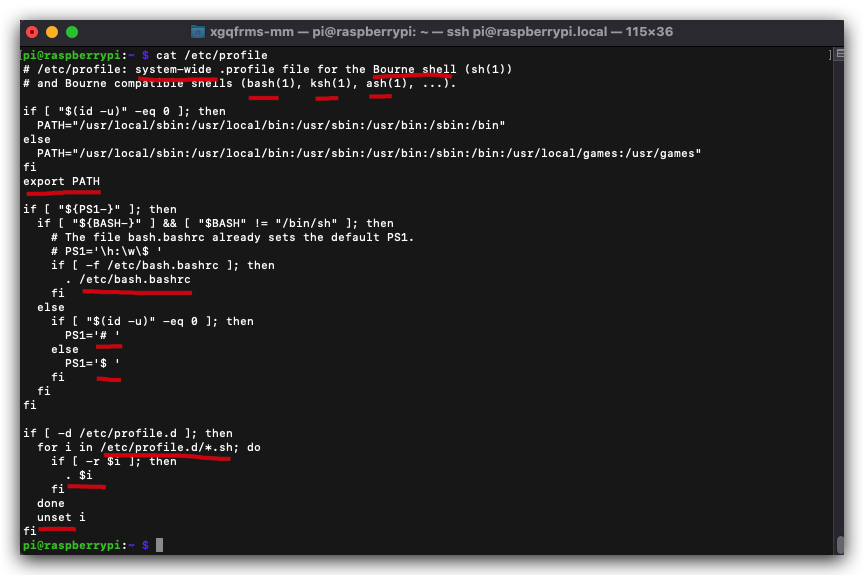
$ cat /etc/profile
$ cat /etc/profile
# /etc/profile: system-wide .profile file for the Bourne shell (sh(1))
# and Bourne compatible shells (bash(1), ksh(1), ash(1), ...).
if [ "$(id -u)" -eq 0 ]; then
PATH="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin"
else
PATH="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/local/games:/usr/games"
fi
export PATH
if [ "${PS1-}" ]; then
if [ "${BASH-}" ] && [ "$BASH" != "/bin/sh" ]; then
# The file bash.bashrc already sets the default PS1.
# PS1='\h:\w\$ '
if [ -f /etc/bash.bashrc ]; then
. /etc/bash.bashrc
fi
else
if [ "$(id -u)" -eq 0 ]; then
PS1='# '
else
PS1='$ '
fi
fi
fi
if [ -d /etc/profile.d ]; then
for i in /etc/profile.d/*.sh; do
if [ -r $i ]; then
. $i
fi
done
unset i
fi
# 配置文件目录 `/etc/profile.d`
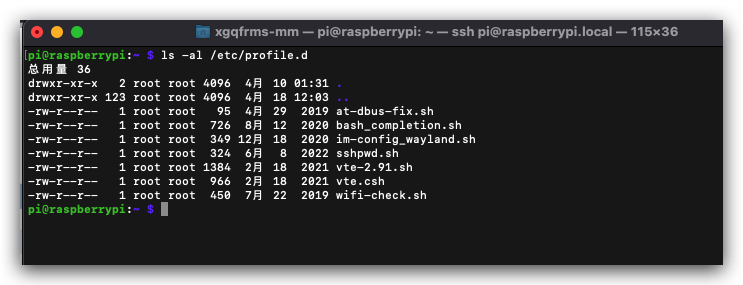
$ ls -al /etc/profile.d
# 配置文件目录 `/etc/profile.d`
$ ls -al /etc/profile.d
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ ls -al /etc/profile.d
总用量 36
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 4月 10 01:31 .
drwxr-xr-x 123 root root 4096 4月 18 12:03 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 95 4月 29 2019 at-dbus-fix.sh
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 726 8月 12 2020 bash_completion.sh
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 349 12月 18 2020 im-config_wayland.sh
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 324 6月 8 2022 sshpwd.sh
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1384 2月 18 2021 vte-2.91.sh
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 966 2月 18 2021 vte.csh
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 450 7月 22 2019 wifi-check.sh
pi@raspberrypi:~ $
- 用户的 shell 启动配置文件
$HOME/.profile
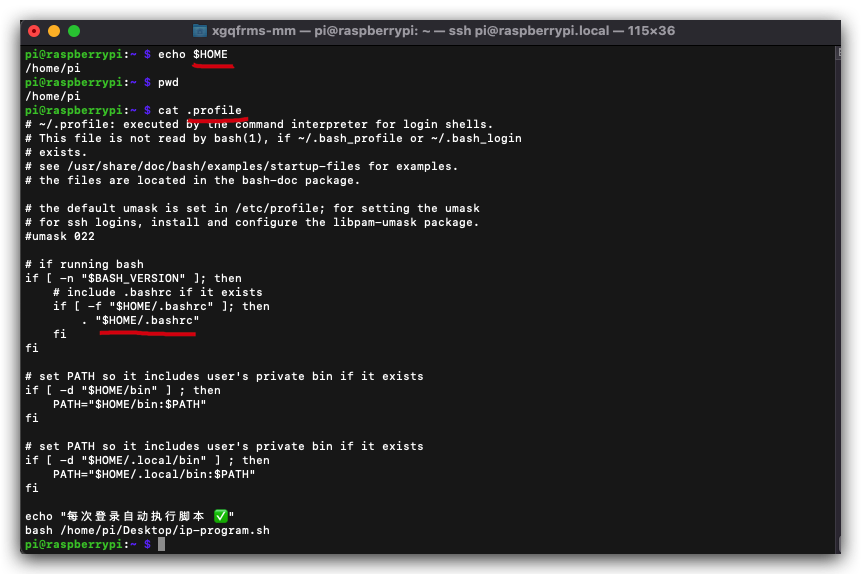
$ cat $HOME/.profile
# 等价于
$ cd ~ && cat .profile
$ cat $HOME/.profile
# 等价于
$ cd ~ && cat .profile
# ~/.profile: executed by the command interpreter for login shells.
# This file is not read by bash(1), if ~/.bash_profile or ~/.bash_login
# exists.
# see /usr/share/doc/bash/examples/startup-files for examples.
# the files are located in the bash-doc package.
# the default umask is set in /etc/profile; for setting the umask
# for ssh logins, install and configure the libpam-umask package.
#umask 022
# if running bash
if [ -n "$BASH_VERSION" ]; then
# include .bashrc if it exists
if [ -f "$HOME/.bashrc" ]; then
. "$HOME/.bashrc"
fi
fi
# set PATH so it includes user's private bin if it exists
if [ -d "$HOME/bin" ] ; then
PATH="$HOME/bin:$PATH"
fi
# set PATH so it includes user's private bin if it exists
if [ -d "$HOME/.local/bin" ] ; then
PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$PATH"
fi
echo "每次登录自动执行脚本 ✅"
bash /home/pi/Desktop/ip-program.sh
demos
(🐞 反爬虫测试!打击盗版⚠️)如果你看到这个信息, 说明这是一篇剽窃的文章,请访问 https://www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms/ 查看原创文章!
parent shell vs child shell

eric@rpi4b:~ $ printenv NVM_USER_ENV
eric@rpi4b:~ $ printenv | grep NVM_USER_ENV
eric@rpi4b:~ $ printenv | grep NVM_USER
NVM_USER=xgqfrms_pi4b
eric@rpi4b:~ $ printenv NVM_USER
xgqfrms_pi4b
eric@rpi4b:~ $ env NVM_USER
env: “NVM_USER”: 没有那个文件或目录
eric@rpi4b:~ $ export NVM_USER_ENV=eric_env
eric@rpi4b:~ $ printenv | grep NVM_USER
NVM_USER_ENV=eric_env
NVM_USER=xgqfrms_pi4b
eric@rpi4b:~ $ export NVM_USER_ENV=eric_env_new
eric@rpi4b:~ $ printenv | grep NVM_USER
NVM_USER_ENV=eric_env_new
NVM_USER=xgqfrms_pi4b
eric@rpi4b:~ $ bash
fix vim bug ✅
eric@rpi4b:~ $ echo $NVM_USER
xgqfrms_pi4b
eric@rpi4b:~ $ printenv | grep NVM_USER
NVM_USER_ENV=eric_env_new
NVM_USER=xgqfrms_pi4b
eric@rpi4b:~ $ echo $NVM_USER_ENV
eric_env_new
eric@rpi4b:~ $ export NVM_USER_ENV=eric_env_child
eric@rpi4b:~ $ echo $NVM_USER_ENV
eric_env_child
eric@rpi4b:~ $ exit
exit
eric@rpi4b:~ $ printenv | grep NVM_USER
NVM_USER_ENV=eric_env_new
NVM_USER=xgqfrms_pi4b
eric@rpi4b:~ $
eric@rpi4b:~ $ printenv | grep NVM_USER
NVM_USER_ENV=eric_env_new
NVM_USER=xgqfrms_pi4b

eric@rpi4b:~ $ printenv | grep NVM_USER
NVM_USER_ENV=eric_env_new
NVM_USER=xgqfrms_pi4b
eric@rpi4b:~ $ bash
fix vim bug ✅
eric@rpi4b:~ $ echo $NVM_USER_ENV
eric_env_new
eric@rpi4b:~ $ export NVM_USER_ENV_CHILD=child_shell_env
eric@rpi4b:~ $ echo $NVM_USER_CHILD
eric@rpi4b:~ $ echo $NVM_USER_ENV_CHILD
child_shell_env
eric@rpi4b:~ $ exit
exit
eric@rpi4b:~ $ echo $NVM_USER_ENV_CHILD
eric@rpi4b:~ $ printenv | grep NVM_USER
NVM_USER_ENV=eric_env_new
NVM_USER=xgqfrms_pi4b
eric@rpi4b:~ $
raspi-config
# GUI 交互式命令行界面
$ sudo raspi-config
在本质上还是直接修改 /boot/config.txt 配置文件
https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/computers/configuration.html#the-raspi-config-tool
refs
https://github.com/xgqfrms?tab=repositories&q=shell&type=&language=&sort=
©xgqfrms 2012-2021
www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms 发布文章使用:只允许注册用户才可以访问!
原创文章,版权所有©️xgqfrms, 禁止转载 🈲️,侵权必究⚠️!
本文首发于博客园,作者:xgqfrms,原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms/p/17343088.html
未经授权禁止转载,违者必究!

