Spring容器之ClassPathXmlApplicationContext和AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
在 Spring Framework 中,AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 和 ClasspathXmlApplicationContext是两个不同的应用程序上下文实现,用于配置和管理 Spring Bean 容器。它们之间的主要区别在于配置的方式和使用场景。
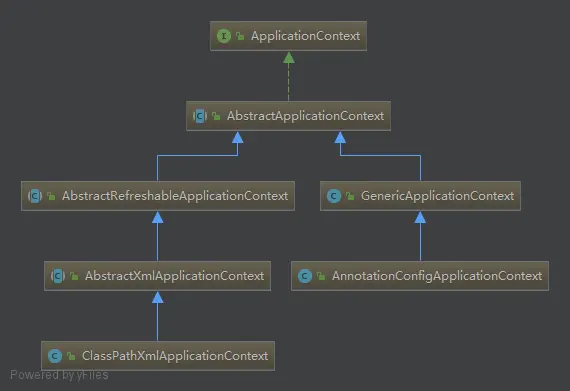
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
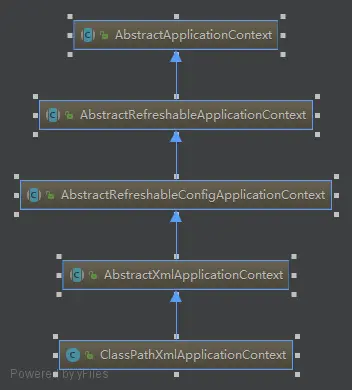
ClasspathXmlApplicationContext是基于 XML 配置的应用程序上下文实现。它从类路径中加载 XML 配置文件,其中包含了 Spring Bean 的定义和配置信息。
在 XML 文件中,你会使用一些特定的标签(如 <bean>)来定义和配置 Spring Bean。这种方式被称为基于 XML 的配置。
优点:
- 配置文件独立于代码,可以在不重新编译代码的情况下进行更改。
- 在一些情况下,XML 配置可能更加直观。
适用场景:
- 喜欢使用 XML 配置的开发人员。
- 需要在不重新编译代码的情况下修改配置。
创建ClasspathXmlApplicationContext容器:
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-context.xml");时序图如下:
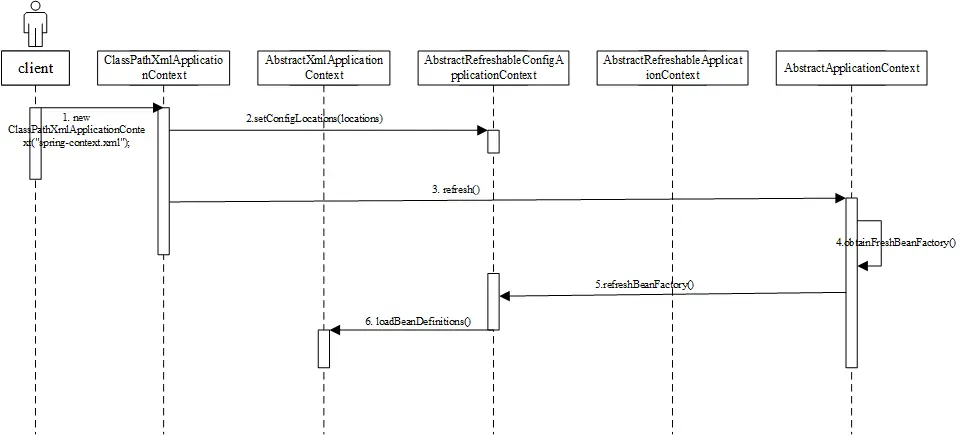
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(),初始化ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {
super(parent);
this.setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
this.refresh();
}
}调用AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext的setConfigLocations(configLocations),设置xml文件路径
public void setConfigLocations(String... locations) {
if (locations != null) {
Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null");
this.configLocations = new String[locations.length];
for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
this.configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim();
}
}
else {
this.configLocations = null;
}
}调用AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext的refresh(),其中obtainFreshBeanFactory方法,获取BeanFactory
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
this.refreshBeanFactory();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.getBeanFactory();
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Bean factory for " + this.getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}调用AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext的refreshBeanFactory方法
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
//创建BeanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}protected DefaultListableBeanFactory createBeanFactory() {
return new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory());
}调用AbstractXmlApplicationContext的loadBeanDefinitions方法,加载bean
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}加载bean主要是对配置文件的读取,并将配置中的bean读取到DefaultListableBeanFactory中。
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext是基于 Java 注解的配置的应用程序上下文实现。它允许你通过 Java 配置类来定义和注册 Spring Bean,而不是使用传统的 XML 配置文件。这种方式被称为基于 Java 的配置(JavaConfig)或者基于注解的配置。
通常,你会在一个或多个 Java 配置类中使用@Configuration注解来定义 Spring Bean,并在这些类中使用@Bean注解来标记方法,以声明要由 Spring 容器管理的 Bean。然后,你可以通过将这些配置类传递给 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext来创建应用程序上下文。
优点:
- 基于代码的配置更加类型安全,IDE 可以提供更好的支持。
- 避免了 XML 配置文件的编写和维护。
适用场景:
- 喜欢在 Java 代码中管理配置的开发人员。
- 希望利用 Java 的强类型特性来配置 Spring Bean。
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext加载bean的逻辑是在AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext的refreshBeanFactory()方法中,但是我们从类图中可以看出,AnnotationConfigApplicationContext并没有实现这个类,那么它是如何加载bean的呢?
创建AnnotationConfigApplicationContext容器:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);初始化
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
this();
register(annotatedClasses);
refresh();
}1)this()
private final AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader;
private final ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner;
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}无参构造函数中主要是初始化AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader和ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner两个类。这里主要关注AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader,跟踪这个类的初始化发现它会注册一堆BeanFactoryPostProcessor处理器,我们只需关注ConfigurationClassPostProcessor。
public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
//...
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// ...
}这个方法主要是把所有的配置类注册成bean。
3)refresh()
BeanFactoryPostProcessor处理器
和BeanPostProcessor原理一致,Spring提供了对BeanFactory进行操作的处理器BeanFactoryProcessor,简单来说就是获取容器BeanFactory,这样就可以在真正初始化bean之前对bean做一些处理操作。BeanFactoryProcessor定义如下:
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子类,也只要一个方法
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException;
}调用逻辑
AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()中调用了invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);这个方法逻辑如下:
- 遍历所有实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的bean
- 调用实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry
- 调用实现了Ordered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry
- 调用普通的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(没有实现Ordered接口和PriorityOrdered接口)的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry
- 遍历所有实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的bean,剩下的操作和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors的处理逻辑是一样的。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 按钮权限的设计及实现