Redux原理探索
Redux
redux的index.js暴露以下几个接口
export {
createStore,
combineReducers,
bindActionCreators,
applyMiddleware,
compose,
__DO_NOT_USE__ActionTypes
}
先看createStore方法,下面是使用方法
const store = createStore(rootReducer)
下面为createStore的实现过程及返回值
//初始化时设置一个默认的action dispatch({ type: ActionTypes.INIT }) return { dispatch, subscribe, getState, replaceReducer, [$$observable]: observable }
createStore返回了一些方法给store
- dispatch是唯一一个改变state的方法,用来更新state数据并触发监听
- subscribe订阅监听,返回一个方法解除监听
- getState返回state数据
- replaceReducer替换掉当前的reducer并初始化数据
dispatch在执行时先进行验证保证dispatch的参数action是有效的,然后执行下述代码
try { isDispatching = true //改变state currentState = currentReducer(currentState, action) } finally { isDispatching = false } //触发监听 const listeners = (currentListeners = nextListeners) for (let i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++) { const listener = listeners[i] listener() } return action
通过currentState = currentReducer(currentState, action)来改变state,其中currentReducer是初始化store时传入的参数rootReducer。
看看currentReducer是什么
export default combineReducers({ todos, visibilityFilter })
从使用方法上看是combineReducers接口的返回值
return function combination(state = {}, action) { let hasChanged = false const nextState = {} for (let i = 0; i < finalReducerKeys.length; i++) { const key = finalReducerKeys[i] const reducer = finalReducers[key] const previousStateForKey = state[key] const nextStateForKey = reducer(previousStateForKey, action) if (typeof nextStateForKey === 'undefined') { const errorMessage = getUndefinedStateErrorMessage(key, action) throw new Error(errorMessage) } //将改变后的state存放到全局变量 nextState[key] = nextStateForKey //判断state是否改变 只要有一个key变了就认为state改变了 hasChanged = hasChanged || nextStateForKey !== previousStateForKey } //根据是否改变选择返回旧state还是新的state return hasChanged ? nextState : state }
返回的是combineReducers闭包函数,在返回之前先对reducer里面的方法进行验证保证方法好用
currentReducer(currentState, action)实际上就是combination(currentState, action),与旧的state进行比较来确定是否更新
componentdidmount(){ const {changeCurrentMonday,changeCurrentMonth} = this.props; changeCurrentMonday(data); }
... const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch) => { return bindActionCreators({ changeCurrentMonday: actions.changeCurrentMonday, changeCurrentMonth: actions.changeCurrentMonth, changeCurrentSchedule: actions.changeCurrentSchedule }, dispatch); } export default connect(null, mapDispatchToProps)(Schedule);
const store = createStore(reducer,applyMiddleware(mid1,mid2));
再回头看看createStore方法,方法一共三个形参:reducer, preloadedState, enhancer
// 第二个参数是function且第三个参数不存在时,将二三参数互换 if (typeof preloadedState === 'function' && typeof enhancer === 'undefined') { enhancer = preloadedState preloadedState = undefined } //确保第三个参数enhancer是一个函数 如果是 用enhancer(createStore)(reducer, preloadedState)作为返回值 if (typeof enhancer !== 'undefined') { if (typeof enhancer !== 'function') { throw new Error('Expected the enhancer to be a function.') } return enhancer(createStore)(reducer, preloadedState) }
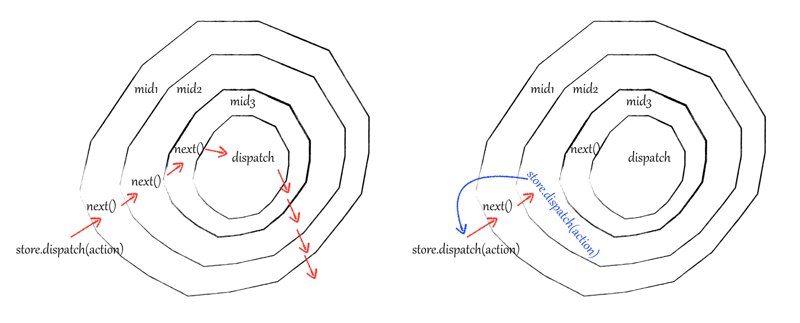
所以上面的createStore执行的实际上是applyMiddleware(mid1,mid2)(createStore)(reducer, preloadedState),applyMiddleware返回一个闭包函数,最终执行的代码为
function(reducer, preloadedState) { const store = createStore(reducer, preloadedState) let dispatch = () => { throw new Error( `Dispatching while constructing your middleware is not allowed. ` + `Other middleware would not be applied to this dispatch.` ) } const middlewareAPI = { getState: store.getState, dispatch: (reducer, preloadedState) => dispatch(reducer, preloadedState) } const chain = middlewares.map(middleware => middleware(middlewareAPI)) dispatch = compose(...chain)(store.dispatch) return { ...store, dispatch } }
applyMiddleware是通过增强dispatch实现的,最终将增强后的dispatch返回,其中middlewareAPI 中的dispatch使用()=>dispatch()是为了保证每一个中间件的dispatch引用独立。
假如有两个中间件func1,func2(中间件格式({state,dispatch})=>(next)=>(action)=>{return next(aciton);})
chain的格式为
[//func1
(next)=>(action)=>{next(action);},
//func2
(next)=>(action)=>{next(action);}]
现在看一下compose实现
export default function compose(...funcs) { if (funcs.length === 0) { return arg => arg } if (funcs.length === 1) { return funcs[0] } return funcs.reduce((a, b) => (...args) => a(b(...args))) }
redux-thunk原理
function createThunkMiddleware(extraArgument) { return ({ dispatch, getState }) => next => action => { if (typeof action === 'function') { return action(dispatch, getState, extraArgument); } return next(action); }; } const thunk = createThunkMiddleware(); thunk.withExtraArgument = createThunkMiddleware; export default thunk;
thunk异步就是通过不调用next(action)跳出循环实现的。
通过dispatch一个异步function(例func1)拦截更新state,在func1中再dispatch一个action实现异步更新state数据。
参考文章:
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000004485808


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号