java中的equals方法

public class TestEquals { public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 这里使用构造方法Cat()在堆内存里面new出了两只猫, * 这两只猫的color,weight,height都是一样的, * 但c1和c2却永远不会相等,这是因为c1和c2分别为堆内存里面两只猫的引用对象, * 里面装着可以找到这两只猫的地址,但由于两只猫在堆内存里面存储在两个不同的空间里面, * 所以c1和c2分别装着不同的地址,因此c1和c2永远不会相等。 */ Cat c1 = new Cat(1, 1, 1); Cat c2 = new Cat(1, 1, 1); System.out.println("c1==c2的结果是:"+(c1==c2));//false System.out.println("c1.equals(c2)的结果是:"+c1.equals(c2));//false } } class Cat { int color, weight, height; public Cat(int color, int weight, int height) { this.color = color; this.weight = weight; this.height = height; } }
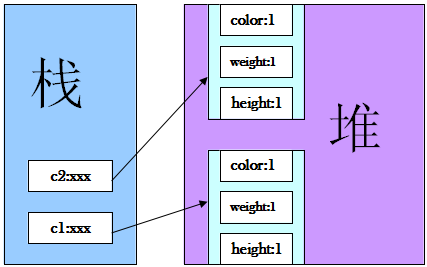
要想判断两个对象是否相等,不能通过比较两个对象的引用是否相等,这是永远都得不到相等的结果的,因为两个对象的引用永远不会相等,所以正确的比较方法是直接比较这两个对象,比较这两个对象的实质是不是一样的,即这两个对象里面的内容是不是相同的,通过比较这两个对象的属性值是否相同而决定这两个对象是否相等。
下面是eclipse自动生成的重写equals方法,重写的生成对象哈希值的方法。
this是一个引用,它指向自身的这个对象。
package equals; public class Cat { String name; int color; float weight; public Cat(String name, int color, float weight) { this.color = color; this.weight = weight; this.name = name; } //生成该对象的哈希值 //把对象的属性变换为数值然后相加(基本数据类型的数值,引用数据类型的hashCode) @Override public int hashCode() { final int prime = 31; int result = 1; result = prime * result + color; result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode()); result = prime * result + Float.floatToIntBits(weight); return result; } //重写equals方法,比较两个对象内容是否相等 @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj)//this是一个引用,它指向自身的这个对象,如果自身的引用和对比对象引用相等肯定同一个对象 return true; if (obj == null) return false; if (getClass() != obj.getClass())//如果两个对象的类对象不是同一个,肯定不同 return false; Cat other = (Cat) obj; if (color != other.color) return false; if (name == null) { if (other.name != null) return false; } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) return false; if (Float.floatToIntBits(weight) != Float.floatToIntBits(other.weight)) return false; return true; } }




