Spring之ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext接口
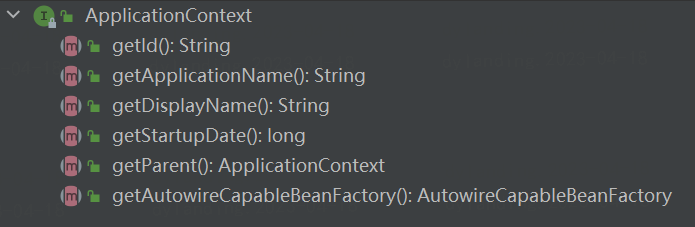
ApplicationContext是Spring的高级容器。
与BeanFactory类似,它可以加载bean定义并根据请求分发bean;此外,它还添加了很多特定的功能,比如:从属性文件解析文本消息、将应用程序事件发布到感兴趣的事件侦听器。
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,
MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
}
ApplicationContext整体可以分为两个体系,一个就是web体系,另一个就是非web体系
非web体系
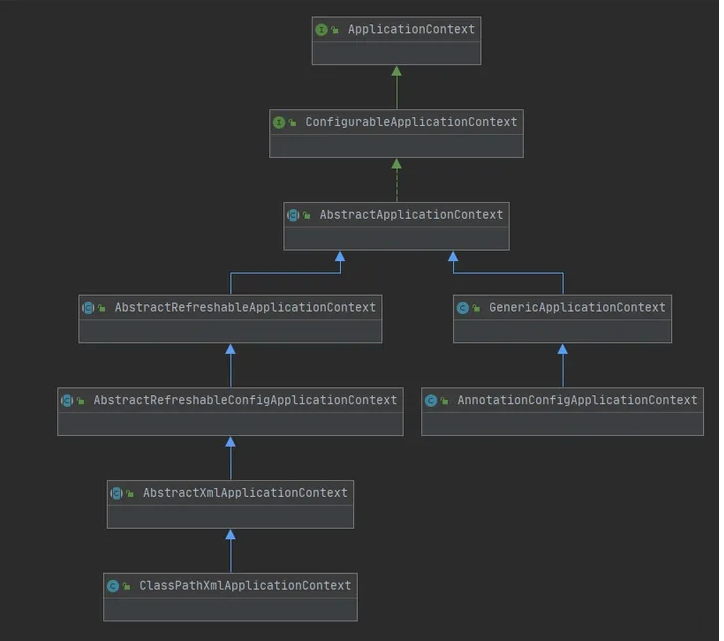
ConfigurableApplicationContext
ApplicationContext接口中的方法比较简单,并且ApplicationContext接口的方法都是只读的,不能对当前容器做任何改变,而ConfigurableApplicationContext接口在ApplicationContext的基础上增加了很多进行配置的方法,比如添加事件监听器,添加后置处理器等等。
public interface ConfigurableApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext, Lifecycle, Closeable {
// 配置路径的分隔符
String CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS = ",; \t\n";
String CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME = "conversionService";
String LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME = "loadTimeWeaver";
String ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME = "environment";
String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME = "systemProperties";
String SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME = "systemEnvironment";
//设置此应用程序上下文的唯一ID。
void setId(String id);
//设置父容器,设置后不能再改了
void setParent(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent);
//设置environment此处为ConfigurableEnvironment 也是可以配置的应用上下文
void setEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment);
//此处修改父类返回值为ConfigurableEnvironment
@Override
ConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment();
//添加一个新的BeanFactoryPostProcessor (refresh()的时候会调用的)
void addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor);
//添加一个事件监听器
void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener);
//注册协议处理器允许处理额外的资源协议
void addProtocolResolver(ProtocolResolver resolver);
//加载或刷新配置的持久表示,最最最重要的一个方法
// 表示可以是xml、可以是注解、可以是外部资源文件等等。
//这个方法执行完成后,所有非懒加载的单例Bean都已经被实例化,Bean工厂肯定也就被创建好了
void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;
//JVH运行时注册一个关闭挂钩,在关闭JVA时关闭此上下文,除非此时已经关闭
void registerShutdownHook();
//关闭此应用程序上下文,释放可能持有的所有资源和锁包括一些销毁、释放资源操作
@Override
void close();
//标识上下文是否激活 refreshO后就会激活
boolean isActive();
//返回此上下文内部的Bean工厂,可以用来访问底层工厂的特定功能。通过此工厂可以设置和验证所需的属性、自定义转换服务
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
}AbstractApplicationContext
这个类实现了ConfigurableApplicationContext,具备了上面接口大部分功能, 但是它没有实现getBeanFactory()方法,这个方法留待子类实现,所以它自己没有实际的管理Bean的能力,只是定义了一系列规范
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext {
// 碰到重复的Bean时,是否允许覆盖原先的BeanDefinition
@Nullable
private Boolean allowBeanDefinitionOverriding;
// 是否允许循环引用
@Nullable
private Boolean allowCircularReferences;
// 默认持有一个DefaultListableBeanFactory
@Nullable
private DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
// 对内部工厂进行操作时所采用的锁
private final Object beanFactoryMonitor = new Object();
public AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext() {
}
public AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
super(parent);
}
public void setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(boolean allowBeanDefinitionOverriding) {
this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding = allowBeanDefinitionOverriding;
}
public void setAllowCircularReferences(boolean allowCircularReferences) {
this.allowCircularReferences = allowCircularReferences;
}
// 刷新Bean工厂,如果当前上下文中已经存在一个容器的话,会先销毁容器中的所有Bean,然后关闭Bean工厂
// 之后在重新创建一个DefaultListableBeanFactory
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
@Override
protected void cancelRefresh(BeansException ex) {
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
if (this.beanFactory != null) {
this.beanFactory.setSerializationId(null);
}
}
super.cancelRefresh(ex);
}
@Override
protected final void closeBeanFactory() {
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
if (this.beanFactory != null) {
this.beanFactory.setSerializationId(null);
this.beanFactory = null;
}
}
}
protected final boolean hasBeanFactory() {
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
return (this.beanFactory != null);
}
}
// 复写了getBeanFactory,默认返回的是通过createBeanFactory创建的一个DefaultListableBeanFactory
@Override
public final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() {
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
if (this.beanFactory == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("BeanFactory not initialized or already closed - " +
"call 'refresh' before accessing beans via the ApplicationContext");
}
return this.beanFactory;
}
}
protected DefaultListableBeanFactory createBeanFactory() {
return new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory());
}
//.......
// 提供了一个抽象的加载BeanDefinition的方法,这个方法没有具体实现,不同的配置方式需要进行不同的实现,
// 到这里,配置的方式不能确定,既可能是以XML的方式,也可能是以java config的方式
// 另外配置文件的加载方式也不能确定
protected abstract void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory)
throws BeansException,
}可以看到这个类可进一步对上下文进行配置,例如进行是否开启循环引用,是否允许进行BeanDefinition的覆盖等等。另外它所提供的一个重要的功能就是使容器具备刷新的功能,换言之,凡是需要刷新功能的容器都需要继承这个类。
AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext
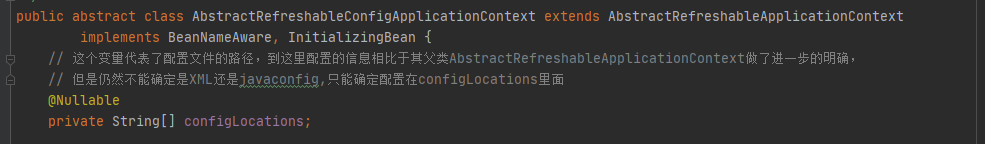
AbstractXmlApplicationContext
public abstract class AbstractXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext {
private boolean validating = true;
public AbstractXmlApplicationContext() {
}
public AbstractXmlApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
super(parent);
}
public void setValidating(boolean validating) {
this.validating = validating;
}
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// 创建XmlBeanDefinitionReader解析器
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
//配置XmlBeanDefinitionReader
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
//自定义初始化XmlBeanDefinitionReader
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
//加载BeanDefinition
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
protected void initBeanDefinitionReader(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) {
reader.setValidating(this.validating);
}
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}
@Nullable
protected Resource[] getConfigResources() {
return null;
}
}可以看到这个类进一步对配置的加载做了明确,首先明确配置的类型为XML,第二步明确了要通过getConfigResources方法来加载需要的配置资源,但是并没有对这个方法做具体事项,因为对于Resource的定义,可能是通过classpath的方法,也可能是通过URL的方式,基于此又多了两个子类
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,从classpath下加载配置文件
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext,基于URL的格式加载配置文件
GenericApplicationContext
这个类已经不是抽象类了,可以直接使用它。但是这个类有一个很大的缺点,它不能去读配置,需要手动去指定读取的方式和位置。
其实从上下文中的分析可以看出,从AbstractApplicationContext到AbstractXmlApplicationContext一步步明确了配置的加载方式,Spring通过这种类的继承将配置的加载分了很多层,可以从AbstractXmlApplicationContext的子类进行扩展。
而GenericApplicationContext只实现了上下文的基本功能,并没有对配置做任何约束,所以在使用它时需要手动往其注入BeanDefinition。这样虽然灵活,但是很麻烦,如果我们使用GenericApplicationContext可能需要进行下面这样的操作:
GenericApplicationContext ctx = new GenericApplicationContext();
//使用XmlBeanDefinitionReader,这个地方我们甚至可以自己定义解析器,不使用Spring容器内部的
XmlBeanDefinitionReader xmlReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(ctx);
//加载ClassPathResource
xmlReader.loadBeanDefinitions(new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml"));
PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader propReader = new PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader(ctx);
propReader.loadBeanDefinitions(new ClassPathResource("otherBeans.properties"));
//调用Refresh方法
ctx.refresh();
//和其他ApplicationContext方法一样的使用方式
DmzService myBean = (DmzService) ctx.getBean("myBean");平常的开发基本用不到这东西。
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
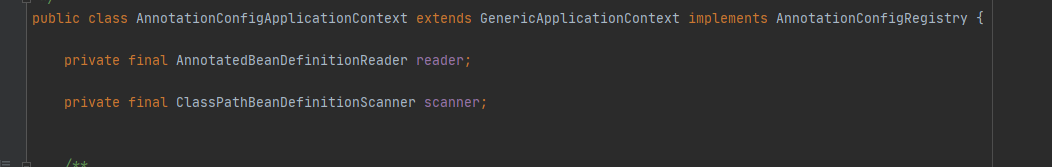
通过AnnotationConfigApplicationContext注册配置类,用ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner扫描配置类上声明的路径,得到所有的BeanDefinition。然后其余的没啥了。这个我们经常使用,因为不需要XML文件了,使用@Configuration配置类即可,更加的方便。
web体系
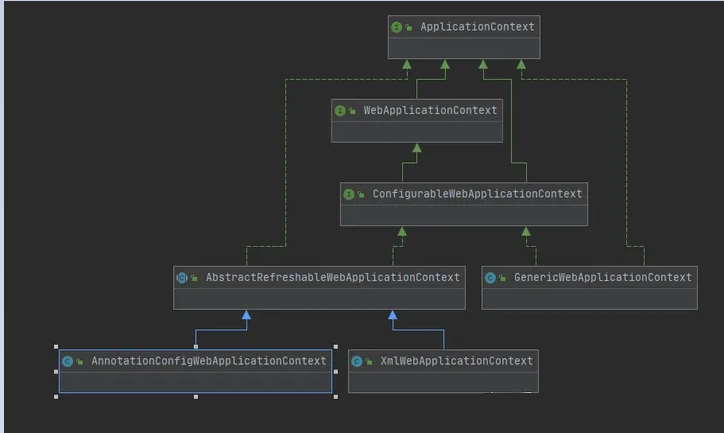
WebApplicationContext
public interface WebApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext {
String ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT";
String SCOPE_REQUEST = "request";
String SCOPE_SESSION = "session";
String SCOPE_APPLICATION = "application";
String SERVLET_CONTEXT_BEAN_NAME = "servletContext";
String CONTEXT_PARAMETERS_BEAN_NAME = "contextParameters";
String CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTES_BEAN_NAME = "contextAttributes";
@Nullable
ServletContext getServletContext();
}定义了一堆常量,以及一个方法,约束了所有的web容器必须能返回一个Servlet的上下文(ServletContext)。
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
public interface ConfigurableWebApplicationContext extends WebApplicationContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext {
String APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ":";
String SERVLET_CONFIG_BEAN_NAME = "servletConfig";
void setServletContext(@Nullable ServletContext servletContext);
void setServletConfig(@Nullable ServletConfig servletConfig);
@Nullable
ServletConfig getServletConfig();
//设置及获取当前上下文的命名空间,命名空间用于区分不同的Web容器的配置,在查找配置时会根据命名空间查找
//默认不进行命名空间配匮,配置会在/WEB-INF/applicationcontext.xml下查找
//如果配置了,会在/WEB-INF+"namespace" +/applicationContext.xml下查找
//根容器没有Namespace
void setNamespace(@Nullable String namespace);
@Nullable
String getNamespace();
void setConfigLocation(String configLocation);
void setConfigLocations(String... configLocations);
@Nullable
String[] getConfigLocations();
}可以看到使用这个类能指定上下文配置加载的位置。
AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext
implements ConfigurableWebApplicationContext, ThemeSource {
//.......
}首先可以看到这个类继承了AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext,代表它需要从指定的位置加载配置,其次它实现了ConfigurableWebApplicationContext,所以它具有web容器的属性。
XmlWebApplicationContext
public class XmlWebApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext {
public static final String DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION = "/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml";
public static final String DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_PREFIX = "/WEB-INF/";
public static final String DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_SUFFIX = ".xml";
// .......
@Override
protected String[] getDefaultConfigLocations() {
if (getNamespace() != null) {
return new String[] {DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_PREFIX + getNamespace() + DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_SUFFIX};
}
else {
return new String[] {DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION};
}
}
}进一步指定了配置文件的加载形式。
- 需要加载XML类型配置
- 对于根容器,加载路径为/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml
- 对于子容器,加载路径为/WEB-INF/+'namespace'+.xml,比如常用的dispatchServlet.xml
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext
指定了以注解的方式配置web容器。
GenericWebApplicationContext
类比GenericApplicationContext,没有指定配置相关的任何东西,全手动。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· AI技术革命,工作效率10个最佳AI工具