Servlet 3.0(不使用web.xml部署描述符,使用ServletContainerInitializer)整合SpringMVC
Servlet3.0是一次Java EE规范的一次重要升级,支持到可以全部采用注解驱动,大大简化了配置web.xml的麻烦。现在启动一个web容器并不强制依赖于web.xml部署描述符了。
最让我们印象深刻的是,之前我们在使用Spring MVC的时候,DispatcherServlet是必须要要在web.xml里配置,现在没有了这个,我们该怎么办呢?
创建一个maven工程
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.buqiong</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-study02</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.0.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
<version>1.18.4</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 记录log日志 logback-core并不需要显示导入-->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring MVC自动数据封装依赖的包 否则可能出现下面的错误,若使用@RequestBody的时候 -->
<!-- Content type 'application/json' not supported 当然还有其余配置,原理了解-->
<!-- 此处需要导入databind包即可, jackson-annotations、jackson-core都不需要显示自己的导入了-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.8</version>
</dependency>
<!-- fastjson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.57</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<!-- 该插件是为了没有web.xml情况下,打war包。编译不要报错 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.6</version>
<configuration>
<failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<!-- 编译环境在1.8编译 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.0</version>
<configuration>
<source>${java.version}</source>
<target>${java.version}</target>
<compilerVersion>${java.version}</compilerVersion>
<encoding>${project.build.sourceEncoding}</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<!--
directory:属性指定资源文件放置的目录。
includes:包含哪些配置文件(.class文件不用写)
filtering:如果设置为false的话,则表示上文的filters配置失效;如果设置为true,则会根据${env}.properties里面的键值对来
填充includes指定文件里的${xxxx}占位符(若不做环境区分,一般就是false即可)
-->
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
<include>**/*.tld</include>
</includes>
<filtering>false</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
</project>然后创建logback.xml一个最小配置:
<configuration scan="true" scanPeriod="60 seconds" debug="false">
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<root level="INFO">
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
</root>
</configuration>写一个最基本的Servlet,然后就可以访问了http://localhost:8888/study02/hello
/**
* @author buqiong
*/
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/hello")
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.getWriter().write("hello servlet...");
}
}我们发现,比之前采用web.xml配置的方式,省事太多了,真的非常方便。
ServletContainerInitializer
之前web容器要整合其余模块,都是通过web.xml来的。那么现在注解驱动的话,怎么做呢?
这就是Servlet3.0给我们提供的特别特别重要的一个类ServletContainerInitializer来整个其它模块组件。通过读Servlet3.0的官方文档如下:

大致可以看出如下意思,它有如下能力:
Shared libraries(共享库) / runtimes pluggability(运行时插件能力)
- Servlet容器启动会扫描,当前应用里面每一个jar包ServletContainerInitializer的实现
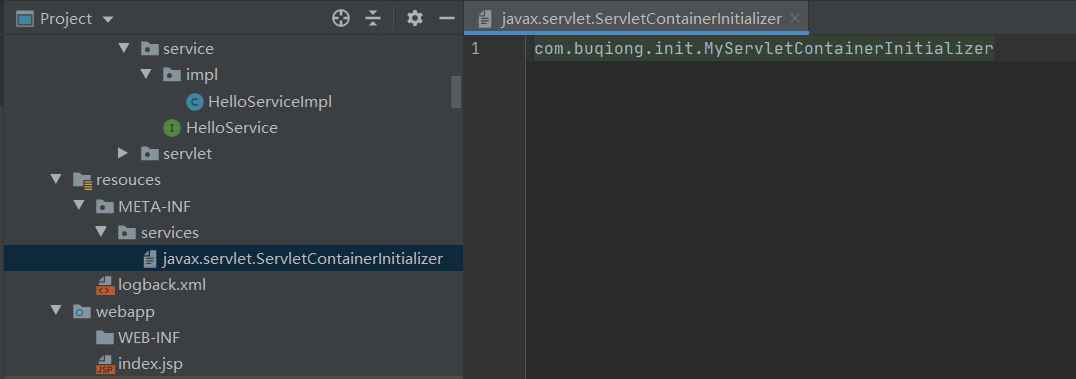
- coder可以自己提供ServletContainerInitializer的实现类;然后自己书写逻辑。但是要记住,一定要必须绑定在META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer这个文件里,文件内容为就是ServletContainerInitializer实现类的全类名;
这样web容器在启动的时候,就会执行该接口的实现方法,从而我们就可以书写我们自己的模块初始化的一些逻辑。

/**
* 容器启动的时候会将@HandlesTypes指定的这个类型下面的子类(实现类,子接口等)传递过来;
* @author buqiong
*/
@HandlesTypes(value = {HelloService.class})
public class MyServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
/**
* 应用启动的时候,会运行onStartup方法;
* @param c 感兴趣的类型的所有子类型;
* @param ctx 代表当前Web应用的ServletContext;一个Web应用一个ServletContext;
* @throws ServletException
*/
@Override
public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> c, ServletContext ctx) throws ServletException {
//这里的c会把所有我们感兴趣的类型都拿到
System.out.println("感兴趣的类型:");
for (Class<?> claz : c) {
System.out.println(claz);
}
//==========================编码形式注册三大组件============================
//注册组件 ServletRegistration
//ServletRegistration.Dynamic servlet = ctx.addServlet("userServlet", new UserServlet());
//配置servlet的映射信息
//servlet.addMapping("/user");
//注册Listener
//ctx.addListener(UserListener.class);
//注册Filter FilterRegistration
//FilterRegistration.Dynamic filter = ctx.addFilter("userFilter", UserFilter.class);
//配置Filter的映射信息
//filter.addMappingForUrlPatterns(EnumSet.of(DispatcherType.REQUEST), true, "/*");
}
}HelloService和实现类简单如下:
/**
* @author buqiong
*/
public interface HelloService {
String sayHello(String name);
}
/**
* @author buqiong
*/
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "hello " + name + "!";
}
}
启动容器,我们会看到:

把我们关心的接口子类型(包含子接口、抽象类、实现类)都放进来了。但是需要注意:不包含自己哦~
使用ServletContext注册Web组件(Servlet、Filter、Listener)
1)使用编码的方式,在项目启动的时候给ServletContext里面添加组件;
2)必须在项目启动的时候来添加(为了安全考虑,若已经启动完成再添加,是无效的)
ServletContainerInitializer得到的ServletContext;
ServletContextListener得到的ServletContext;
/ 不拦截.jsp。而/*都会拦截
DispatcherServlet映射:/
Filter映射:/*
Spring MVC拦截器的映射:/**
整合Spring MVC
整合Spring MVC是重中之重。前面已经说过ServletContainerInitializer了,相信大家能够想到Spring是怎么做的了吧?直接参照Spring官方文档先看看:
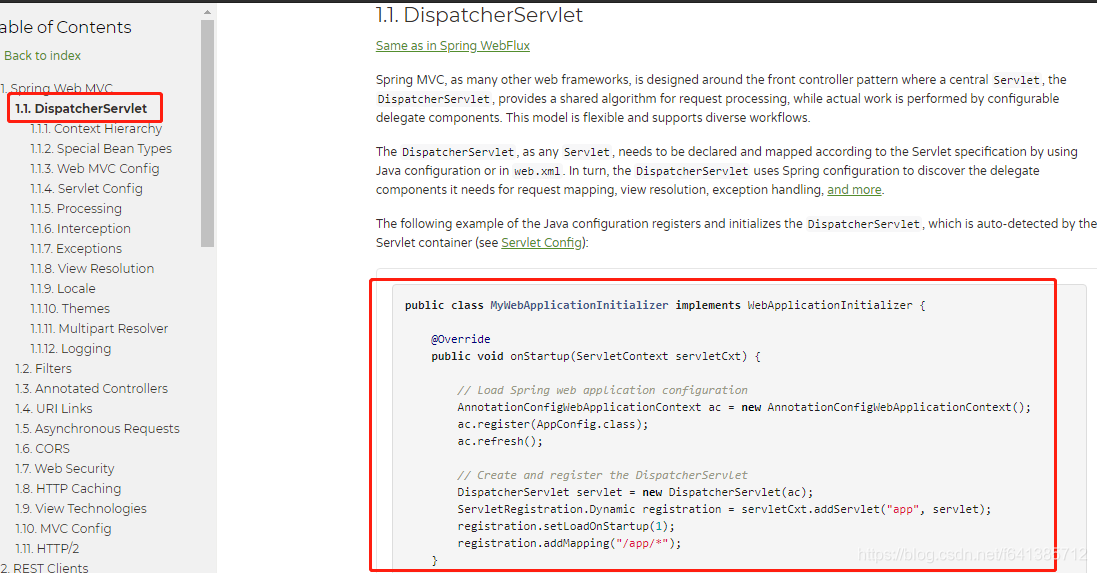
API 使用文档:https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/5.1.5.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/web.html#mvc-servlet
我们看看Spring-web包jar包内:
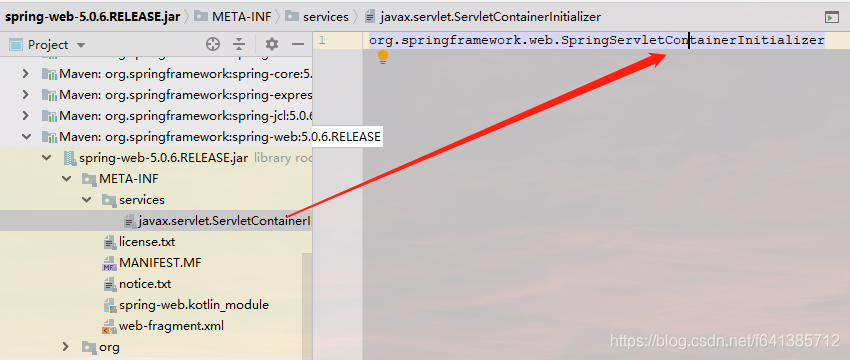
很显然的发现,Spring MVC也是通过这种方式和Servlet容器进行整合的。web容器在启动的时候,就会自动去加载org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer这个类。源码如下(它关心的是WebApplicationInitializer的子类们):
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(@Nullable Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException {
List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = new LinkedList<>();
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
for (Class<?> waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) {
// Be defensive: Some servlet containers provide us with invalid classes,
// no matter what @HandlesTypes says...
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) &&
WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer)
ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass).newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", ex);
}
}
}
}
if (initializers.isEmpty()) {
servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath");
return;
}
servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath");
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
}步骤分析:
(1) spring的应用一启动就会加载感兴趣的WebApplicationInitializer接口的下的所有组件;
(2) 为WebApplicationInitializer组件创建对象(组件不是接口,不是抽象类)
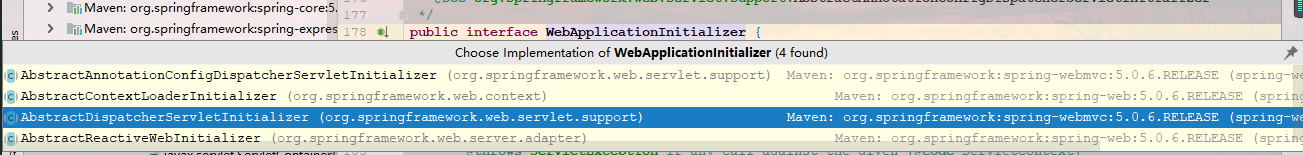
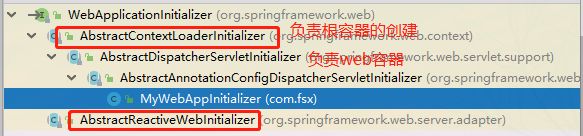
① AbstractContextLoaderInitializer:创建根容器;createRootApplicationContext();
② AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer:
- 创建一个web的ioc容器;createServletApplicationContext();
- 创建了DispatcherServlet;createDispatcherServlet();
- 将创建的DispatcherServlet添加到ServletContext中;
----------- 抽象方法:getServletMappings();
③ AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer:注解方式配置的DispatcherServlet初始化器(本文重点)
- 创建根容器:createRootApplicationContext()
- 创建web的ioc容器: createServletApplicationContext();
------------ 获取配置类;getServletConfigClasses();
说明:虽然父类只有两个abstract抽象方法要求子类必须实现。但是父类的设计都是可以扩展的,若你想定制化自己的需求,都是可以通过复写父类的protected的方式扩展的
比如:你想定制化自己的DispatcherServlet(父类默认值是单纯的new一下),那么你就可以通过复写createDispatcherServlet()去定制~。
Spring容器推荐使用父子容器的概念
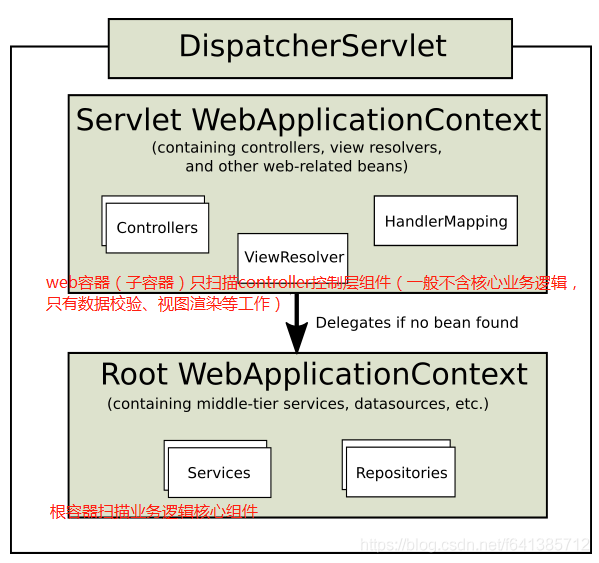
从上面分析得知,我们要使用注解驱动的话。只需要我们自己实现AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer这个抽象类就行了,这样web容器启动的时候就能处理我们实现的这个类的内容。示例如下(采用父子容器):
/**
* 此处@ControllerAdvice、RestControllerAdvice 这个注解不要忘了,属于Controller层处理全局异常的,应该交给web去扫描
* @author linhongwei
*/
@ComponentScan(value = "com.buqiong", excludeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, classes = {Controller.class, ControllerAdvice.class, RestControllerAdvice.class})
})
@Configuration
public class RootConfig {
}
/**
* 实际使用时,记得排除掉@Controller和@ControllerAdvice、@RestControllerAdvice,不要与RootConfig配置重复扫描
* @author buqiong
*/
@ComponentScan(value = "com.buqiong", useDefaultFilters = false,
includeFilters = {@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, classes = {Controller.class, ControllerAdvice.class, RestControllerAdvice.class})}
)
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
}1)@RestControllerAdvice是Spring4.3后提供的注解。@ControllerAdvice是Spring3.2提供的。它俩的区别就像@Controller和@RestController的区别。(也就是说@RestControllerAdvice可以省略@ResponseBody不用写了~~~)
2)useDefaultFilters默认值为true,表示默认情况下@Component、@Repository、@Service、@Controller都会扫描。useDefaultFilters=false加上includeFilters我们就可以只扫描指定的组件了,比如Spring MVC的web子容器只扫描Controller组件。excludeFilters的时候,就不需要去设置useDefaultFilters=false,这样子我们直接排除掉即可哟~
特别注意:useDefaultFilters的正确使用,不要造成重复扫描。否则很有可能造成事务不生效,并且你还非常不好定位这个错误。
然后我们自己来实现AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer的一个初始化实现类:
/**
* 自己实现 基于注解驱动的ServletInitializer来初始化DispatcherServlet
*/
public class MyWebAppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
/**
* 根容器的配置类;(Spring的配置文件) 父容器;
*/
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class<?>[]{RootConfig.class};
}
/**
* web容器的配置类(SpringMVC配置文件) 子容器;
*/
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class<?>[]{AppConfig.class};
}
//获取DispatcherServlet的映射信息
// 注意:
// /:拦截所有请求(包括静态资源(xx.js,xx.png)),但是不包括*.jsp;
// /*:拦截所有请求;连*.jsp页面都拦截;jsp页面是tomcat的jsp引擎解析的;
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"};
}
// 若你想定制化父类的一些默认行为 这里都是可以复写父类的protected方法的~~~~
// Spring MVC也推荐你这么干~
@Override
protected FrameworkServlet createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext servletAppContext) {
DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet = (DispatcherServlet) super.createDispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
// dispatcherServlet.setDetectAllHandlerAdapters(false);
return dispatcherServlet;
}
}我们写个测试类试试:
@Controller
public class HelloController {
/**
* 记得在实现类上添加@Service注解
*/
@Autowired
HelloService helloService;
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/sayHello")
public String sayHello() {
System.out.println(helloService); //com.buqiong.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl@3a29e4d
return "hello...";
}
}这样我们就可以正常访问controller的请求了。
web容器中的Spring的应用 一启动就会 加载感兴趣的WebApplicationInitializer接口的下的所有组件,并且为WebApplicationInitializer组件创建对象(组件不是接口,不是抽象类)。
特别注意的是:
按照上面的配置,我偶然的发现了,RootConfig仍然去扫描了我的controller,导致我的controller被扫描了两次,怎么回事呢?
找了好久,终于找到原因了,并不是@ComponentScan或者excludeFilters的问题,而是因为咱们在执行RootConfig的时候,虽然不去扫描Controller注解了,但是它会扫描AppConfig.java这个配置类,从而间接的又去扫描了@Controller了,因此最正确的做法应该如下:
/**
* 此处@ControllerAdvice、RestControllerAdvice 这个注解不要忘了,属于Controller层处理全局异常的,应该交给web去扫描
*
* @author linhongwei
*/
@ComponentScan(value = "com.buqiong", excludeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, classes = {Controller.class, ControllerAdvice.class, RestControllerAdvice.class}),
//排除掉web容器的配置文件,否则会重复扫描
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE, classes = {AppConfig.class})
})
@Configuration
public class RootConfig {
}这样子,我们的Controller就只会被扫描一次了,容器也就非常的干净了,强烈建议这么干。
当然,如果你还是当初xml的方式来做的,分别是两个配置文件下,只要不自己import之类,就不会出现此种问题~
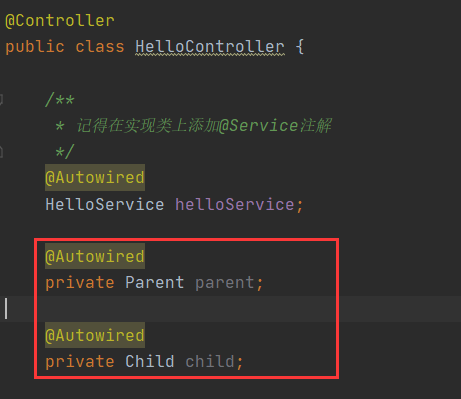
容器完全隔离后的好处是非常明显的,比如我们的web组件,就放在AppConfig里,其它的放在RootConfig里,不要什么都往RootConfig里面塞,比如如下:
//web子容器里注册一个Child
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public Child child() {
return new Child();
}
}
//父容器里注册一个Parent
public class RootConfig {
@Bean
public Parent parent() {
return new Parent();
}
}然后我们会发现在Controller层注入这两个Bean是正常的:
但是在Service层注入,启动的时候就会报错了
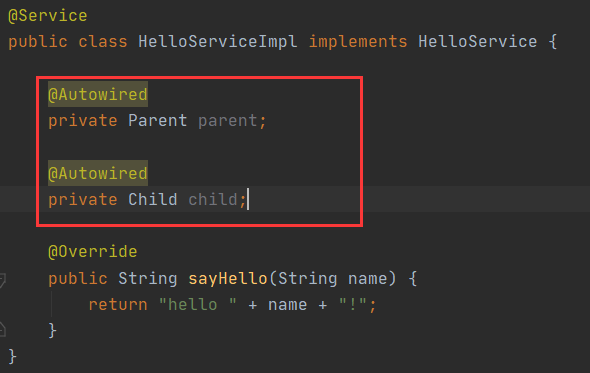
报错如下:

这里说个结论:
- 父子容器的关系跟内部类的关系一样。子容器能得到父容器的Bean,但是父容器得不到子容器的Bean
- 父子容器中,属性值都不是互通的。@Value注入的时候需要注意一下
定制Spring MVC
之前我们使用xml文件的时候,我们可以配置Spring MVC等相关选项。
比如视图解析器、视图映射、静态资源映射、拦截器。
1)首先,在配置文件里加上注解@EnableWebMvc:开启SpringMVC定制配置功能;
2)其次,实现WebMvcConfigurer接口。通过这个接口我们可以发现,里面有很多方法,但大多数情况下我们并不需要配置这么多项,因此Spring MVC也考虑到了这一点,提供给我们一个WebMvcConfigurerAdapter来extends就行,Adapter都是空实现~,这样我们需要配置什么,复写对应方法就行
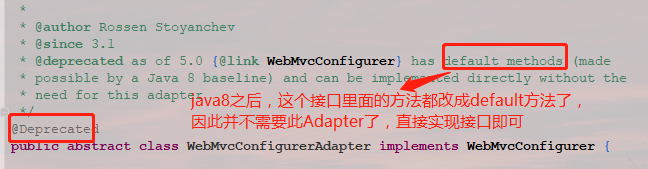
从以上可以看出,如果你的项目是构建在Spring5.0(基于java8)以上的,直接实现接口即可。不用再继承此Adapter了~
@EnableWebMvc
@Configuration //一定要说明这个文件是个配置文件
public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//视图解析器
@Override
public void configureViewResolvers(ViewResolverRegistry registry) {
//默认所有的页面都从 /WEB-INF/ xxx .jsp
//registry.jsp();
registry.jsp("/WEB-INF/views/", ".jsp");
}
// 开启静态资源的请求转发到默认servlet上,不配置页面报错404,(默认servlet不是DispatcherServlet!理解的)
@Override
public void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.enable();
}
//自定义添加拦截器=========这个比较常用
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
//registry.addInterceptor(new MyFirstInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**");
}
}这样我们就可以通过此配置文件,个性化定制我们的Spring MVC了。
Spring MVC中WebMvcConfigurerAdapter、WebMvcConfigurationSupport与WebMvcConfigurer
WebMvcConfigurationSupport与WebMvcConfigurer的关系
说结论:最佳实践还是继承WebMvcConfigurerAdapter(或直接实现接口WebMvcConfigurer),只不过要多加一个@EnableWebMvc注解而已。
若是SpringBoot环境,请不要加@EnableWebMvc注解,因为springboot已经实例化了WebMvcConfigurationSupport,如果添加了该注解,默认的WebMvcConfigurationSupport配置类是不会生效的。
HandlerInterceptor与WebRequestInterceptor的异同
WebRequestInterceptor间接实现了HandlerInterceptor,只是它们之间使用WebRequestHandlerInterceptorAdapter适配器类联系。
这两个Spring MVC的拦截器接口比较就简单了:
1)两个接口都可用于Controller层请求拦截,接口中定义的方法作用也是一样的。
2)WebRequestInterceptor的入参WebRequest是包装了HttpServletRequest 和HttpServletResponse的,通过WebRequest获取Request中的信息更简便直接。
3)WebRequestInterceptor的preHandle是没有返回值的,说明该方法中的逻辑并不影响后续的方法执行,所以这个接口实现就是为了获取Request中的信息,没有阻止请求的作用
4)HandlerInterceptor的功能更强大也更基础,可以在preHandle方法中就直接拒绝请求进入controller方法。
最佳实践:HandlerInterceptor能够实现所有WebRequestInterceptor做的事,更偏底层些。因此建议使用HandlerInterceptor。
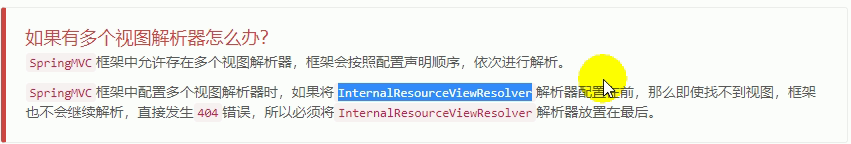
最后需要注意一点的是,关于自定义视图解析的自定义配置。此处还有一种方法是直接向容器里面注册Bean即可,如下:
//自定义一个视图解析器
@Bean
public ViewResolver viewResolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver resolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
resolver.setPrefix("WEB-INF/views/");
resolver.setSuffix(".html");
resolver.setExposeContextBeansAsAttributes(true);
return resolver;
}
Spring Boot环境下并不建议启用@EnableWebMvc。
Filter的执行顺序问题
在web.xml中,我们知道,执行顺序是谁在前边执行谁。但是现在没有这个web.xml了,怎么定这个执行顺序呢?
若是在Spring Boot环境,我们很好的确定Bean的执行顺序,我们可以用@Order注解:
@Bean
@Order(Integer.MAX_VALUE)也可以这样:
registration.setOrder(Integer.MAX_VALUE);Spring boot 会按照order值的大小,从小到大的顺序来依次过滤。也就是说,数字越小,越先执行
那么问题来了,现在我们只根据@WebFilter来排序Filter的执行顺序,怎么破呢?很多人曾经给出答案说没办法,是无序的。
其实不然,经过我的实践发现,servlet容器是根据Filter的类名按照自然顺序排序的。什么意思呢?比如我有两个Filter:UserLoginFilter和ApiLog。因为这两个文件的首字母A排U之前,所以每次都会限制性ApiLog。
那么我们就是想先要执行UserLoginFilter怎么办呢?这里有个小技巧,我们可以这么来写即可:
Filter0_UserLogin.java
Filter1_ApiLog.java完美。但是在Spring Boot环境下的话,还是用Order来控制更加优雅
总结
从Servlet3.0开始,Spring3.2开始,就推荐全部使用注解来驱动应用了。在当下流行的SpringBoot环境中,注解驱动可以说体现的淋漓尽致,完全摒弃了之前的xml配置文件,化简为繁。
关于启动Spring容器的说明
启动Spring容器有三种方式:spring容器启动的三种方式
需要说明的是:
若我们采用原始的方式,配置ContextLoaderListener监听器启动的时候会创建一个web容器,部分源代码如下:

可以看出,它配置的是一个Web容器。这样我们的Spring容器就启动了~
关于DispatchServlet的配置,只是让支持了Spring MVC的功能,能够分发请求了。
非Boot环境,如何用main方法启动Spring MVC的web上下文
我们知道我们自己new一个上下文也是ok的。但是如果我们要new一个web上下文呢?比如我想new一个AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(RootConfig.class);
System.out.println(applicationContext.containsBean("person")); // true
}这样Spring上下文就正常启动了。
请注意:若构造函数没有放入Config文件,而是后期自己register进去的,那么请手动refresh()。因为空构造函数式不会自动refresh的
那如果我想一个web环境呢?比如我想new一个 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext。首先我们看看该类源码:它只有一个的构造函数。 若我们模仿着这么做:
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext webApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
//webApplicationContext.setParent(applicationContext);
webApplicationContext.register(WebMvcConfig.class); // 注册上web环境的的配置类
webApplicationContext.refresh(); // 手动刷新
System.out.println(webApplicationContext.containsBean("helloController "));
}如果这样,你会看到报错:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: javax/servlet/ServletRequest没错。这属于Servlet的web组件,它一般都在tomcat等容器里面,我们maven自己导入一般也会规定为<scope>provided</scope>。
即使我们把scope去掉真的导入进来,再运行依然报错:
threw exception; nested exception is java.lang.IllegalStateException: No ServletContext set显然web容器的初始化,它是依赖于Servlet上下文的,而我们并没有初始化掉这个上下文,所以就报错了。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 按钮权限的设计及实现