Linux command line packages management tools: apt-get vs apt All In One
Linux command line packages management tools: apt-get vs apt All In One
apt 是基于apt-get 的一个命令行工具,只能用于和用户进行交互,但是不能在脚本中使用;
apt-get 是一个底层的命令,即可以用来和用户进行直接的交互, 也可以在脚本中使用; ✅
apt-get 旧,面向 ower-level and "back-end", 兼容性好 ✅(Linux 高级用户)
$ man apt-get

$ man apt-get

APT-GET(8) APT APT-GET(8)
NAME
apt-get - APT package handling utility -- command-line interface
SYNOPSIS
apt-get [-asqdyfmubV] [-o=config_string] [-c=config_file] [-t=target_release] [-a=architecture] {update
| upgrade | dselect-upgrade | dist-upgrade |
install pkg [{=pkg_version_number | /target_release}]... | remove pkg... | purge pkg... |
source pkg [{=pkg_version_number | /target_release}]... |
build-dep pkg [{=pkg_version_number | /target_release}]... |
download pkg [{=pkg_version_number | /target_release}]... | check | clean | autoclean |
autoremove | {-v | --version} | {-h | --help}}
DESCRIPTION
apt-get is the command-line tool for handling packages, and may be considered the user's "back-end" to
other tools using the APT library. Several "front-end" interfaces exist, such as aptitude(8),
synaptic(8) and wajig(1).
Unless the -h, or --help option is given, one of the commands below must be present.
update
update is used to resynchronize the package index files from their sources. The indexes of
available packages are fetched from the location(s) specified in /etc/apt/sources.list. For
example, when using a Debian archive, this command retrieves and scans the Packages.gz files, so
that information about new and updated packages is available. An update should always be performed
before an upgrade or dist-upgrade. Please be aware that the overall progress meter will be
incorrect as the size of the package files cannot be known in advance.
upgrade
upgrade is used to install the newest versions of all packages currently installed on the system
from the sources enumerated in /etc/apt/sources.list. Packages currently installed with new
versions available are retrieved and upgraded; under no circumstances are currently installed
packages removed, or packages not already installed retrieved and installed. New versions of
currently installed packages that cannot be upgraded without changing the install status of another
package will be left at their current version. An update must be performed first so that apt-get
knows that new versions of packages are available.
dist-upgrade
dist-upgrade in addition to performing the function of upgrade, also intelligently handles changing
dependencies with new versions of packages; apt-get has a "smart" conflict resolution system, and
it will attempt to upgrade the most important packages at the expense of less important ones if
apt 新,基于 apt-get 面向终端用户 (Linux 小白用户)
The
aptcommand is meant to be pleasant for end users and does not need to be backward compatible like apt-get(8).
$ man apt
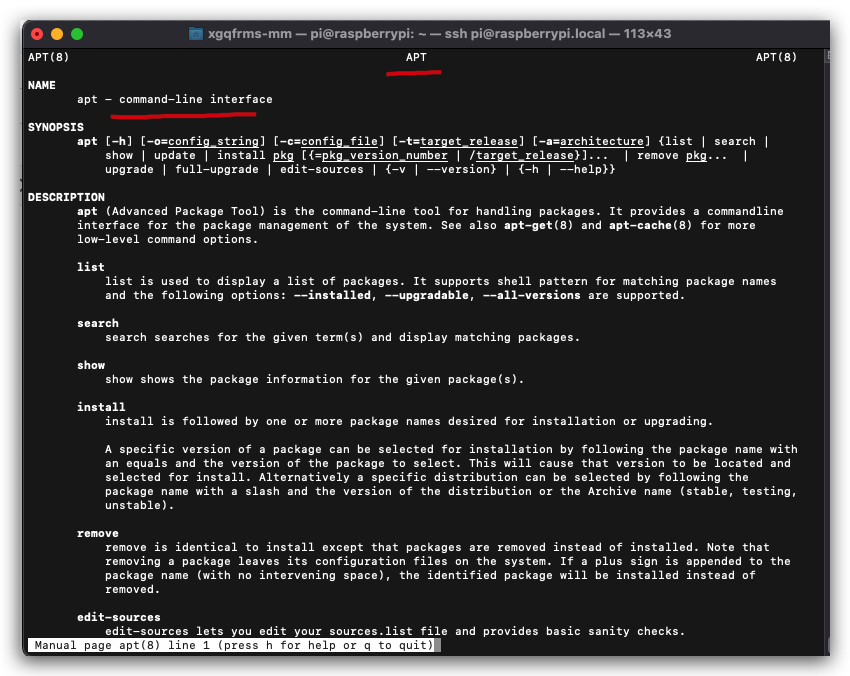
$ man apt

APT(8) APT APT(8)
NAME
apt - command-line interface
SYNOPSIS
apt [-h] [-o=config_string] [-c=config_file] [-t=target_release] [-a=architecture] {list | search |
show | update | install pkg [{=pkg_version_number | /target_release}]... | remove pkg... |
upgrade | full-upgrade | edit-sources | {-v | --version} | {-h | --help}}
DESCRIPTION
apt (Advanced Package Tool) is the command-line tool for handling packages. It provides a commandline
interface for the package management of the system. See also apt-get(8) and apt-cache(8) for more
low-level command options.
list
list is used to display a list of packages. It supports shell pattern for matching package names
and the following options: --installed, --upgradable, --all-versions are supported.
search
search searches for the given term(s) and display matching packages.
show
show shows the package information for the given package(s).
install
install is followed by one or more package names desired for installation or upgrading.
A specific version of a package can be selected for installation by following the package name with
an equals and the version of the package to select. This will cause that version to be located and
selected for install. Alternatively a specific distribution can be selected by following the
package name with a slash and the version of the distribution or the Archive name (stable, testing,
unstable).
remove
remove is identical to install except that packages are removed instead of installed. Note that
removing a package leaves its configuration files on the system. If a plus sign is appended to the
package name (with no intervening space), the identified package will be installed instead of
removed.
edit-sources
edit-sources lets you edit your sources.list file and provides basic sanity checks.
对比
| apt-get | apt | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| apt-get install | apt install | 安装软件包 |
apt-get remove apt remove 删除软件包
apt-get remove apt remove 更换所有包
apt-get purge aptpurge 移除软件包及配置文件
apt-get upgrade apt upgrade 更新所有软件包(自动处理依赖项)
apt-get autoremove apt autoremove 自动删除不需要的包
apt-get dist-upgrade apt full-upgrade 在升级软件包时自动处理依赖关系
apt-cache search apt search 搜索应用程序
apt-cache show apt show 显示装细节
demos
(🐞 反爬虫测试!打击盗版⚠️)如果你看到这个信息, 说明这是一篇剽窃的文章,请访问 https://www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms/ 查看原创文章!
refs
https://askubuntu.com/questions/445384/what-is-the-difference-between-apt-and-apt-get
https://www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms/p/17267400.html#5169206
©xgqfrms 2012-2021
www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms 发布文章使用:只允许注册用户才可以访问!
原创文章,版权所有©️xgqfrms, 禁止转载 🈲️,侵权必究⚠️!
本文首发于博客园,作者:xgqfrms,原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms/p/17330609.html
未经授权禁止转载,违者必究!


