Linux shell set command All In One
Linux shell set command All In One
erros ❌
unbound-variable
# $1: unbound variable
if (($1))
then
echo $1
# arg=$1
# tsGenerator $arg
# tsGenerator $1
# tsGenerator
else
echo "❌"
fi
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# 显示所有的已经执行的命令
# set -eux
# set -ex
# bug
set -u
echo "\$1 = $1"
echo "\$2 = $2"
# 一个参数
# $ /auto-ts-files-generator.sh 33
# 两个参数
# $ ./auto-ts-files-generator.sh 33 regular-expressions
It is well appreciated that when set -u is active Bash will report an error if an unbound variable is referenced, e.g.:
很好理解,当 set -u 处于活动状态时,如果引用了未绑定的变量,Bash 将报告错误,例如:
https://bnikolic.co.uk/blog/bash-unbound-variable
https://replit.com/@bnwebcode/bash-unbound-variable
https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/463034/bash-throws-error-line-8-1-unbound-variable
: bad substitution
# : bad substitution ❌
if [ -n "${$2:-}" ]; then
echo "\$2 = $2"
filename=$2
else
filename=$fallback
fi
solutions
set +u
-u Treats unset parameters as an error when substituting.
Using + rather than - causes these flags to be turned off.
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_21481459/article/details/104202174
demos
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# 显示所有的已经执行的命令
set -eux
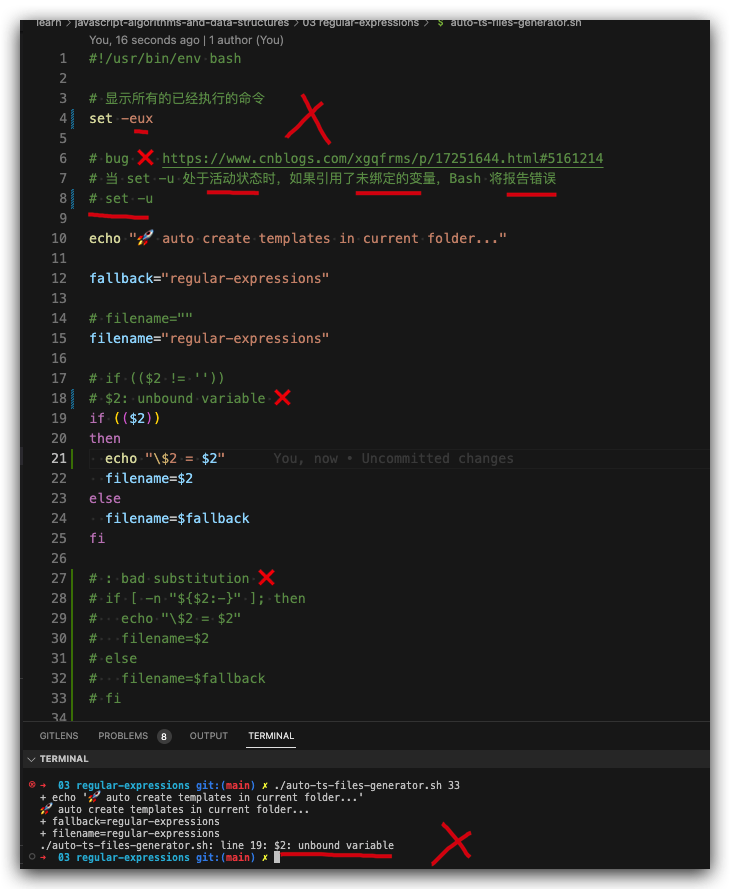
# bug ❌ https://www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms/p/17251644.html#5161214
# 当 set -u 处于活动状态时,如果引用了未绑定的变量,Bash 将报告错误
# set -u\
# ✅
set +u
echo "🚀 auto create templates in current folder..."
fallback="regular-expressions"
# filename=""
filename="regular-expressions"
# if (($2 != ''))
# $2: unbound variable ❌
if (($2))
then
filename=$2
else
filename=$fallback
fi
# : bad substitution ❌
# if [ -n "${$2:-}" ]; then
# echo "\$2 = $2"
# filename=$2
# else
# filename=$fallback
# fi
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# 显示所有的已经执行的命令
set -eux
# bug ❌ https://www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms/p/17251644.html#5161214
# 当 set -u 处于活动状态时,如果引用了未绑定的变量,Bash 将报告错误
# set -u
set +u
echo "🚀 auto create templates in current folder..."
fallback="regular-expressions"
# filename=""
filename="regular-expressions"
# if (($2 != ''))
# $2: unbound variable ❌
if (($2))
then
echo "\$2 = $2"
filename=$2
else
filename=$fallback
fi
# : bad substitution ❌
# if [ -n "${$2:-}" ]; then
# echo "\$2 = $2"
# filename=$2
# else
# filename=$fallback
# fi
# ✅ single quotes string
TS_TEMPLATE='
"use strict";
/**
*
* @author xgqfrms
* @license MIT
* @copyright xgqfrms
* @created 2023-03-23
* @modified
*
* @description
* @description
* @difficulty Easy
* @ime_complexity O(n)
* @space_complexity O(n)
* @augments
* @example
* @link https://www.freecodecamp.org/chinese/learn/javascript-algorithms-and-data-structures/'$filename'/
* @link https://www.freecodecamp.org/learn/javascript-algorithms-and-data-structures/'$filename'/
* @solutions
*
* @best_solutions
*
*/
export { };
const log = console.log;
'
# tsGenerator: command not found ❌ function 必须先定义,然后再使用
function tsGenerator() {
# function scope $1, 必须在调用函数的时候传递进来
index=1
while(( $index <= $1 ))
do
echo 👻 index = $index
name=""
if (( $index < 10 ))
then
name="0$index.ts"
elif (( $index >= 10 ))
then
name="$index.ts"
else
echo "❌"
fi
echo -e filename = $name
# printf "$TS_TEMPLATE"
printf "$TS_TEMPLATE" > $name
let "index++"
done
return 0
}
# scipt scope $1 ✅
if (($1))
then
echo "🎮 arg = $1"
tsGenerator $1
else
echo "❌"
fi
# 一个参数
# $ /auto-ts-files-generator.sh 33
# 两个参数
# $ ./auto-ts-files-generator.sh 33 regular-expressions
FreeBSD
man set
$ man set
BUILTIN(1) General Commands Manual BUILTIN(1)
NAME
builtin, !, %, ., :, @, [, {, }, alias, alloc, bg, bind, bindkey, break,
breaksw, builtins, case, cd, chdir, command, complete, continue, default, dirs,
do, done, echo, echotc, elif, else, end, endif, endsw, esac, eval, exec, exit,
export, false, fc, fg, filetest, fi, for, foreach, getopts, glob, goto, hash,
hashstat, history, hup, if, jobid, jobs, kill, limit, local, log, login,
logout, ls-F, nice, nohup, notify, onintr, popd, printenv, printf, pushd, pwd,
read, readonly, rehash, repeat, return, sched, set, setenv, settc, setty,
setvar, shift, source, stop, suspend, switch, telltc, test, then, time, times,
trap, true, type, ulimit, umask, unalias, uncomplete, unhash, unlimit, unset,
unsetenv, until, wait, where, which, while – shell built-in commands
SYNOPSIS
See the built-in command description in the appropriate shell manual page.
DESCRIPTION
Shell builtin commands are commands that can be executed within the running
shell's process. Note that, in the case of csh(1) builtin commands, the
command is executed in a subshell if it occurs as any component of a pipeline
except the last.
If a command specified to the shell contains a slash ‘/’, the shell will not
execute a builtin command, even if the last component of the specified command
matches the name of a builtin command. Thus, while specifying “echo” causes a
builtin command to be executed under shells that support the echo builtin
command, specifying “/bin/echo” or “./echo” does not.
While some builtin commands may exist in more than one shell, their operation
may be different under each shell which supports them. Below is a table which
lists shell builtin commands, the standard shells that support them and whether
they exist as standalone utilities.
Only builtin commands for the csh(1) and sh(1) shells are listed here. Consult
a shell's manual page for details on the operation of its builtin commands.
Beware that the sh(1) manual page, at least, calls some of these commands
“built-in commands” and some of them “reserved words”. Users of other shells
may need to consult an info(1) page or other sources of documentation.
Commands marked “No**” under External do exist externally, but are implemented
as scripts using a builtin command of the same name.
Command External csh(1) sh(1)
! No No Yes
% No Yes No
. No No Yes
: No Yes Yes
@ No Yes Yes
[ Yes No Yes
{ No No Yes
} No No Yes
alias No** Yes Yes
alloc No Yes No
bg No** Yes Yes
bind No No Yes
bindkey No Yes No
break No Yes Yes
breaksw No Yes No
builtin No No Yes
builtins No Yes No
case No Yes Yes
cd No** Yes Yes
chdir No Yes Yes
command No** No Yes
complete No Yes No
continue No Yes Yes
default No Yes No
dirs No Yes No
do No No Yes
done No No Yes
echo Yes Yes Yes
echotc No Yes No
elif No No Yes
else No Yes Yes
end No Yes No
endif No Yes No
endsw No Yes No
esac No No Yes
eval No Yes Yes
exec No Yes Yes
exit No Yes Yes
export No No Yes
false Yes No Yes
fc No** No Yes
fg No** Yes Yes
filetest No Yes No
fi No No Yes
for No No Yes
foreach No Yes No
getopts No** No Yes
glob No Yes No
goto No Yes No
hash No** No Yes
hashstat No Yes No
history No Yes No
hup No Yes No
if No Yes Yes
jobid No No Yes
jobs No** Yes Yes
kill Yes Yes Yes
limit No Yes No
local No No Yes
log No Yes No
login Yes Yes No
logout No Yes No
ls-F No Yes No
nice Yes Yes No
nohup Yes Yes No
notify No Yes No
onintr No Yes No
popd No Yes No
printenv Yes Yes No
printf Yes No Yes
pushd No Yes No
pwd Yes No Yes
read No** No Yes
readonly No No Yes
rehash No Yes No
repeat No Yes No
return No No Yes
sched No Yes No
set No Yes Yes
setenv No Yes No
settc No Yes No
setty No Yes No
setvar No No Yes
shift No Yes Yes
source No Yes No
stop No Yes No
suspend No Yes No
switch No Yes No
telltc No Yes No
test Yes No Yes
then No No Yes
time Yes Yes No
times No No Yes
trap No No Yes
true Yes No Yes
type No** No Yes
ulimit No** No Yes
umask No** Yes Yes
unalias No** Yes Yes
uncomplete No Yes No
unhash No Yes No
unlimit No Yes No
unset No Yes Yes
unsetenv No Yes No
until No No Yes
wait No** Yes Yes
where No Yes No
which Yes Yes No
while No Yes Yes
SEE ALSO
csh(1), dash(1), echo(1), false(1), info(1), kill(1), login(1), nice(1),
nohup(1), printenv(1), printf(1), pwd(1), sh(1), test(1), time(1), true(1),
which(1), zsh(1)
HISTORY
The builtin manual page first appeared in FreeBSD 3.4.
AUTHORS
This manual page was written by Sheldon Hearn <sheldonh@FreeBSD.org>.
macOS 13.1 December 21, 2010 macOS 13.1
set & unset
set [ {+|-}options | {+|-}o [ option_name ] ] ... [ {+|-}A [ name ] ]
[ arg ... ]
Set the options for the shell and/or set the positional
parameters, or declare and set an array. If the -s option is
given, it causes the specified arguments to be sorted before
assigning them to the positional parameters (or to the array
name if -A is used). With +s sort arguments in descending
order. For the meaning of the other flags, see zshoptions(1).
Flags may be specified by name using the -o option. If no option
name is supplied with -o, the current option states are printed:
see the description of setopt below for more information on the
format. With +o they are printed in a form that can be used as
input to the shell.
If the -A flag is specified, name is set to an array containing
the given args; if no name is specified, all arrays are printed
together with their values.
If +A is used and name is an array, the given arguments will
replace the initial elements of that array; if no name is
specified, all arrays are printed without their values.
The behaviour of arguments after -A name or +A name depends on
whether the option KSH_ARRAYS is set. If it is not set, all
arguments following name are treated as values for the array,
regardless of their form. If the option is set, normal option
processing continues at that point; only regular arguments are
treated as values for the array. This means that
set -A array -x -- foo
sets array to `-x -- foo' if KSH_ARRAYS is not set, but sets the
array to foo and turns on the option `-x' if it is set.
If the -A flag is not present, but there are arguments beyond
the options, the positional parameters are set. If the option
list (if any) is terminated by `--', and there are no further
arguments, the positional parameters will be unset.
If no arguments and no `--' are given, then the names and values
of all parameters are printed on the standard output. If the
only argument is `+', the names of all parameters are printed.
For historical reasons, `set -' is treated as `set +xv' and `set
- args' as `set +xv -- args' when in any other emulation mode
than zsh's native mode.
$ man zshbuiltins
# $ man zshbuiltins | grep set
# Unknown locale, assuming C
$ locale
LANG=""
LC_COLLATE="C"
LC_CTYPE="UTF-8"
LC_MESSAGES="C"
LC_MONETARY="C"
LC_NUMERIC="C"
LC_TIME="C"
LC_ALL=
# fix
$ export LANG="en_US.UTF-8"
$ locale
LANG="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_COLLATE="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_CTYPE="UTF-8"
LC_MESSAGES="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_MONETARY="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_NUMERIC="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_TIME="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_ALL=
https://pubs.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/007904875/utilities/set.html
unset [ -fmv ] name ...
Each named parameter is unset. Local parameters remain local
even if unset; they appear unset within scope, but the previous
value will still reappear when the scope ends.
Individual elements of associative array parameters may be unset
by using subscript syntax on name, which should be quoted (or
the entire command prefixed with noglob) to protect the
subscript from filename generation.
If the -m flag is specified the arguments are taken as patterns
(should be quoted) and all parameters with matching names are
unset. Note that this cannot be used when unsetting associative
array elements, as the subscript will be treated as part of the
pattern.
The -v flag specifies that name refers to parameters. This is
the default behaviour.
unset -f is equivalent to unfunction.
https://pubs.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/007904875/utilities/unset.html
refs
https://www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms/p/17251644.html#5161214
©xgqfrms 2012-2021
www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms 发布文章使用:只允许注册用户才可以访问!
原创文章,版权所有©️xgqfrms, 禁止转载 🈲️,侵权必究⚠️!
本文首发于博客园,作者:xgqfrms,原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms/p/17252980.html
未经授权禁止转载,违者必究!

