继承和多态的相关问题
探索一
继承条件下的构造方法调用
1.继承如果是多重继承,在调用构造函数方面,先从父类调用
再依次是下面的子类。因为构造函数的作用是在创建了一个类型后
为了能用,得把这个类型初始化,分配内存空间。
从父类依次到子类就是保证实例变量都可以被正确的初始化。
探索二
super的用法
package TestInherits; class Grandparent { public Grandparent() { System.out.println("GrandParent Created."); } public Grandparent(String string) { System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string); } } class Parent extends Grandparent { public Parent() { super("Hello.Grandparent."); System.out.println("Parent Created"); // super("Hello.Grandparent."); } } class Child extends Parent { public Child() { System.out.println("Child Created"); } } public class TestInherits { public static void main(String args[]) { Child c = new Child(); } }
如果用了super调用基类,那么这个super必须写在第一行
super一出现,直接访问父类中的构造函数,因为这个super
的类型是String类型,所以调用的父类中参数为String的类型。
探索三
奇怪的现象
public class ExplorationJDKSource { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(new A()); } } class A{}
这个程序的运行结果
ExplorationJDKSource.A@7852e922
public void println(Object x),这一方法内部调用了valueOf方法
valueOf方法内部又调用了Object.toString方法
public String toString(){
return getClass().getName()+"@"+Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
}
hashCode方法是本地方法,由JVM设计者实现:public native int hashCode();
探索四
在子类中,若要调用父类中被覆盖的方法,可以使用super关键字
1 public class FatherAndSon { 2 3 public static void main(String args[]) { 4 FatherAndSon s=new FatherAndSon(); 5 s.Test(); 6 } 7 public void Test() { 8 Son s=new Son(); 9 s.test(); 10 11 } 12 class Father {//声明父类 13 public void test() {//声明父类中的测试代码 14 System.out.println("father"); 15 16 } 17 } 18 class Son extends Father{//声明子类,并继承父类 19 public void test() {//覆盖父类的测试类 20 System.out.println("son"); 21 super.test();//使用super调用父类的测试类 22 } 23 } 24 }
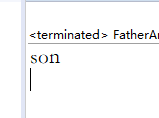
当super被注释时的输出,父类的测试类没有输出,也就没有被调用。
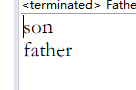
调用super时的输出,明显父类的测试类也被调用了,说明当父类中的方法被覆盖的时候,要想访问父类中方法就要使用super字符。
多态:
探索一
public class ParentChildTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Parent parent=new Parent(); parent.printValue(); Child child=new Child(); child.printValue(); parent=child; parent.printValue(); parent.myValue++; //System.out.println(parent.myValue); parent.printValue(); ((Child)parent).myValue++; //System.out.println(parent.myValue); //System.out.println(child.myValue); parent.printValue(); } } class Parent{ public int myValue= 100; public void printValue() { System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); } } class Child extends Parent{ public int myValue=200; public void printValue() { System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); } }
结果为:
Parent.printValue(),myValue=100
Child.printValue(),myValue=200
Child.printValue(),myValue=200
Child.printValue(),myValue=200
Child.printValue(),myValue=201
当子类和父类方法名和内容相同时,具体调用哪一个,由对象
决定,对象调哪个就用那个方法




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步