数据结构-队列 All In One
数据结构-队列 All In One
队列,又称为伫列(queue),计算机科学中的一种抽象资料类型,是先进先出(FIFO, First-In-First-Out)的线性表。
在具体应用中通常用链表或者数组来实现。
队列只允许在后端(称为 rear)进行插入操作,在前端(称为front)进行删除操作。
队列的操作方式和堆栈类似,唯一的区别在于队列只允许新数据在后端进行添加。
单向队列
function Queue(size) {
this.size = size;
this.arr = [];
/*
this.push = function(value) {
if(this.arr.length < this.size) {
this.arr.push(value);
} else {
console.log(`❌ Queue overflow!`)
}
}
this.pop = function() {
if(this.arr.length > 0) {
this.arr.shift();
}
}
*/
}
// 原型链
Queue.prototype.push = function(value) {
if(this.arr.length < this.size) {
this.arr.push(value);
} else {
console.log(`❌ Queue overflow!`)
}
};
Queue.prototype.pop = function() {
if(this.arr.length > 0) {
this.arr.shift();
}
};
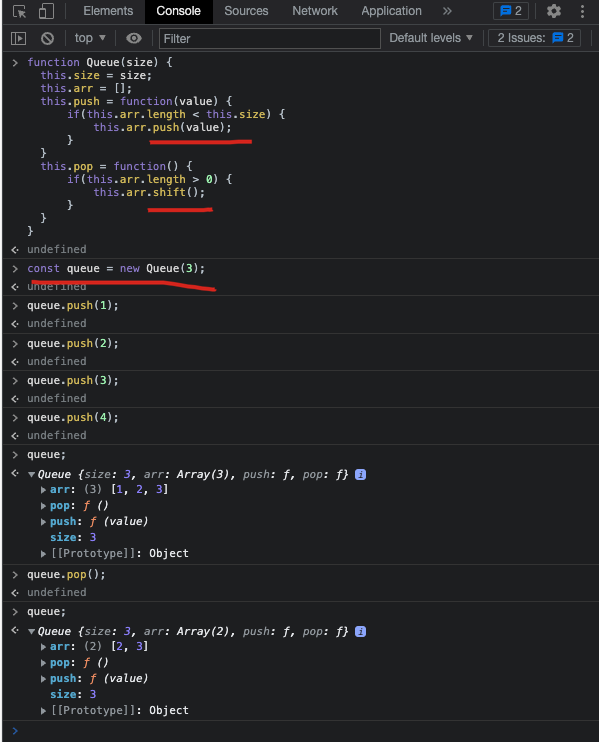
const queue = new Queue(3);
queue.push(1);
queue.push(2);
queue.push(3);
queue.push(4);
// ❌ Queue overflow!
queue;
queue.pop();
queue;
class Queue {
size: number;
arr: any[];
constructor(size: number) {
this.size = size;
this.arr = [];
}
push(value: any): void {
if(this.arr.length < this.size) {
this.arr.push(value);
} else {
console.log(`❌ Queue overflow!`)
}
}
pop() {
if(this.arr.length > 0) {
this.arr.shift();
}
}
}
双向队列
队列是一种先进先出的结构,只能在队伍的开头添加元素,队伍的结尾删除元素。
双向队列的概念就是同时允许在队伍的开头和结尾添加和删除元素。
https://www.cnblogs.com/tylerdonet/p/5847628.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/wuzhiblog/p/js_data_structure_5_2.html
循环队列
js 可以使用数组,代替双指针,是因为 js 数组长度是动态变化的,不会浪费空间;
C++,Java, Python 等静态类型语言,必须指定数组的长度,而且不可以改变大小;
/**
* @param {number} k
*/
var MyCircularQueue = function(k) {
this.arr = [];
this.size = k;
// MyCircularQueue(k): 构造器,设置队列长度为 k 。
};
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {boolean}
*/
MyCircularQueue.prototype.enQueue = function(value) {
// enQueue(value): 向循环队列插入一个元素。如果成功插入则返回真。
if(this.arr.length < this.size) {
this.arr.push(value);
return true;
}
return false;
};
/**
* @return {boolean}
*/
MyCircularQueue.prototype.deQueue = function() {
// deQueue(): 从循环队列中删除一个元素。如果成功删除则返回真。
if(this.arr.length > 0) {
this.arr.shift();
return true;
}
return false;
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
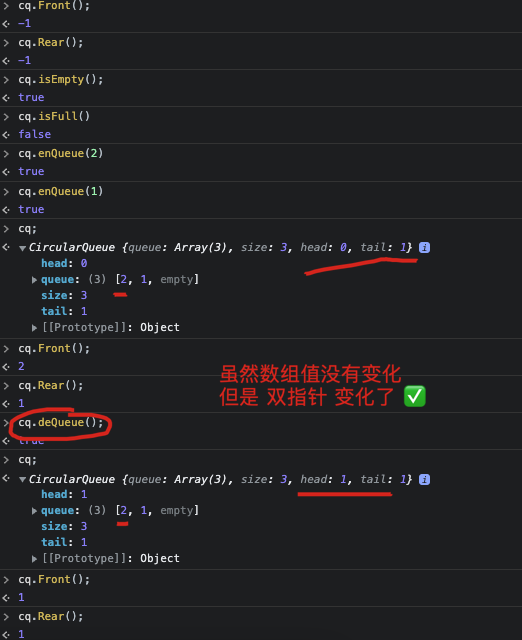
MyCircularQueue.prototype.Front = function() {
// Front: 从队首获取元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
if(this.arr.length === 0) {
return -1;
}
return this.arr[0];
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
MyCircularQueue.prototype.Rear = function() {
// Rear: 获取队尾元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
if(this.arr.length === 0) {
return -1;
}
return this.arr[this.arr.length - 1];
};
/**
* @return {boolean}
*/
MyCircularQueue.prototype.isEmpty = function() {
// isEmpty(): 检查循环队列是否为空。
return this.arr.length === 0;
};
/**
* @return {boolean}
*/
MyCircularQueue.prototype.isFull = function() {
// isFull(): 检查循环队列是否已满。
return this.arr.length === this.size;
};
/**
* Your MyCircularQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new MyCircularQueue(k)
* var param_1 = obj.enQueue(value)
* var param_2 = obj.deQueue()
* var param_3 = obj.Front()
* var param_4 = obj.Rear()
* var param_5 = obj.isEmpty()
* var param_6 = obj.isFull()
*/
双指针方案
class CircularQueue {
queue: any[];
// queue: number[];
size: number;
head: number;
tail: number;
constructor(k: number) {
// this.queue = [];
// 定长数组
this.queue = new Array(k);
// this.queue = [...``.padEnd(k)].map(Number);
// this.queue = [...``.padEnd(k)].map(i => -1);
this.size = k;
this.head = -1;
this.tail = -1;
}
enQueue(value: number): boolean {
if (this.isFull()) {
return false;
}
if (this.isEmpty()) {
this.head = 0;
}
// index 取余
this.tail = (this.tail + 1) % this.size;
this.queue[this.tail] = value;
return true;
}
deQueue(): boolean {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
if (this.head === this.tail) {
this.head = -1;
this.tail = -1;
return true;
}
this.head = (this.head + 1) % this.size;
return true;
}
Front(): number {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return this.queue[this.head];
}
Rear(): number {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return this.queue[this.tail];
}
isEmpty(): boolean {
return this.head === -1;
}
isFull(): boolean {
return ((this.tail + 1) % this.size) === this.head;
}
}
单链表方案
单链表与数组实现方法的时间和空间复杂度相同,但是单链表的效率更高,因为这种方法不会预分配内存;
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class CircularQueue {
/** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the queue to be k. */
constrcutor(k) {
this.capacity = k;
this.count = 0;
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
/** Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
enQueue(value) {
if (this.count === this.capacity) {
return false;
}
let newNode = new Node(value);
if (this.count == 0) {
this.head = this.tail = newNode;
} else {
// ???
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.count += 1;
return true;
}
/** Delete an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
deQueue() {
if (this.count === 0) {
return false;
}
this.head = this.head.next;
this.count -= 1;
return true;
}
/** Get the front item from the queue. */
Front() {
if (this.count === 0) {
return -1;
} else {
return this.head.value;
}
}
/** Get the last item from the queue. */
Rear() {
if (this.count === 0) {
return -1;
} else {
return this.tail.value;
}
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not. */
isEmpty() {
return (this.count === 0);
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is full or not. */
isFull() {
return (this.count === this.capacity);
}
}
图解算法数据结构 All In One
https://www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms/p/16366896.html
LeetCode
https://leetcode.com/explore/learn/card/queue-stack/
https://leetcode.cn/leetbook/detail/queue-stack/
622. 设计循环队列
https://leetcode.com/problems/design-circular-queue/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-circular-queue/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-circular-queue/solution/she-ji-xun-huan-dui-lie-by-leetcode/
任何数据结构中都不存在环形结构,但是可以使用一维 数组 模拟,通过操作数组的索引构建一个 虚拟 的环。很多复杂数据结构都可以通过数组实现。
对于一个固定大小的数组,任何位置都可以是队首,只要知道队列长度,就可以根据下面公式计算出队尾位置:
tailIndex = (headIndex + count - 1) % capacity
tailI = (head + count - 1) % size
其中 capacity 是数组长度,count 是队列长度,headIndex 和 tailIndex 分别是队首 head 和队尾 tail 索引。
算法
设计数据结构的关键是如何设计属性,好的设计属性数量更少。
属性数量少说明属性之间冗余更低。
属性冗余度越低,操作逻辑越简单,发生错误的可能性更低。
属性数量少,使用的空间也少,操作性能更高。
但是,也不建议使用最少的属性数量。 一定的冗余可以降低操作的时间复杂度,达到时间复杂度和空间复杂度的相对平衡。
属性含义
queue:一个固定大小的数组,用于保存循环队列的元素。
headIndex:一个整数,保存队首 head 的索引。
count:循环队列当前的长度,即循环队列中的元素数量。使用 headIndex 和 count 可以计算出队尾元素的索引,因此不需要队尾属性。
capacity:循环队列的容量,即队列中最多可以容纳的元素数量。
该属性不是必需的,因为队列容量可以通过数组属性得到,但是由于该属性经常使用,所以我们选择保留它。
这样可以不用在 Python 中每次调用 len(queue) 中获取容量。
但是在 Java / JavaScript 中通过 queue.length 获取容量更加高效。
为了保持一致性,在两种方案中都保留该属性。
refs
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/队列
©xgqfrms 2012-2020
www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms 发布文章使用:只允许注册用户才可以访问!
原创文章,版权所有©️xgqfrms, 禁止转载 🈲️,侵权必究⚠️!
本文首发于博客园,作者:xgqfrms,原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms/p/16395197.html
未经授权禁止转载,违者必究!

