【JUC】阻塞队列&生产者和消费者
阻塞队列
线程1往阻塞队列添加元素【生产者】
线程2从阻塞队列取出元素【消费者】
当队列空时,获取元素的操作会被阻塞

当队列满时,添加元素的操作会被阻塞
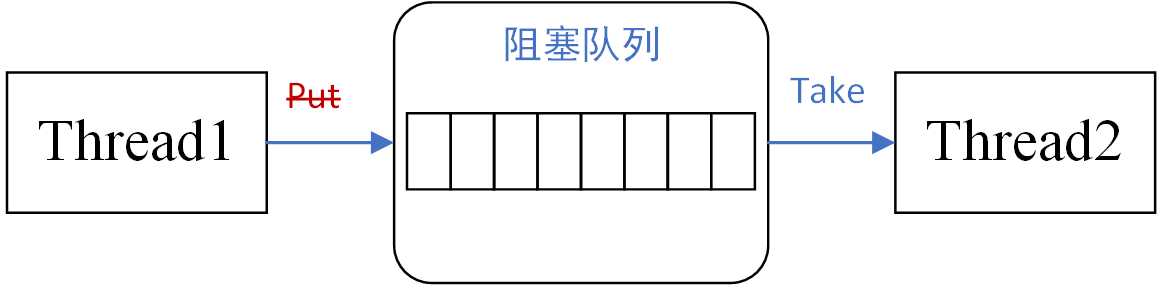
阻塞队列的优势:在多线程领域,发生阻塞时,线程被挂起,条件满足时,被挂起的线程自动被唤醒。使用阻塞队列,不需要关心什么时候需要阻塞线程(开发效率差,可能存在线程不安全的误操作),阻塞队列这种数据结构可以自动控制。
源码架构:BlockingQueue有多个实现类,下面列举7个常用的。
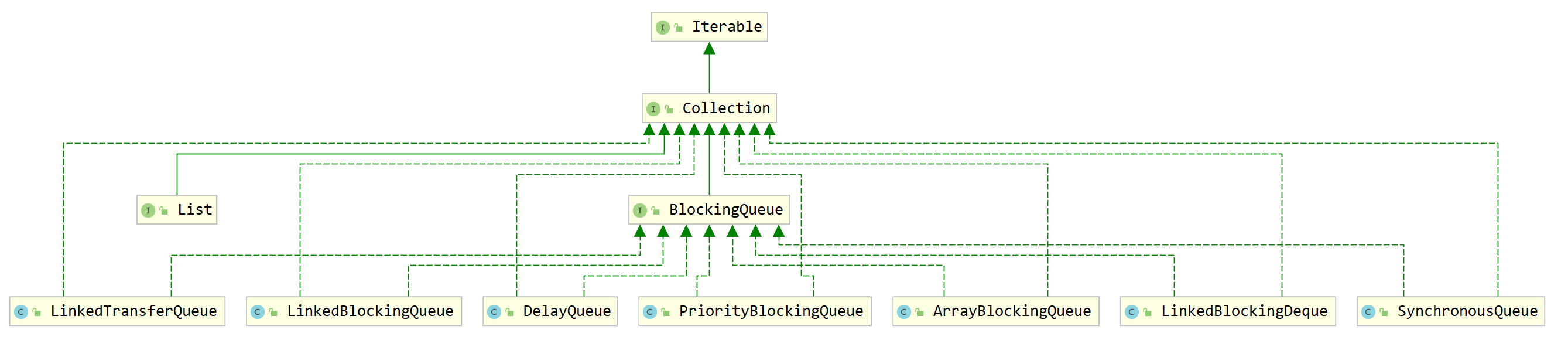
ArrayBlockingQueue:由数组组成的有界阻塞队列
LinkedBlockingQueue:由链表组成的有界阻塞队列(大小默认值为Integer.MAX_VALUE:2147483647)
PriorityBlockingQueue:支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列
DelayQueue:使用优先级队列实现的延迟无界阻塞队列
SynchronousQueue:不存储元素的阻塞队列,单个元素队列
LinkedTransferQueue:由链表组成的无界阻塞队列。
LinkedBlockingDeque:由链表组成的双向阻塞队列。
【线程池的底层就是标红的三个实现类实现的】
公共方法
| 抛出异常 | 特殊值 | 阻塞 | 超时 | |
| 插入 | add(e) | offer(e) | put(e) | offer(e,time,unit) |
| 移除 | remove(e) | poll(e) | take() | poll(time,unit) |
| 检查 | element() | peek() |
【抛出异常】
add方法:抛异常
1 import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; 2 import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; 3 4 public class BlockingQueueDemo { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);//参数是容量 7 System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("a")); 8 System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("b")); 9 System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("c")); 10 System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("d")); 11 } 12 }
输出结果:

true true true Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Queue full at java.util.AbstractQueue.add(AbstractQueue.java:98) at java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue.add(ArrayBlockingQueue.java:312) at day03CountDownLatch.BlockingQueueDemo.main(BlockingQueueDemo.java:13)
remove方法:抛异常
1 public class BlockingQueueDemo { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);//参数是容量 4 System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("a")); 5 System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove()); 6 System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove()); 7 } 8 }
输出:如果指定移除某元素,但是队列中不存在,不会抛异常,会返回false

true a Exception in thread "main" java.util.NoSuchElementException at java.util.AbstractQueue.remove(AbstractQueue.java:117) at day03CountDownLatch.BlockingQueueDemo.main(BlockingQueueDemo.java:12)
element方法:取出队首元素,如果为空返回异常:java.util.NoSuchElementException
【不抛异常 返回特定值】
offer方法:可以添加返回true,不可以添加返回false
poll方法:可以移除返回队首元素,并从队列移除,不可以移除返回null
peek方法:取出队首元素
【一直阻塞】
put方法:队满时,生产者线程往队列put元素,队列会一直阻塞生产线程直到可以put数据或响应中断退出。
take方法:队空时,消费者线程从队列取元素,队列会阻塞消费者线程直到队列可用。
【超时不候】
offer方法:定时阻塞,过时返回特殊值
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 2 BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2);//参数是容量 3 System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a",2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); 4 System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("b",2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); 5 System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("c",2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); 6 }
输出:

true true false
SynchronousQueue
SynchronousQueue没有容量,不存储元素。每一个put操作必须等待take操作,否则不能继续添加元素,反之亦然。产生一个,消费一个。
【比如:我想吃螺丝粉了(take),我才去做螺蛳粉(put);我不做螺蛳粉(put),我就不能吃螺蛳粉(take)】
1 public class BlockingQueueDemo { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 3 BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new SynchronousQueue<>(); 4 new Thread(()->{ 5 try { 6 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 做螺蛳粉1"); 7 blockingQueue.put("1"); 8 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 做螺蛳粉2"); 9 blockingQueue.put("2"); 10 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 做螺蛳粉3"); 11 blockingQueue.put("3"); 12 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 } 15 },"A").start(); 16 new Thread(()->{ 17 try { 18 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 19 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 吃螺蛳粉"+blockingQueue.take()); 20 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 21 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 吃螺蛳粉"+blockingQueue.take()); 22 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 23 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 吃螺蛳粉"+blockingQueue.take()); 24 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } 27 },"B").start(); 28 } 29 }
输出:如果线程B没有3个take,程序就会一直处于阻塞状态。

A 做螺蛳粉1
B 吃螺蛳粉1
A 做螺蛳粉2
B 吃螺蛳粉2
A 做螺蛳粉3
B 吃螺蛳粉3
生产者-消费者
高并发:线程操纵资源类。判断资源,生产者操作资源,唤醒通知消费者。严防多线程并发状态下的虚假唤醒。
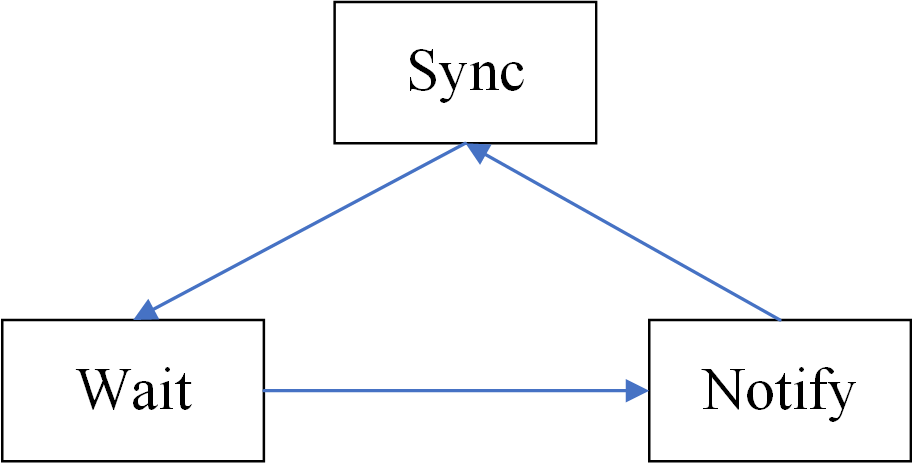
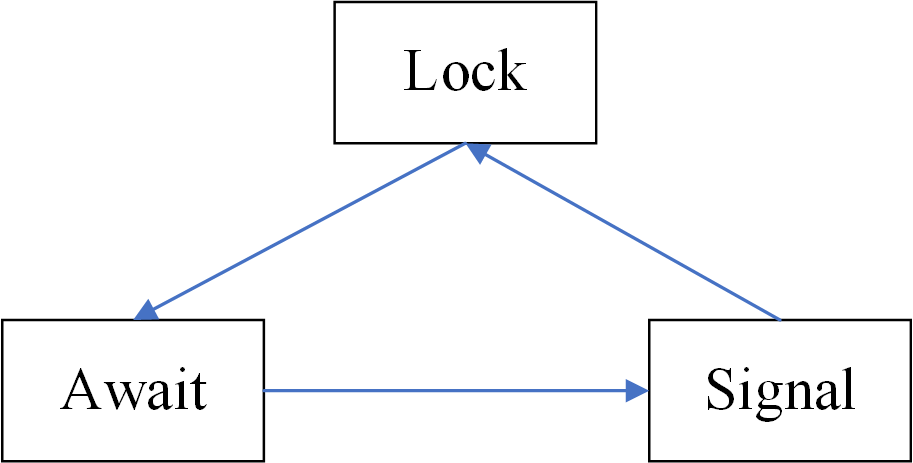
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; /** * 一个初始值为零的变量,两个线程对其交替操作,一个加1一个减1, */ class Cakes { private int cakeNumber = 0; private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); private Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); public void increment() throws InterruptedException { lock.lock(); try{ //判断 (多线程判断用while) while(cakeNumber != 0){ //等待 不能生产 condition.await(); } //进行操作(生产蛋糕) cakeNumber++; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"烹饪" + cakeNumber+"个蛋糕"); //通知唤醒 condition.signalAll(); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ lock.unlock(); } } public void decrement() throws InterruptedException { lock.lock(); try{ //判断 (多线程判断用while) while(cakeNumber ==0){ //等待 不能消费 condition.await(); } //进行操作 cakeNumber--; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"吃完蛋糕,还剩" + cakeNumber+"个蛋糕"); //通知唤醒 condition.signalAll(); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ lock.unlock(); } } } public class CakeShop { public static void main(String[] args) { Cakes shareData = new Cakes(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { try { shareData.increment(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } },"厨师").start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { try { shareData.decrement(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } },"顾客").start(); } }
输出结果:

厨师烹饪1个蛋糕
顾客吃完蛋糕,还剩0个
厨师烹饪1个蛋糕
顾客吃完蛋糕,还剩0个
厨师烹饪1个蛋糕
顾客吃完蛋糕,还剩0个
厨师烹饪1个蛋糕
顾客吃完蛋糕,还剩0个
厨师烹饪1个蛋糕
顾客吃完蛋糕,还剩0个
什么是虚假唤醒(spurious wakeup)?
-
在多核处理器下,pthread_cond_signal可能会激活多于一个线程(阻塞在条件变量上的线程)。所以,当一个线程调用pthread_cond_signal()后,多个调用pthread_cond_wait()或pthread_cond_timedwait()的线程返回。它们在没有被唤醒的情况下苏醒执行。
-
虽然虚假唤醒在pthread_cond_wait()函数中可以解决,为了发生概率很低的情况而降低边缘条件效率是不值得的,纠正这个问题会降低对所有基于它的所有更高级的同步操作的并发度。所以pthread_cond_wait()的实现上没有去解决它。
-
挂起等待条件变量来达到线程间同步通信的效果,而底层wait函数在设计之初为了不减慢条件变量操作的效率并没有去保证每次唤醒都是由notify触发,而是把这个任务交由上层应用去实现,即使用者需要定义一个while循环去判断是否条件真能满足程序继续运行的需求,当然这样的实现也可以避免因为设计缺陷导致程序异常唤醒的问题。
Condition的signal()和signalAll()的区别?
- signal 是随机解除一个等待集中的线程的阻塞状态;
- signalAll 是解除所有等待集中的线程的阻塞状态。
- signal 方法的效率会比 signalAll 高,但是它存在危险。因为它一次只解除一个线程的阻塞状态。如果等待集中有多个线程都满足了条件,也只能唤醒一个,其他的线程可能会导致死锁。
使用阻塞队列实现生产者和消费者
1 class CakeHouse { 2 private volatile boolean flag = true; 3 private AtomicInteger cakeNumber = new AtomicInteger(); 4 BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = null; 5 6 public CakeHouse(BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue) { 7 this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue; 8 System.out.println(blockingQueue.getClass().getName()); 9 } 10 11 public void closeDoor(){ 12 this.flag = false; 13 } 14 15 public void myProduct() throws InterruptedException { 16 String curCake = null; 17 boolean retValue; 18 while (flag){ 19 curCake = cakeNumber.incrementAndGet() + " "; 20 retValue = blockingQueue.offer(curCake, 2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 21 if(retValue){ 22 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":成功制作出"+"蛋糕"+curCake); 23 }else { 24 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":蛋糕"+curCake+"制作失败了"); 25 } 26 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 27 } 28 System.out.println("蛋糕店快要关门了~厨师停止烹饪~"); 29 } 30 31 public void myConsumer() throws InterruptedException { 32 String res = null; 33 while (flag){ 34 res = blockingQueue.poll(2L,TimeUnit.SECONDS); 35 if(null == res || res.equalsIgnoreCase("")){ 36 flag = false; 37 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"耐心不足,离开蛋糕店。"); 38 return; 39 } 40 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":我买到了蛋糕"+res); 41 System.out.println(); 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 public class ProdConsumerBlockQueue { 46 public static void main(String[] args) { 47 CakeHouse myResource = new CakeHouse(new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(5)); 48 new Thread(()->{ 49 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"开始烹饪了"); 50 try { 51 myResource.myProduct(); 52 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 53 e.printStackTrace(); 54 } 55 },"厨师").start(); 56 new Thread(()->{ 57 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"来店里消费了"); 58 try { 59 myResource.myConsumer(); 60 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 61 e.printStackTrace(); 62 } 63 },"顾客").start(); 64 try { 65 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); 66 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 67 e.printStackTrace(); 68 } 69 System.out.println("-------------------------------------"); 70 System.out.println("店主:下班时间到了!"); 71 myResource.closeDoor(); 72 } 73 }
输出结果:

java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue 厨师开始烹饪了 顾客来店里消费了 厨师:成功制作出蛋糕1 顾客:我买到了蛋糕1 厨师:成功制作出蛋糕2 顾客:我买到了蛋糕2 厨师:成功制作出蛋糕3 顾客:我买到了蛋糕3 厨师:成功制作出蛋糕4 顾客:我买到了蛋糕4 厨师:成功制作出蛋糕5 顾客:我买到了蛋糕5 ------------------------------------- 店主:下班时间到了! 蛋糕店快要关门了~厨师停止烹饪~ 顾客耐心不足,离开蛋糕店。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号