谈谈Spring MVC执行流程之FrameworkServlet、DispatcherServlet分析
问题剖析:
- 一个请求url是怎么样找到Handler进行处理的?
- 拦截器为何preHandler顺序执行,postHandler就倒序执行呢?
- Spring MVC是怎么样去优雅的处理异常的?
- …...
请求处理流程:
了解之前,我们先宏观看看,一个请求达到Spring MVC,它的一个处理流程。
这里我首先贴上一张非常权威的流程图,也是Spring in Action这本书里提供的,springmvc的核心组件和请求处理流程:
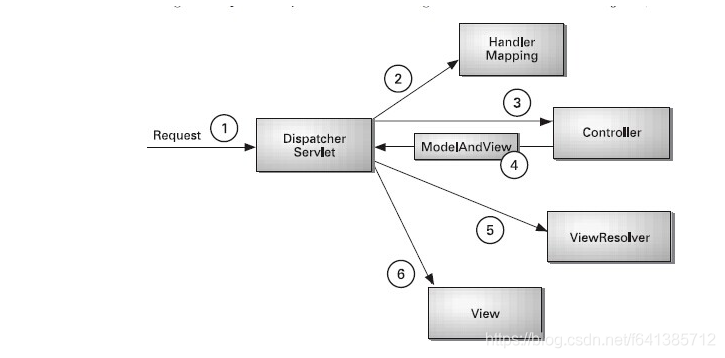
描述:
- DispatcherServlet是spring mvc中的前端控制器(front controller),负责接收request并将request转发给对应的处理组件。
- HanlerMapping是spring mvc中完成url到controller映射的组件。DispatcherServlet接收request,然后从HandlerMapping查找处理request的controller。
- Controller处理request,并返回ModelAndView对象,Controller是spring mvc中负责处理request的组件(类似于struts2中的Action),ModelAndView是封装结果视图的组件
- ④ ⑤ ⑥:视图解析器解析ModelAndView对象并返回对应的视图给客户端
下面这张图更能描述处理的一些细节:
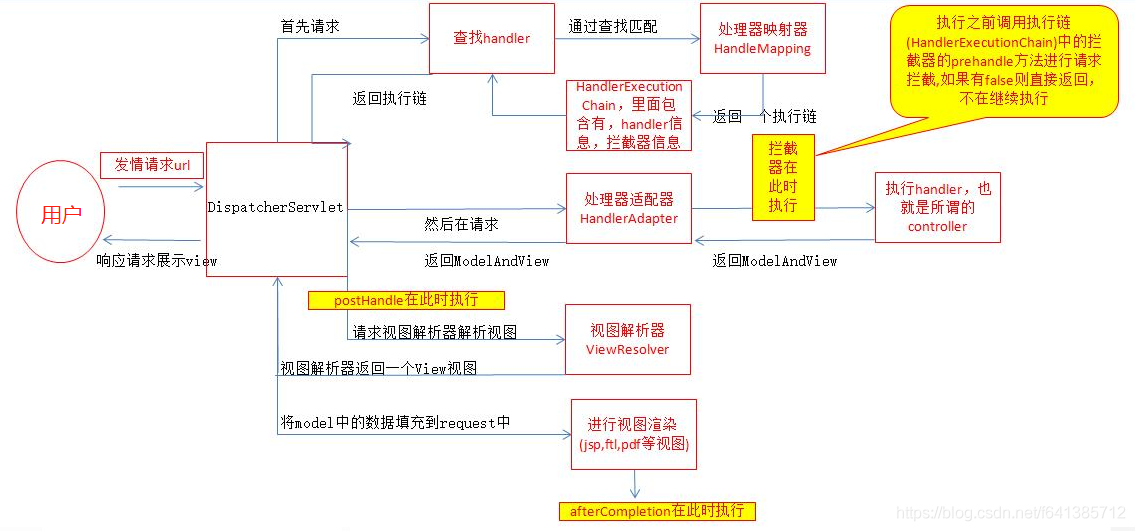
- 用户发送的所有请求(包括上传附件等任何请求),统一先交给DispatcherServlet
- 然后DispatcherServlet调用合适的HandlerMapping ,从而找到一个Handler(Controller中的方法以及拦截器),然后封装成HandlerExecutionChain返回给控制器DispatcherServlet
- 调用处理器适配器HandlerAdapter去执行handler(注意:执行之前需要先请求执行链中的拦截器的preHandle方法进行拦截,返回true就继续执行,返回false就不继续执行了)
- 处理器执行完后,返回给控制器DispatcherServlet一个ModelAndView(里面放有视图信息,模型数据信息)。 然后就执行postHandle方法
- 控制器调用视图解析器解析视图,根据逻辑名(xxxx/xxxx/xxxx.jsp)解析成真正的视图view(jsp,ftl等),然后返给控制器一个View
- 控制器开始渲染视图(视图渲染器可以是第三方或自己实现),然后将模型数据填充到request中。
- DispatcherServlet响应用户请求,展示jsp等视图信息
DispatcherServlet执行流程的源码分析
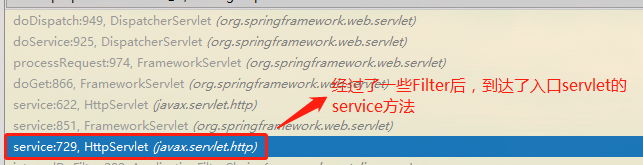
我们从调用栈可以很直接的看到调用关系。
FrameworkServlet复写了service方法如下:
/**
* Override the parent class implementation in order to intercept PATCH requests.
* 官方doc说得很清楚,复写是为了支持到PATCH请求(PATCH方法是新引入的,是对PUT方法的补充,用来对已知资源进行局部更新,目前使用得非常少,但SpringMVC也给与了支持)
* 备注:源生的servlet并不支持PATCH请求
*/
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());
if (httpMethod == HttpMethod.PATCH || httpMethod == null) {
processRequest(request, response);
}
else {
super.service(request, response);
}
}因为我们是get请求,所以我们重点只需要看看子类复写的doGet方法即可。但是猛的发现,FrameworkServlet复写所有的doGet/doPost等等都交给了processRequest(request, response);方法。
doOptions稍微有点特殊,它处理一些是否允许跨域的问题,TRACE请求:主要用于测试或诊断,可忽略
FrameworkServlet#processRequest方法解析
该方法作为FrameworkServlet的实现,其实也是提供了一些模版实现,最终会开口给子类的模版设计模式,在Spring源码中大量存在。此处我们关注点在于:FrameworkServlet为我们做了哪些事情(相对来说比较复杂点)~
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 记录抛出的异常~~~(若有的话)
Throwable failureCause = null;
//拿到之前的LocaleContext上下文(因为可能在Filter里已经设置过了)
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
// 以当前的request创建一个Local的上下文,后面会继续处理
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
// 这里面build逻辑注意:previousAttributes若为null,或者就是ServletRequestAttributes类型,那就new ServletRequestAttributes(request, response);
// 若不为null,就保持之前的绑定结果,不再做重复绑定了(尊重原创)
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
// 拿到异步管理器。这里是首次获取,会new WebAsyncManager(),然后放到request的attr里面
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
//这里需要注意:给异步上下文恒定注册了RequestBindingInterceptor这个拦截器(作用:绑定当前的request、response、local等)
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
//这句话很明显,就是吧request和Local上下文、RequestContext绑定
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
//模版设计模式:由子类DispatcherServlet去实现实际逻辑
doService(request, response);
} catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
} finally { //这个时候已经全部处理完成,视图已经渲染了
//doService()方法完成后,重置上下文,也就是解绑
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
//关键:不管执行成功与否,都会发布一个事件,说我处理了这个请求(有需要监听的,就可以监听这个事件了,每次请求都会有)
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}publishRequestHandledEvent()发布请求处理完后的事件
private void publishRequestHandledEvent(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
long startTime, @Nullable Throwable failureCause) {
//当publishEvents设置为true和 webApplicationContext 不为空就会处理这个事件的发布
if (this.publishEvents && this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// 计算出处理该请求花费的时间
long processingTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.webApplicationContext.publishEvent(
//ServletRequestHandledEvent这个事件:目前来说只有这里会发布
new ServletRequestHandledEvent(this,
request.getRequestURI(), request.getRemoteAddr(),
request.getMethod(), getServletConfig().getServletName(),
WebUtils.getSessionId(request), getUsernameForRequest(request),
processingTime, failureCause, response.getStatus()));
}
}下面我们来写个监听器,专门来监听这个事件:
/**
* 专门监听ServletRequestHandledEvent时间的监听器
*
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class ServletReqestHandledEventListener implements ApplicationListener<ServletRequestHandledEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ServletRequestHandledEvent event) {
//url=[/demowar_war/controller/hello]; client=[127.0.0.1]; method=[GET]; servlet=[dispatcher]; session=[null]; user=[null]; time=[143ms]; status=[OK]
log.info(event.getDescription());
log.info("返回状态码为:" + event.getStatusCode()); //返回状态码为:200
log.info("异常信息为:" + event.getFailureCause()); //异常信息为:null
log.info("处理请求耗时为:" + event.getProcessingTimeMillis()); //处理请求耗时为:143
log.info("事件源为:" + event.getSource()); //事件源为:org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet@3e7fadbb
}
}DispatcherServlet#doService方法解析
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// 如果该请求是include的请求(请求包含) 那么就把request域中的数据保存一份快照版本
// 等doDispatch结束之后,会把这个快照版本的数据覆盖到新的request里面去
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
// 说得很清楚,把一些常用对象放进请求域 方便Handler里面可以随意获取
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext()); //这个是web子容器哦
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
// 如果是重定向,放置得更多一些~~~~
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
try {
// DispatcherServlet最重要的方法,交给他去分发请求你、找到handler处理等等
doDispatch(request, response);
} finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
//如果是include请求 会上上面的数据快照,重新放置到request里面去
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}DispatcherServlet#doDispatch方法解析
首先根据请求的路径找到HandlerMethod(带有Method反射属性,也就是对应Controller中的方法),然后匹配路径对应的拦截器,有了HandlerMethod和拦截器构造个HandlerExecutionChain对象。
HandlerExecutionChain对象的获取是通过HandlerMapping接口提供的方法中得到的。
有了HandlerExecutionChain之后,通过HandlerAdapter对象进行处理得到ModelAndView对象,HandlerMethod内部handler的时候,使用了各种HandlerMethodArgumentResolver实现类来处理HandlerMethod的参数(非常重要),使用各种HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler实现类来处理返回值。 最终返回值被处理成ModelAndView对象,这期间发生的异常会被HandlerExceptionResolver接口实现类进行处理。
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// 此处用processedRequest 需要注意的是:若是处理上传,processedRequest 将和request不再指向同一对象
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
// 异常链处理器
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
//checkMultipart 这个方法很重要,判断是否是上传需求。且看下面的具体分析:::
//如果请求是POST请求,并且请求头中的Context-Type是以multipart/开头的就认为是文件上传的请求
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
// 标记一下:是否是文件上传的request了
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 找到一个处理器,如果没有找到对应的处理类的话,这里通常会返回404,如果throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound属性值为true的情况下会抛出异常
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// 根据实际的handler去找到一个合适的HandlerAdapter,方法详细逻辑同getHandler,因此不再解释
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// 如果是GET请求,如果内容没有变化的话,则直接返回
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 这段代码很有意思:执行处理器连里的拦截器们,具体参阅下面详细:
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// 真正执行我们自己书写的controller方法的逻辑。返回一个ModelAndView
// 这也是一个很复杂的过程(序列化、数据绑定等等),需要后面专题讲解
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
// 如果异步启动了,这里就先直接返回了,也就不会再执行拦截器PostHandle之类的
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
//意思是:如果我们没有设置viewName,就采用默认的。否则采用我们自己的
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 执行所有的拦截器的postHandle方法,并且把mv给他
// 这里有一个小细节:这个时候拦截器是【倒序】执行的
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
} catch (Exception ex) { // 这两个catcher什么都不做,只是把异常记录下来
dispatchException = ex;
} catch (Throwable err) {
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
//这个方法很重要,顾名思义,他是来处理结果的,渲染视图、处理异常等等的 下面详细分解
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}checkMultipart
multipartResolver 我们说过,值是有可能为null的(如果你没有配置对应的Bean的话)
//DispatcherServlet#doDispatch中的processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
protected HttpServletRequest checkMultipart(HttpServletRequest request) throws MultipartException {
// 配置了multipartResolver,并且是文件上传的请求 才会继续往下走
if (this.multipartResolver != null && this.multipartResolver.isMultipart(request)) {
// 如果该请求已经是MultipartHttpServletRequest 那就输出一个日志走人
if (WebUtils.getNativeRequest(request, MultipartHttpServletRequest.class) != null) {
logger.debug("日志。。。");
} else if (hasMultipartException(request) ) { // 判断是否有MultipartException 一般没有
logger.debug("Multipart resolution failed for current request before - " +
"skipping re-resolution for undisturbed error rendering");
} else {
try {
// 这里特别注意,不管是哪种multipartResolver的实现,内部都是new了一个新的MultipartHttpServletRequest的实现类,所以不再指向原来的request了,所以一定要注意
return this.multipartResolver.resolveMultipart(request);
} catch (MultipartException ex) {
if (request.getAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
logger.debug("Multipart resolution failed for error dispatch", ex);
// Keep processing error dispatch with regular request handle below
} else {
throw ex;
}
}
}
}
// If not returned before: return original request.
// 如果前面没有返回,就原样返回,相当于啥都不做
return request;
}这里需要注意的是:org.springframework.web.multipart.support.MultipartFilter,如果在web.xml中配置这个过滤器的话,则会在过滤器中提前判断是不是文件上传的请求,并将请求转换为MultipartHttpServletRequest类型。这个过滤器中默认使用的MultipartResolver为StandardServletMultipartResolver。
在CommonsMultipartResolver中有一个属性叫resolveLazily
private boolean resolveLazily = false;这个属性值代表是不是延迟解析文件上传,默认为false。最终返回的是一个DefaultMultipartHttpServletRequest的类。这里有一个重要的方法是:parseRequest,这个方法干的事是解析文件上传请求。它的底层是commons-fileupload那一套,不同的是Spring在获取FileItem之后,又进行了一下封装,封装为便于Spring框架整合。
getHandler
//DispatcherServlet#doDispatch中的mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
// 会把配置的所有的HandlerMapping 都拿出来查找,只要找到一个就返回
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(
"Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}SpringMVC默认加载三个请求处理映射类:RequestMappingHandlerMapping、SimpleUrlHandlerMapping、和BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping。
这三个类有一个共同的父类:AbstractHandlerMapping。在上面代码中hm.getHandler(request)这个getHandler方法在AbstractHandlerMapping中,它的子类都没有重写这个方法。因此我们还有必要去AbstractHandlerMapping这个类中看一下这个方法:
@Override
@Nullable
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 这个是留给子类去重写实现的:查找handler处理器的~ 比如根据URL去查找匹配等等
// 备注:获取hadnler的过程,非常的复杂,这个必须后面单独的专题再说吧
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
//构建出一个处理器链 注意:和handler绑定了,并且内部还去拿到了所有的拦截器,然后添加到处理器连里面去 getHandlerExecutionChain() 方法自己去看,可以看明白
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
//是不是cors请求,cors是跨域请求
if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.globalCorsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}HandlerExecutionChain#applyPreHandle
//DispatcherServlet#doDispatch中的mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)
boolean applyPreHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {
for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; i++) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
// 注意:如果是拦截器返回了false,就立马触发所有拦截器的AfterCompletion 方法。并且马上return false
if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, this.handler)) {
triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
return false;
}
this.interceptorIndex = i;
}
}
return true;
}processDispatchResult
//DispatcherServlet#doDispatch中的processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv,
@Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
//如果有异常,就进入异常处理逻辑,返回到异常页面
if (exception != null) {
// 含有异常页面视图的异常
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
} else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
//1、会执行所有的我们的自己配置(或者默认配置)了的HandlerExceptionResolver处理器
//2、上面需要注意了,但凡处理方法返回的不是null,有mv的返回。那后面的处理器就不会再进行处理了。具有短路的效果,一定要注意 是通过null来判断的
//3、处理完成后,得到error的视图mv,最后会设置一个viewName,然后返回出去
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
// 若视图不为空,不为null,就开始执行render()方法,开始渲染视图了
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
render(mv, request, response);
// 如果有错误视图,这里清除掉所有的请求域里的所有的错误属性
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
//处理异步=========我们发现,它不执行后面的AfterCompletion方法了,注意一下即可
if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Concurrent handling started during a forward
return;
}
// 执行拦截器的AfterCompletion 方法
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}至此,只剩一个视图渲染的方法:render()
//DispatcherServlet#processDispatchResult里面调用
protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// 通过localeResolver吧local解析出来,放到response里面去
Locale locale = (this.localeResolver != null ? this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request) : request.getLocale());
response.setLocale(locale);
//==================视图:关键中的关键==================
View view;
String viewName = mv.getViewName();
// 如果已经有viewName了(绝大多数情况)
if (viewName != null) {
// 视图解析器 根据String类型的名字,解析出来一个视图(视图解析器有多个)
// 还是那个原理:只要有一个返回了不为null的,后面的就不会再解析了
view = resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
// 如果解析不出来视图,那就抛出异常,说不能解析该视图
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name '" + mv.getViewName() +
"' in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
} else { //没有视图名称,但是必须有视图内容,否则抛出异常
view = mv.getView();
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " +
"View object in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
try {
//设置响应马 status
if (mv.getStatus() != null) {
response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value());
}
// 根据model里的数据,正式渲染(关于此部分逻辑,后续再说,也比较复杂)
view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw ex;
}
}至此,整个Spring MVC处理请求的一个过程算是结束了。
Spring MVC作为现在Java Web开发中实际的规范,大多数时候我们只需要着眼关注我们自己书写的Controller本身了,但是如果我们想做一些优雅处理:全局异常处理、数据绑定处理、序列化反序列化定制化处理等等,理解这些工作流程,现在就如有神助了。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 按钮权限的设计及实现