BZOJ3624: [Apio2008]免费道路
考虑到这 k 条0边中肯定是有一些边是必须要加的
而其他的0边是可以被其他边替代的,并不影响连通性
那首先要确定哪些0边是必要的0边
先拿所有1边做生成树,然后考虑加入0边
加入后会使联通块个数减少的0边就是必须要加的
不过还有以下特殊情况:
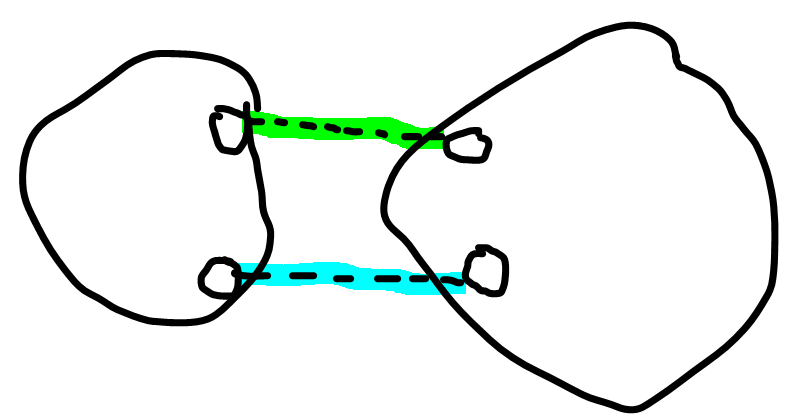
显然这两条边中只能找一条做为必要的边
那就找到了之后把它加进选入边集中就行
这时就会有一种不合法的情况,就是必需的边数 > k
之后把必需边加入的边先加进去
之后不断加入0边直到总共加入 k 条
这里又会出现不合法的情况,就是加不够 k 条
之后把所有1边加入就可以了
这里还会有一种不合法的情况,就是你建不出来一棵生成树
这样就可以过了
这题其实思路挺自然的,静下心来想肯定是会的
代码:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cctype>
#include <cstdio>
#include <locale>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 20005, MAXM = 100005;
struct EDGE {
int x, y, typ;
bool imp, intree;
}edge[MAXM];
int n, m, k, tot, blk;
int fa[MAXN];
inline int rd() {
register int x = 0, c = getchar();
while (!isdigit(c)) c = getchar();
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = x * 10 + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return x;
}
inline void resetfa() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) fa[i] = i;
}
int findfa(int x) {
return ((fa[x] == x) ? (x) : (fa[x] = findfa(fa[x])));
}
inline bool link(int x, int y) {
int fx = findfa(x), fy = findfa(y);
if (fx == fy) return false;
fa[fx] = fy;
return true;
}
inline bool stick(int x, int y) {
return (findfa(x) == findfa(y));
}
int main() {
n = rd(); m = rd(); k = rd();
resetfa();
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
edge[i].x = rd(); edge[i].y = rd();
edge[i].typ = rd();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) if (edge[i].typ) {
link(edge[i].x, edge[i].y);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) if (!edge[i].typ && !stick(edge[i].x, edge[i].y)) {
link(edge[i].x, edge[i].y);
edge[i].imp = true;
++tot;
}
if (tot > k) {
puts("no solution");
return 0;
}
resetfa();
blk = n;
tot = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) if (edge[i].imp) {
link(edge[i].x, edge[i].y);
++tot;
--blk;
edge[i].intree = true;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m && tot < k; ++i) if (!edge[i].typ && !edge[i].imp) {
if (link(edge[i].x, edge[i].y)) {
++tot;
--blk;
edge[i].intree = true;
}
}
if (tot < k) {
puts("no solution");
return 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m && blk != 1; ++i) if (edge[i].typ) {
if (link(edge[i]. x, edge[i].y)) {
--blk;
edge[i].intree = true;
}
}
if (blk != 1) {
puts("no solution");
return 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) if (edge[i].intree) {
printf("%d %d %d\n", edge[i].x, edge[i].y, edge[i].typ);
}
return 0;
}
禁止诸如开发者知识库/布布扣/码迷/学步园/马开东等 copy 他人博文乃至博客的网站转载
,用户转载请注明出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/xcysblog/


