Splay学习笔记
前置知识
二叉搜索树
一种二叉树的树形数据结构,其定义如下:
-
左子树上的所有节点的权值均小于其根节点的权值
-
右子树上的所有节点的权值均大于其根节点的权值
-
二叉搜索树的左右子树均为二叉搜索树
Splay
简介
一种自平衡二叉搜索树,通过不断将某个节点旋转到根节点,使得整棵树仍然满足二叉查找树的性质,且保持平衡而不至于退化为链
维护的信息
| \(root\) | \(tot\) | \(fa[i]\) | \(child[i][0/1]\) | \(val[i]\) | \(cnt[i]\) | \(size[i]\) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根节点 | 节点总数 | 父亲 | 左右儿子 | 点权 | 出现次数 | 子树大小 |
基本操作
-
\(update(x)\) 更新\(x\)节点的\(size\)
-
\(clear(x)\) 摧毁节点\(x\)
-
\(get(x)\) 判断\(x\)是其父亲的左儿子还是右儿子
\(code\)
void clear(int x){child[x][0] = child[x][1] = size[x] = fa[x] = val[x] = 0;}
void update(int x){if(!x) return; size[x] = size[child[x][0]]+size[child[x][1]]+1;}
int get(int x){return x==child[fa[x]][1];}
-
旋转
为调换\(Splay\)中父子节点的位置,我们使用旋转操作,将一个节点向上移动一个位置,并保证:
-
整棵\(Splay\)的中序遍历不变
-
受影响的节点维护的信息依然正确有效
-
\(root\)必须指向旋转后的根节点
具体步骤
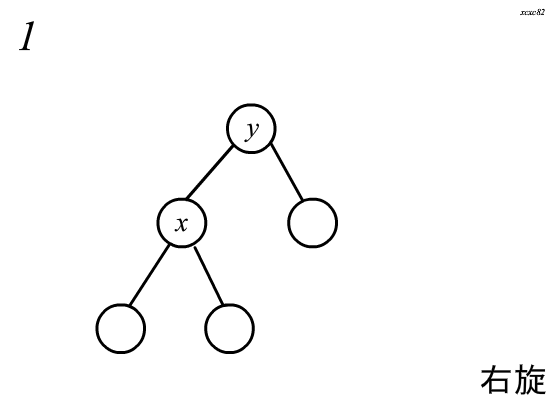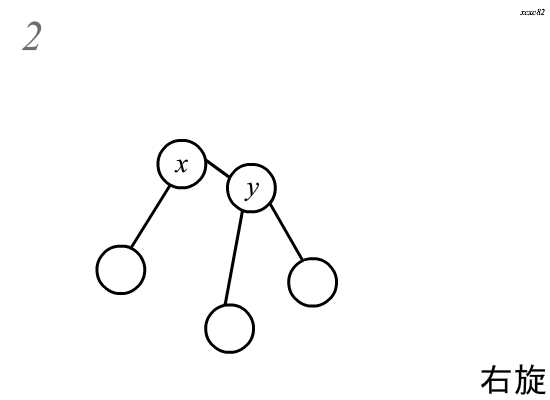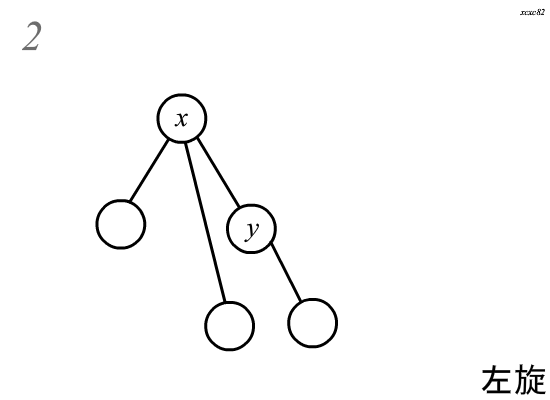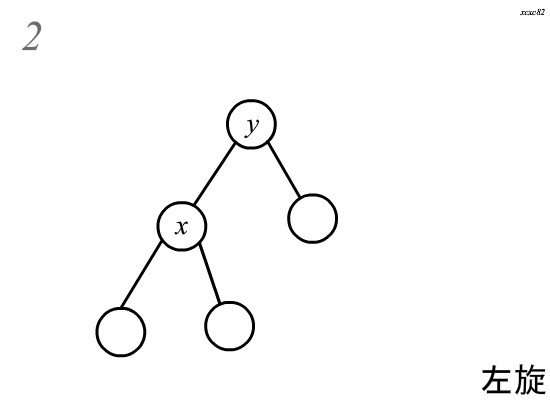
\(Splay\)中的旋转分为两种,左旋和右旋,这里以右旋为例:
旋转分为四个步骤\(:\)
(假设需要旋转的节点为\(x\),其父亲为\(y\))
\(1.\)将\(y\)的左儿子指向\(x\)的右儿子,且\(x\)的右儿子的父亲指向\(y\)
child[y][0] = child[x][1];
fa[child[x][1]] = y;
\(2.\)将\(x\)的右儿子指向\(y\),且\(y\)的父亲指向\(x\)
child[x][1] = y;
fa[y] = x;
\(3.\)如果\(y\)还有父亲\(z\),将\(y\)原来在\(z\)中所在的位置指向\(x\),且\(x\)的父亲指向\(y\)
fa[x] = z;
child[z][y==child[z][1]] = x;
\(4.\)更新\(x\)和\(y\)的\(size\)
\(code\)
void rotate(int x){
int y = fa[x],z=fa[y];
int chy = get(x),chx = chy^1;
child[y][chy] = child[x][chx];
fa[child[x][chx]] = y;
child[x][chx] = y;
fa[y] = x;
fa[x] = z;
if(z) child[z][y==child[z][1]] = x;
update(y),update(x);
}
-
\(Splay\)操作
\(Splay\)规定,每访问一个节点后,都要强制将该节点旋转到根的位置
具体步骤
为保证不退化成链,\(Splay\)操作一共分三步
\(1.\)如果父节点为目标位置,则向上旋转
\(2.\)如果当前节点与父节点的“关系”和父节点与祖父节点的“关系”相同,则先旋转父节点,再旋转自身
\(3.\)如果不满足以上条件,则将自身连续旋转两次
重复以上操作,直到旋转到根
\(code\)
void splay(int x,int goal){
for (int f; (f=fa[x])!=goal; rotate(x)){
if (fa[f]!=goal) rotate(get(x)==get(f)?f:x);
}
if (!goal) root=x;
}
-
插入
设插入的值为\(k\)
- 若树为空树,直接插入根
if(!root){
val[++tot] = k;
cnt[tot]++;
root = tot;
update(root);
return;
}
- 否则,根据二叉搜索树的性质向下查找,直到查找到权值等于\(k\)的节点或空节点
同时需要将该节点\(Splay\)到根的位置
int now = root,f = 0;
while(1){
if(val[now]==k){
cnt[now]++;
update(now);
update(f);
Splay(now);
break;
}
f = now;
now = child[now][val[now]<k];
if(!now){
val[++tot] = k;
cnt[tot]++;
fa[tot] = f;
child[f][val[f]<k] = tot;
update(tot);
update(f);
Splay(tot);
break;
}
}
-
排名
-
查询给定值的排名
设\(x\)为需要查询的值
根据二叉搜索树的性质:
-
若\(x\)比当前节点的权值小,向左子树查找
-
若\(x\)比当前节点的权值大,将答案\(ans\)加上左子树的\(size\)和当前节点\(cnt\)的大小,向其右子树查找。
-
若\(x\)与当前节点的权值相同,返回\(ans+1\)
\(code\)
int rank(int k){
int ans = 0,now = root;
while(1){
if(k<val[now]) now = child[now][0];
else{
ans+=size[child[now][0]];
if(k==val[now]){
Splay(now);
return ans+1;
}
ans+=cnt[now];
now = child[now][1];
}
}
}
-
查询给定排名的值
设\(k\)为剩余排名,根据二叉搜索树的性质:
-
若\(k\)小于左子树的\(size\)且左子树非空,向左子树查找
-
否则将\(k\)减去左子树的大小和根的\(cnt\)
若此时\(k\)的值小于等于\(0\),返回根节点的权值
否则继续向右子树查找
\(code\)
int kth(int k){
int now = root;
while(1){
if(child[now][0]&&k<=size[child[now][0]]){
now = child[now][0];
}
else{
k-=cnt[now]+size[child[now][0]];
if(k<=0){
Splay(now);
return val[now];
}
now = child[now][1];
}
}
}
-
前驱&&后继
一个数的前驱定义为小于\(x\)的最大的数
后继定义为大于\(x\)的最小的数
显然,一个数的前驱是其左子树中最靠右的节点,后继是其右子树的最靠左的节点
将\(x\)旋转到根后查询即可
\(code\)
int pre(){
int now = child[root][0];
while(child[now][1]) now = child[now][1];
return now;
}
int next(){
int now = child[root][1];
while(child[now][0]) now = child[now][0];
return now;
}
-
删除操作
首先将要删除的节点\(x\)旋转到根的位置
- 如果有不止一个\(x\),那么直接将\(cnt[x]\)减\(1\)即可
否则
-
若没有儿子节点,直接将当前节点清空
-
若只有一个儿子,清空当前节点,再把根节点跟新为儿子
-
若有两个儿子,先将\(x\)的前驱旋转到根,并将\(x\)的右子树连接到\(x\)的前驱上
\(code\)
void del(int k){
rank(k);
if(cnt[root]>1){
cnt[root]--;
update(root);
return;
}
if(!child[root][0]&&!child[root][1]){
clear(root);
root = 0;
return;
}
if(!child[root][0]){
int now = root;
root = child[root][1];
fa[root] = 0;
clear(now);
return;
}
if(!child[root][1]){
int now = root;
root = child[root][0];
fa[root] = 0;
clear(now);
return;
}
int now = root,x = pre();
fa[child[now][1]] = x;
child[x][1] = child[now][1];
clear(now);
update(root);
}
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 100005;
int child[MAXN][2],size[MAXN],root,tot,fa[MAXN],val[MAXN],cnt[MAXN];
#define ci(Q) scanf("%d",&Q)
struct splay{
void update(int x){size[x] = size[child[x][0]]+size[child[x][1]]+cnt[x];}
bool pd(int x){return x==child[fa[x]][1];}
void clear(int x){fa[x] = child[x][0] = child[x][1] = size[x] = val[x] = cnt[x] = 0;}
void rotate(int x){
int y = fa[x] , z = fa[y];
int chy = pd(x) ,chx = chy^1;
child[y][chy] = child[x][chx];
fa[child[x][chx]] = y;
child[x][chx] = y,fa[y] = x,fa[x] = z;
if(z) child[z][y==child[z][1]] = x;
update(x),update(y);
}
void Splay(int x){
for(int f = fa[x];f=fa[x],f;rotate(x)){
if(fa[f]) rotate(pd(x)==pd(f)?f:x);
}
root = x;
}
void insert(int k){
if(!root){
val[++tot] = k;
cnt[tot]++;
root = tot;
update(root);
return;
}
int now = root,f = 0;
while(1){
if(val[now]==k){
cnt[now]++;
update(now);
update(f);
Splay(now);
break;
}
f = now;
now = child[now][val[now]<k];
if(!now){
val[++tot] = k;
cnt[tot]++;
fa[tot] = f;
child[f][val[f]<k] = tot;
update(tot);
update(f);
Splay(tot);
break;
}
}
}
int rank(int k){
int ans = 0,now = root;
while(1){
if(k<val[now]) now = child[now][0];
else{
ans+=size[child[now][0]];
if(k==val[now]){
Splay(now);
return ans+1;
}
ans+=cnt[now];
now = child[now][1];
}
}
}
int kth(int k){
int now = root;
while(1){
if(child[now][0]&&k<=size[child[now][0]]){
now = child[now][0];
}
else{
k-=cnt[now]+size[child[now][0]];
if(k<=0){
Splay(now);
return val[now];
}
now = child[now][1];
}
}
}
int pre(){
int now = child[root][0];
while(child[now][1]) now = child[now][1];
Splay(now);
return now;
}
int next(){
int now = child[root][1];
while(child[now][0]) now = child[now][0];
Splay(now);
return now;
}
void del(int k){
rank(k);
if(cnt[root]>1){
cnt[root]--;
update(root);
return;
}
if(!child[root][0]&&!child[root][1]){
clear(root);
root = 0;
return;
}
if(!child[root][0]){
int now = root;
root = child[root][1];
fa[root] = 0;
clear(now);
return;
}
if(!child[root][1]){
int now = root;
root = child[root][0];
fa[root] = 0;
clear(now);
return;
}
int now = root,x = pre();
fa[child[now][1]] = x;
child[x][1] = child[now][1];
clear(now);
update(root);
}
}tree;
int main(){
int n,op,x;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&op,&x);
if(op==1) tree.insert(x);
else if(op==2) tree.del(x);
else if(op==3) printf("%d\n",tree.rank(x));
else if(op==4) printf("%d\n",tree.kth(x));
else if(op==5) tree.insert(x),printf("%d\n",val[tree.pre()]),tree.del(x);
else tree.insert(x),printf("%d\n",val[tree.next()]),tree.del(x);
}
return 0;
}
文艺平衡树(Splay维护区间信息)
大致题意
给一个长度为\(n\)的序列,序列中第\(a_i\)项的初始值为\(i\)
有\(m\)次区间翻转操作,输出经过 \(m\) 次变换后的结果
分析
按点的编号建立一颗\(Splay\)
每次翻转时
先将\(val = l-1\)和\(val = r+1\)的节点分别转到根和根的儿子节点
根据\(Splay\)的性质,整颗树的中序遍历不变
因此只需要将\(child[child[root][1]][0]\)下的所有子树交换
通过给打懒标记的方式来实现交换操作即可
\(code\)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 100005;
const int inf = 114514191;
int child[MAXN][2],a[MAXN],size[MAXN],root,tot,fa[MAXN],val[MAXN],cnt[MAXN],tag[MAXN];
struct Splay{
void pushdown(int x){
if(!tag[x]) return;
tag[child[x][1]]^=1;
tag[child[x][0]]^=1;
swap(child[x][1],child[x][0]);
tag[x] = 0;
}
void update(int x){size[x] = size[child[x][0]]+size[child[x][1]]+cnt[x];}
bool pd(int x){return x==child[fa[x]][1];}
void clear(int x){fa[x] = child[x][0] = child[x][1] = size[x] = val[x] = cnt[x] = 0;}
void rotate(int x){
int y = fa[x] , z = fa[y];
int chy = pd(x) ,chx = chy^1;
child[y][chy] = child[x][chx];
fa[child[x][chx]] = y;
child[x][chx] = y,fa[y] = x,fa[x] = z;
if(z) child[z][y==child[z][1]] = x;
update(x),update(y);
}
int build(int l,int r,int f){
if(l>r) return 0;
int mid = (l+r)>>1;
int now = ++tot;
fa[now] = f;
cnt[now]++;
val[now] = a[mid];
size[now]++;
child[now][0] = build(l,mid-1,now);
child[now][1] = build(mid+1,r,now);
update(now);
return now;
}
void splay(int x,int goal){
for (int f; (f=fa[x])!=goal; rotate(x)){
if (fa[f]!=goal) rotate(pd(x)==pd(f)?f:x);
}
if (!goal) root=x;
}
int kth(int k){
int now = root;
while(1){
pushdown(now);
if(child[now][0]&&k<=size[child[now][0]]){
now = child[now][0];
}
else{
int t = cnt[now]+size[child[now][0]];
if(k<=t){
return now;
}
k-=t;
now = child[now][1];
}
}
}
void reverse(int x,int y){
int l = kth(x-1),r = kth(y+1);
splay(l,0),splay(r,l);
int now = child[root][1];
now = child[now][0];
tag[now]^=1;
}
void dfs(int x){
pushdown(x);
if(child[x][0]) dfs(child[x][0]);
if(val[x]!=inf&&val[x]!=-inf) cout<<val[x]<<" ";
if(child[x][1]) dfs(child[x][1]);
}
}tree;
int main(){
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
a[1] = -inf,a[n+2] = inf;//给区间[1,n]的序列翻转
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) a[i+1] = i;
root = tree.build(1,n+2,0);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int l,r;
cin>>l>>r;
tree.reverse(l+1,r+1);
}
tree.dfs(root);
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号