BZOJ1117: [POI2009]救火站Gas
看到这道题感觉跟 BZOJ2525 和 BZOJ1217 很像
其实他真的很像
不过这题有了对于个数的限制,或许要用 dp ?
看一眼数据范围,n <= 1e5, k <= 20
所以用数组完全可以记录下完整的信息
那到底是 dp 还是贪心呢?
参考 BZOJ2525 的 check 函数 或 BZOJ1217 整道题的算法流程,感觉是可以贪心的
就是 dfs 贪心,每个节点 O(k) 的转移一下信息,O(nk) 的复杂度可以接受
但多了个数的限制贪心还合理吗?
答案是肯定的,我们尝试找一种贪心策略
以下称每个救火站的 s 个贡献为 “贡献”
显然,贪心策略一定是要基于 "当前子树中有即将超过距离限制的点时就加一个救火站" 的
那么接下来要考虑的是如果加多了怎么办
如果画图,可能会有助于理解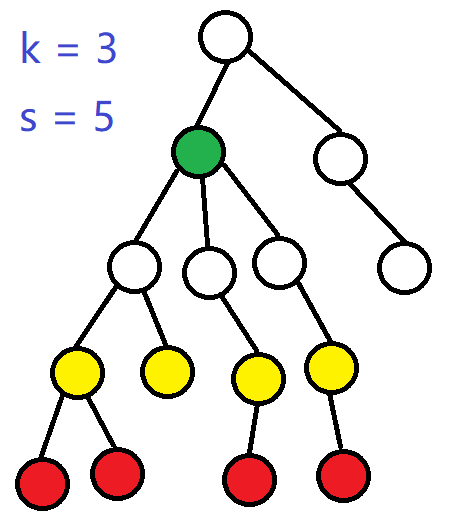
上面的情况只要 s > 4 即可
当前 dfs 回溯到了绿点,则红点必须在这一层 dfs 中被完全覆盖
那么多出的 (s - sumred) 个贡献就是我们要决策的那剩余贡献
考虑向上回溯一层后,黄点会变为红点,
而对于回溯后到达的点来说,绿点的贡献已经不能到达新的红点
那么这时候就应该在上一层 dfs 中更新一些黄点
同时,有一个显然的性质:绿点的贡献越向上回溯作用越小
所以如果在刚才的一层 dfs 中不去覆盖黄点的话,
在当前的 dfs 会不得不新设一些绿点,
而如果刚才覆盖了黄点,那现在这一层不一定会多设立绿点
那现在贪心的策略就很显然了,
对于每一堆 管辖距离dst 相同的贡献,我们只更新未覆盖点中距离为 dfs 和 dst - 1 的
之后就可以做这道题了
胡乱 yy 一发觉得会有类似菊花图一样的东西来使某子树中的总剩余贡献爆 int
所以开 long long
如果对于根节点写了特判注意中间变量的 long long
我怕出一些奇怪的锅所以写了特判,所以一直WA...
特判的流程就是用根节点的剩余可用贡献的后缀和去更新未覆盖节点
其实和 dfs 中的操作是一样的,所以也可以不写特判改一下 dfs
写特判的代码:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 100005, MAXD = 25;
struct EDGE{
int nxt, to;
EDGE(int NXT = 0, int TO = 0) {nxt = NXT; to = TO;}
}edge[MAXN << 1];
int n, s, k, totedge;
int head[MAXN], fur[MAXN][MAXD];
ll ans, rem[MAXN][MAXD];
inline int rd() {
register int x = 0;
register char c = getchar();
while (!isdigit(c)) c = getchar();
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = x * 10 + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return x;
}
inline void add(int x, int y) {
edge[++totedge] = EDGE(head[x], y);
head[x] = totedge;
edge[++totedge] = EDGE(head[y], x);
head[y] = totedge;
return;
}
void dfs(int x, int frm) {
fur[x][0] = 1;
for (int i = head[x]; i; i = edge[i].nxt) if (edge[i].to != frm) {
int y = edge[i].to;
dfs(y, x);
for (int j = 1; j <= k; ++j) {
fur[x][j] += fur[y][j - 1];
rem[x][j - 1] += rem[y][j];
}
}
int tmp = 0;
if (fur[x][k]) {
tmp = (fur[x][k] + s - 1) / s;
ans += tmp;
rem[x][k] += tmp * s - fur[x][k];
fur[x][k] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= k; ++i) if (rem[x][i]) {
for (int j = i; j >= max(i - 1, 0); --j) if (fur[x][j]) {
if (rem[x][i] >= fur[x][j]) {
rem[x][i] -= fur[x][j];
fur[x][j] = 0;
} else {
fur[x][j] -= rem[x][i];
rem[x][i] = 0;
}
}
}
return;
}
int main() {
n = rd(); s = rd(); k = rd();
register int xx, yy;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
xx = rd(); yy = rd();
add(xx, yy);
}
dfs(1, 0);
ll tot = 0ll;
for (int i = k; i >= 0; --i) {
tot += rem[1][i];
if (tot >= fur[1][i]) {
tot -= fur[1][i];
fur[1][i] = 0;
} else {
fur[1][i] -= tot;
tot = 0;
}
}
tot = 0ll;
for (int i = k; i >= 0; --i) tot += fur[1][i];
ans += (tot + s - 1) / s;
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}
不写特判的代码:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 100005, MAXD = 25;
struct EDGE{
int nxt, to;
EDGE(int NXT = 0, int TO = 0) {nxt = NXT; to = TO;}
}edge[MAXN << 1];
int n, s, k, totedge;
int head[MAXN], fur[MAXN][MAXD];
ll ans, rem[MAXN][MAXD];
inline int rd() {
register int x = 0;
register char c = getchar();
while (!isdigit(c)) c = getchar();
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = x * 10 + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return x;
}
inline void add(int x, int y) {
edge[++totedge] = EDGE(head[x], y);
head[x] = totedge;
edge[++totedge] = EDGE(head[y], x);
head[y] = totedge;
return;
}
void dfs(int x, int frm) {
fur[x][0] = 1;
for (int i = head[x]; i; i = edge[i].nxt) if (edge[i].to != frm) {
int y = edge[i].to;
dfs(y, x);
for (int j = 1; j <= k; ++j) {
fur[x][j] += fur[y][j - 1];
rem[x][j - 1] += rem[y][j];
}
}
int tmp = 0;
if (fur[x][k]) {
tmp = (fur[x][k] + s - 1) / s;
ans += tmp;
rem[x][k] += tmp * s - fur[x][k];
fur[x][k] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= k; ++i) if (rem[x][i]) {
for (int j = i; j >= 0 && (j >= i - 1 || x == 1); --j) if (fur[x][j]) {
if (rem[x][i] >= fur[x][j]) {
rem[x][i] -= fur[x][j];
fur[x][j] = 0;
} else {
fur[x][j] -= rem[x][i];
rem[x][i] = 0;
}
}
}
return;
}
int main() {
n = rd(); s = rd(); k = rd();
register int xx, yy;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
xx = rd(); yy = rd();
add(xx, yy);
}
dfs(1, 0);
ll tot = 0ll;
for (int i = k; i >= 0; --i) tot += fur[1][i];
ans += (tot + s - 1) / s;
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}


