【VUE】Vue 快速入门 笔记基础01
一、vue相关了解
1、概述
Vue.js是一种流行的JavaScript框架,用于构建响应式、交互式的前端Web界面。它采用了基于组件的开发模式,允许在单个页面中使用多个可重用的组件,提高了代码的复用性和维护性。
只关心视图层,自底向上.遵守SOC关注点分离原则(术有专攻,只关注一点) HTML + CSS + JS : 视图 : 给用户看,刷新后台给的数据 MVVM,是Model-View-ViewModel的简写,是M-V-VM三部分组成。它本质上就是MVC 的改进版。采用双向数据绑定,MVVM 就是将其中的View 的状态和行为抽象化
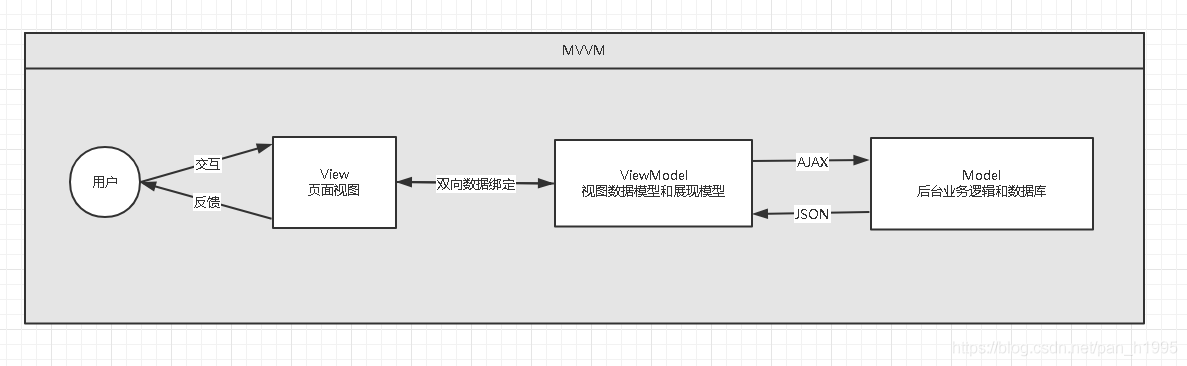
2、 MVVM
MVVM是什么?
MVVM(Model-View-ViewModel)是一种软件设计模式,由微软WPF(用于替代WinForm,以前就是用这个技术开发桌面应用程序的)和Silverlight(类似于Java Applet,简单点说就是在浏览器上运行WPF)的架构师Ken Cooper和Ted Peters开发,是一种简化用户界面的事件驱动编程方式。由John Gossman(同样也是WPF和Sliverlight的架构师)与2005年在他的博客上发表。
MVVM源自于经典的MVC(Model-View-Controller)模式。MVVM的核心是ViewModel层,负责转换Model中的数据对象来让数据变得更容易管理和使用。其作用如下:
该层向上与视图层进行双向数据绑定
向下与Model层通过接口请求进行数据交互
MVVM已经相当成熟了,主要运用但不仅仅在网络应用程序开发中。当下流行的MVVM框架有Vue.js,Anfular JS
Model 层: 对应数据层的域模型,它主要做域模型的同步。通过 Ajax/fetch 等 API 完成客户端和服务端业务 Model 的同 步。在层间关系⾥,它主要⽤于抽象出 ViewModel 中视图的 Model 。
View 层: 作为视图模板存在,在 MVVM ⾥,整个 View 是⼀个动态模板。除了定义结构、布局外,它展示的是 ViewModel 层的数据和状态。 View 层不负责处理状态, View 层做的是 数据绑定的声明、 指令的声明、 事件绑定的声明。
ViewModel 层: 把 View 需要的层数据暴露,并对 View 层的 数据绑定声明、 指令声明、 事件绑定声明 负责,也就是处理 View 层的具体业务逻辑。 ViewModel 底层会做好绑定属性的监听。当 ViewModel 中数据变化, View 层会得到更 新;⽽当 View 中声明了数据的双向绑定(通常是表单元素),框架也会监听 View 层(表单)值的变化。⼀旦值变 化,View 层绑定的 ViewModel 中的数据也会得到⾃动更新。
3、七大属性
el属性
用来指示Vue编译器从什么地方开始解析Vue的语法,可以说是一个占位符。
data属性
用来组织从view中抽象出来的属性,可以说将视图的数据抽象出来存放在data中。
methods属性
放置页面中的业务逻辑,js方法一般都放置在methods中
template属性
用来设置模板,会替换页面元素,包括占位符。
render属性
创建真正的virtual Dom 用js来渲染组件
computed属性
用来计算
watch属性
watch:funtion(new,old){}
监听data中的数据的变化
两个参数,一个返回新值,一个返回旧值
4、el:挂载点
- el挂载点的范围:命中元素及其子元素
- 可以id选择器"#“,可以类选择器”."
- 只能使用于双标签之上,不可以用于body,html标签。
二、vue代码示例
1、基础示例1
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 挂载元素 -->
<div id="app">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<ul>
<li>{{arr[0]}}</li>
<li>{{arr[1]}}</li>
<li>{{arr[2]}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<!-- <script src="lib/vue.js"></script> -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.7.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
//创建vue实例对象
var vm=new Vue({
el:'#app',
//data 对象就是需要渲染的数据
data:{
message:"hello,vue!",
arr:['内容1','内容2','内容3']
},
mounted() {
console.log(this.$el);
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>

2、v-once指令
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=`, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>v-once指令</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>此内容会岁数据变化自动更改{{ content }}</p>
<p v-once>此内容不会随数据变化自动化更改{{ content }}</p>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.7.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var vm=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
content:'内容文本'
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
3、 v-text指令
- 单引号与双引号都可用
- v-text是整体替换,{{}}是局部替换
- 标签优先级比局部替换{{}}要高,以标签优先。
- 里面可以用表达式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>v-text指令</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p v-text="100">这是p标签的原始内容</p>
<p v-text="content">这是p标签的原始内容</p>
<p v-text="content2"></p>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.7.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script> const vm=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
content:'内容文本',
content2:'<span>apan的内容 </span>',
}
})</script>
</body>
</html>
4、 v-html指令
v-text标签只会解析成文本
v-html会被解析为标签
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Vue 测试实例 </title>
<!--引入VUE-->
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue/2.7.0/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 绑定元素 -->
<div id="name1">
<p v-text="msg2"></p>
<p v-html="msg2"></p>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: '#name1', // 这里对应上面绑定的元素
data: { // 里面存放数据+
msg1: ' 111 ',
msg2: '<a href="https://www.baidu.com" >百度</a>'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
5、v-bind 设置元素的属性
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>v-bind指令</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p v-bind:title="myTitle">p标签的内容</p>
<p :title="myTitle">p标签的内容</p>
<p :class="`num`+1 + 2 + 3">p标签的内容</p>
<p :class="prefix + num "></p>
<p v-bind="attrObj">这是p标签的内容</p>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.7.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const vm=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
myTitle:'内容文本',
prefix:'demo',
num:10,
attrObj:{
id:'box',
title:'示例内容',
class:'clearFix',
'data-title':'这是data-title内容'
}
}
})</script>
</body>
</html>
6、v-bind style 绑定事件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>v-bind指令</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p v-bind:title="myTitle">p标签的内容</p>
<p :title="myTitle">p标签的内容</p>
<p :class="`num`+1 + 2 + 3">p标签的内容</p>
<p :class="prefix + num "></p>
<p v-bind="attrObj">这是p标签的内容</p>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.7.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const vm=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
myTitle:'内容文本',
prefix:'demo',
num:10,
attrObj:{
id:'box',
title:'示例内容',
class:'clearFix',
'data-title':'这是data-title内容'
}
}
})</script>
</body>
</html>
7、v-for 根据数据生成列表结构
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="item in arr">元素内容为:{{ item }}</li>
<li v-for="(item,index) in arr">元素内容为:{{ item }},索引为:{{ index }}</li>
<li v-for="(value,key,index) in obj">元素内容为:{{ value }},键为:{{ key }}索引为:{{ index }}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.7.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var vm= new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
arr:['a内容1','a内容2','a内容3'],
obj:{
content1:'b内容1',
content2:'b内容2',
content3:'b内容3'
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
8、v-if , v-else , v-else-if
v-if
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul v-if="true">
<li v-for="item in items">{{ item }}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.7.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var vm= new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
items:{
content1:'b内容1',
content2:'b内容2',
content3:'b内容3'
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
v-else
根据表达式真假切换元素显示状态
本质是操作dom元素
true使得元素存在于元素树,反之从dom树中移除
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:v-bind="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--view层,模板,开始数据绑定,v-if标签绑定data1-->
<div id="div1">
<button @click="fun1">点击按钮切换judge属性</button>
<!-- judge为ture为yes,不满足则为NO -->
<h1 v-if="judge">Yes</h1>
<h1 v-else>No</h1>
</div>
<!--1.导入Vue.js-->
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue/2.7.0/vue.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var vm = new Vue({
el: "#div1",
/*Model:数据*/
data: {
judge: true
},
methods: {
fun1:function(){
this.judge=!this.judge;
}
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
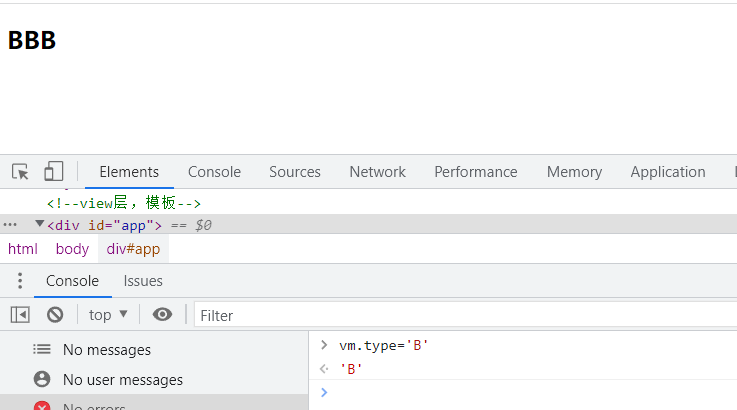
v-else-if
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:v-bind="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--view层,模板-->
<div id="app">
<h2 v-if="type==='A'">AAA</h2>
<h2 v-else-if="type==='B'">BBB</h2>
<h2 v-else-if="type==='C'">CCC</h2>
<h2 v-else>DDD</h2>
</div>
<!--1.导入Vue.js-->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.5.21/dist/vue.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
/*Model:数据*/
data: {
//这里的type代表通用的意思,不是DOM的ID绑定
type: 'A'
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
9、v-show指令
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p v-show="flase">标签内容1</p>
<p v-show="22 > 11">标签内容2</p>
<p v-show="bool">标签内容3</p>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.7.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var vm =new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
bool:true
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
本文来自博客园,作者:橘子偏爱橙子,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/xfbk/p/17454722.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号