基于边缘的模板匹配
Introduction
Template matching is an image processing problem to find the location of an object using a template image in another search image when its pose (X, Y, θ) is unknown. In this article, we implement an algorithm that uses an object’s edge information for recognizing the object in the search image.
Background
Template matching is inherently a tough problem due to its speed and reliability issues. The solution should be robust against brightness changes when an object is partially visible or mixed with other objects, and most importantly, the algorithm should be computationally efficient. There are mainly two approaches to solve this problem, gray value based matching (or area based matching) and feature based matching (non area based).
Gray value based approach: In gray value based matching, the Normalized Cross Correlation (NCC) algorithm is known from old days. This is typically done at every step by subtracting the mean and dividing by the standard deviation. The cross correlation of template t(x, y) with a sub image f(x, y) is:
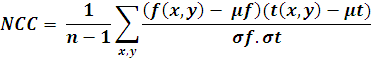
Where n is the number of pixels in t(x, y) and f(x, y).
Though this method is robust against linear illumination changes, the algorithm will fail when the object is partially visible or the object is mixed with other objects. Moreover, this algorithm is computationally expensive since it needs to compute the correlation between all the pixels in the template image to the search image.
Feature based approach: Several methods of feature based template matching are being used in the image processing domain. Like edge based object recognition where the object edges are features for matching, in Generalized Hough transform, an object’s geometric features will be used for matching.
In this article, we implement an algorithm that uses an object’s edge information for recognizing the object in a search image. This implementation uses the Open-Source Computer Vision library as a platform.
The algorithm
Here, we are explaining an edge based template matching technique. An edge can be defined as points in a digital image at which the image brightness changes sharply or has discontinuities. Technically, it is a discrete differentiation operation, computing an approximation of the gradient of the image intensity function.
There are many methods for edge detection, but most of them can be grouped into two categories: search-based and zero-crossing based. The search-based methods detect edges by first computing a measure of edge strength, usually a first-order derivative expression such as the gradient magnitude, and then searching for local directional maxima of the gradient magnitude using a computed estimate of the local orientation of the edge, usually the gradient direction. Here, we are using such a method implemented by Sobel known as Sobel operator. The operator calculates the gradient of the image intensity at each point, giving the direction of the largest possible increase from light to dark and the rate of change in that direction.
We are using these gradients or derivatives in X direction and Y direction for matching.
This algorithm involves two steps. First, we need to create an edge based model of the template image, and then we use this model to search in the search image.
Creating an edge based template model
We first create a data set or template model from the edges of the template image that will be used for finding the pose of that object in the search image.
Here we are using a variation of Canny’s edge detection method to find the edges. You can read more on Canny’s edge detection here. For edge extraction, Canny uses the following steps:
Step 1: Find the intensity gradient of the image
Use the Sobel filter on the template image which returns the gradients in the X (Gx) and Y (Gy) direction. From this gradient, we will compute the edge magnitude and direction using the following formula:
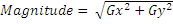
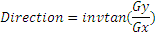
We are using an OpenCV function to find these values.
cvSobel( src, gx, 1,0, 3 ); //gradient in X direction cvSobel( src, gy, 0, 1, 3 ); //gradient in Y direction for( i = 1; i < Ssize.height-1; i++ ) { for( j = 1; j < Ssize.width-1; j++ ) { _sdx = (short*)(gx->data.ptr + gx->step*i); _sdy = (short*)(gy->data.ptr + gy->step*i); fdx = _sdx[j]; fdy = _sdy[j]; // read x, y derivatives //Magnitude = Sqrt(gx^2 +gy^2) MagG = sqrt((float)(fdx*fdx) + (float)(fdy*fdy)); //Direction = invtan (Gy / Gx) direction =cvFastArctan((float)fdy,(float)fdx); magMat[i][j] = MagG; if(MagG>MaxGradient) MaxGradient=MagG; // get maximum gradient value for normalizing. // get closest angle from 0, 45, 90, 135 set if ( (direction>0 && direction < 22.5) || (direction >157.5 && direction < 202.5) || (direction>337.5 && direction<360) ) direction = 0; else if ( (direction>22.5 && direction < 67.5) || (direction >202.5 && direction <247.5) ) direction = 45; else if ( (direction >67.5 && direction < 112.5)|| (direction>247.5 && direction<292.5) ) direction = 90; else if ( (direction >112.5 && direction < 157.5)|| (direction>292.5 && direction<337.5) ) direction = 135; else direction = 0; orients[count] = (int)direction; count++; } }
Once the edge direction is found, the next step is to relate the edge direction that can be traced in the image. There are four possible directions describing the surrounding pixels: 0 degrees, 45 degrees, 90 degrees, and 135 degrees. We assign all the directions to any of these angles.
Step 2: Apply non-maximum suppression
After finding the edge direction, we will do a non-maximum suppression algorithm. Non-maximum suppression traces the left and right pixel in the edge direction and suppresses the current pixel magnitude if it is less than the left and right pixel magnitudes. This will result in a thin image.
for( i = 1; i < Ssize.height-1; i++ ) { for( j = 1; j < Ssize.width-1; j++ ) { switch ( orients[count] ) { case 0: leftPixel = magMat[i][j-1]; rightPixel = magMat[i][j+1]; break; case 45: leftPixel = magMat[i-1][j+1]; rightPixel = magMat[i+1][j-1]; break; case 90: leftPixel = magMat[i-1][j]; rightPixel = magMat[i+1][j]; break; case 135: leftPixel = magMat[i-1][j-1]; rightPixel = magMat[i+1][j+1]; break; } // compare current pixels value with adjacent pixels if (( magMat[i][j] < leftPixel ) || (magMat[i][j] < rightPixel ) ) (nmsEdges->data.ptr + nmsEdges->step*i)[j]=0; Else (nmsEdges->data.ptr + nmsEdges->step*i)[j]= (uchar)(magMat[i][j]/MaxGradient*255); count++; } }
Step 3: Do hysteresis threshold
Doing the threshold with hysteresis requires two thresholds: high and low. We apply a high threshold to mark out thosee edges we can be fairly sure are genuine. Starting from these, using the directional information derived earlier, other edges can be traced through the image. While tracing an edge, we apply the lower threshold, allowing us to trace faint sections of edges as long as we find a starting point.
_sdx = (short*)(gx->data.ptr + gx->step*i); _sdy = (short*)(gy->data.ptr + gy->step*i); fdx = _sdx[j]; fdy = _sdy[j]; MagG = sqrt(fdx*fdx + fdy*fdy); //Magnitude = Sqrt(gx^2 +gy^2) DirG =cvFastArctan((float)fdy,(float)fdx); //Direction = tan(y/x) ////((uchar*)(imgGDir->imageData + imgGDir->widthStep*i))[j]= MagG; flag=1; if(((double)((nmsEdges->data.ptr + nmsEdges->step*i))[j]) < maxContrast) { if(((double)((nmsEdges->data.ptr + nmsEdges->step*i))[j])< minContrast) { (nmsEdges->data.ptr + nmsEdges->step*i)[j]=0; flag=0; // remove from edge ////((uchar*)(imgGDir->imageData + imgGDir->widthStep*i))[j]=0; } else { // if any of 8 neighboring pixel is not greater than max contraxt remove from edge if( (((double)((nmsEdges->data.ptr + nmsEdges->step*(i-1)))[j-1]) < maxContrast) && (((double)((nmsEdges->data.ptr + nmsEdges->step*(i-1)))[j]) < maxContrast) && (((double)((nmsEdges->data.ptr + nmsEdges->step*(i-1)))[j+1]) < maxContrast) && (((double)((nmsEdges->data.ptr + nmsEdges->step*i))[j-1]) < maxContrast) && (((double)((nmsEdges->data.ptr + nmsEdges->step*i))[j+1]) < maxContrast) && (((double)((nmsEdges->data.ptr + nmsEdges->step*(i+1)))[j-1]) < maxContrast) && (((double)((nmsEdges->data.ptr + nmsEdges->step*(i+1)))[j]) < maxContrast) && (((double)((nmsEdges->data.ptr + nmsEdges->step*(i+1)))[j+1]) < maxContrast)) { (nmsEdges->data.ptr + nmsEdges->step*i)[j]=0; flag=0; ////((uchar*)(imgGDir->imageData + imgGDir->widthStep*i))[j]=0; } } }
Step 4: Save the data set
After extracting the edges, we save the X and Y derivatives of the selected edges along with the coordinate information as the template model. These coordinates will be rearranged to reflect the start point as the center of gravity.
Find the edge based template model
The next task in the algorithm is to find the object in the search image using the template model. We can see the model we created from the template image which contains a set of points: ![]() , and its gradients in X and Y direction
, and its gradients in X and Y direction ![]() , where i = 1…n, n is the number of elements in the Template (T) data set.
, where i = 1…n, n is the number of elements in the Template (T) data set.
We can also find the gradients in the search image (S) ![]() , where u = 1...number of rows in the search image, v = 1… number of columns in the search image.
, where u = 1...number of rows in the search image, v = 1… number of columns in the search image.
In the matching process, the template model should be compared to the search image at all locations using a similarity measure. The idea behind similarity measure is to take the sum of all normalized dot products of gradient vectors of the template image and search the image over all points in the model data set. This results in a score at each point in the search image. This can be formulated as follows:
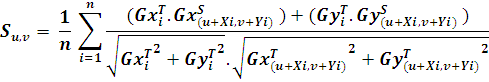
In case there is a perfect match between the template model and the search image, this function will return a score 1. The score corresponds to the portion of the object visible in the search image. In case the object is not present in the search image, the score will be 0.
cvSobel( src, Sdx, 1, 0, 3 ); // find X derivatives cvSobel( src, Sdy, 0, 1, 3 ); // find Y derivatives for( i = 0; i < Ssize.height; i++ ) { for( j = 0; j < Ssize.width; j++ ) { partialSum = 0; // initilize partialSum measure for(m=0;m<noOfCordinates;m++) { curX = i + cordinates[m].x ; // template X coordinate curY = j + cordinates[m].y ; // template Y coordinate iTx = edgeDerivativeX[m]; // template X derivative iTy = edgeDerivativeY[m]; // template Y derivative if(curX<0 ||curY<0||curX>Ssize.height-1 ||curY>Ssize.width-1) continue; _Sdx = (short*)(Sdx->data.ptr + Sdx->step*(curX)); _Sdy = (short*)(Sdy->data.ptr + Sdy->step*(curX)); iSx=_Sdx[curY]; // get curresponding X derivative from source image iSy=_Sdy[curY];// get curresponding Y derivative from source image if((iSx!=0 || iSy!=0) && (iTx!=0 || iTy!=0)) { //partial Sum = Sum of(((Source X derivative* Template X drivative) //+ Source Y derivative * Template Y derivative)) / Edge //magnitude of(Template)* edge magnitude of(Source)) partialSum = partialSum + ((iSx*iTx)+(iSy*iTy))* (edgeMagnitude[m] * matGradMag[curX][curY]); }
In practical situations, we need to speed up the searching procedure. This can be achieved using various methods. The first method is using the property of averaging. When finding the similarity measure, we need not evaluate for all points in the template model if we can set a minimum score (Smin) for the similarity measure. For checking the partial score Su,v at a particular point J, we have to find the partial sum Sm. Sm at point m can be defines as follows:
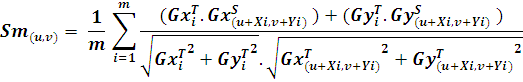
It is evident that the remaining terms of the sum are smaller or equal to 1. So we can stop the evaluation if ![]() .
.
Another criterion can be that the partial score at any point should be greater than the minimum score. I.e., ![]() . When this condition is used, matching will be extremely fast. But the problem is, if the missing part of the object is checked first, the partial sum will be low. In that case, that instance of the object will not be considered as a match. We can modify this with another criterion where we check the first part of the template model with a safe stopping criteria and the remaining with a hard criteria,
. When this condition is used, matching will be extremely fast. But the problem is, if the missing part of the object is checked first, the partial sum will be low. In that case, that instance of the object will not be considered as a match. We can modify this with another criterion where we check the first part of the template model with a safe stopping criteria and the remaining with a hard criteria, ![]() . The user can specify a greediness parameter (g) where the fraction of the template model is examined with a hard criteria. So that if g=1, all points in the template model are checked with the hard criteria, and if g=0, all the points will be checked with a safe criteria only. We can formulate this procedure as follows.
. The user can specify a greediness parameter (g) where the fraction of the template model is examined with a hard criteria. So that if g=1, all points in the template model are checked with the hard criteria, and if g=0, all the points will be checked with a safe criteria only. We can formulate this procedure as follows.
The evaluation of the partial score can be stopped at:
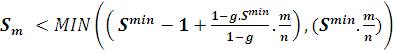
// stoping criterias to search for model double normMinScore = minScore /noOfCordinates; // precompute minumum score double normGreediness = ((1- greediness * minScore)/(1-greediness)) /noOfCordinates; // precompute greedniness sumOfCoords = m + 1; partialScore = partialSum /sumOfCoords ; // check termination criteria // if partial score score is less than the score than // needed to make the required score at that position // break serching at that coordinate. if( partialScore < (MIN((minScore -1) + normGreediness*sumOfCoords,normMinScore* sumOfCoords))) break;
This similarity measure has several advantages: the similarity measure is invariant to non-linear illumination changes because all gradient vectors are normalized. Since there is no segmentation on edge filtering, it will show the true invariance against arbitrary changes in illumination. More importantly, this similarity measure is robust when the object is partially visible or mixed with other objects.
Enhancements
There are various enhancements possible for this algorithm. For speeding up the search process further, a pyramidal approach can be used. In this case, the search is started at low resolution with a small image size. This corresponds to the top of the pyramid. If the search is successful at this stage, the search is continued at the next level of the pyramid, which represents a higher resolution image. In this manner, the search is continued, and consequently, the result is refined until the original image size, i.e., the bottom of the pyramid is reached.
Another enhancement is possible by extending the algorithm for rotation and scaling. This can be done by creating template models for rotation and scaling and performing search using all these template models.
原文地址:基于边缘的模板匹配
使用opencv3编写的版本
geomatch.h

#ifndef GEOMATCH_H #define GEOMATCH_H #include <math.h> #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> using namespace cv; class geomatch { private: int noOfCordinates; //Number of elements in coordinate array Point *cordinates; //Coordinates array to store model points int modelHeight; //Template height int modelWidth; //Template width double *edgeMagnitude; //gradient magnitude double *edgeDerivativeX; //gradient in X direction double *edgeDerivativeY; //radient in Y direction Point centerOfGravity; //Center of gravity of template bool modelDefined; void CreateDoubleMatrix(double **&matrix,CvSize size); void ReleaseDoubleMatrix(double **&matrix,int size); public: geomatch(void); ~geomatch(void); int CreateGeoMatchModel(Mat templateArr, double, double); double FindGeoMatchModel(Mat srcarr, double minScore, double greediness, Point *resultPoint); void DrawContours(Mat pImage, Point COG, Scalar, int); void DrawContours(Mat pImage, Scalar, int); }; #endif // GEOMATCH_H
geomatch.cpp

#include "geomatch.h" #include <opencv2\opencv.hpp> #include <opencv2\core.hpp> #include <vector> #include <cmath> #include <iostream> using namespace cv; using namespace std; geomatch::geomatch() { noOfCordinates = 0; // Initilize no of cppodinates in model points modelDefined = false; } int geomatch::CreateGeoMatchModel(Mat templateArr, double maxContrast, double minContrast) { Size Ssize; Mat src; templateArr.copyTo(src); // set width and height Ssize.width = src.size().width; Ssize.height = src.size().height; modelHeight = src.size().height; //Save Template height modelWidth = src.size().width; //Save Template width noOfCordinates = 0; //initialize cordinates = new Point[modelWidth *modelHeight];//Allocate memory for coorinates of selected points in template image edgeMagnitude = new double[modelWidth *modelHeight];//Allocate memory for edge magnitude for selected points edgeDerivativeX = new double[modelWidth *modelHeight];//Allocate memory for edge X derivative for selected points edgeDerivativeY = new double[modelWidth *modelHeight];//Allocate memory for edge Y derivative for selected points // Calculate gradient of Template Mat gx(Ssize.height, Ssize.width, CV_16SC1);//create Matrix to store X derivative Mat gy(Ssize.height, Ssize.width, CV_16SC1);//create Matrix to store Y derivative Sobel(src, gx,CV_16S,1,0,3); //gradient in X direction Sobel(src, gy,CV_16S,0,1,3); //gradient in Y direction namedWindow("gx",WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); imshow("gx",gx); // waitKey(50000); Mat nmsEdges(Ssize.height, Ssize.width, CV_32F);//create Matrix to store Final nmsEdgesa; double fdx, fdy; double MagG, DirG; double MaxGradient = -99999.99; double direction; vector<int> orients; vector<vector<double>> magMat; for(int i = 0; i < Ssize.height-1; i++) { vector<double> magrows; magrows.clear(); for(int j = 0; j < Ssize.width-1; j++) { fdx = (double)gx.at<short>(i, j); fdy = (double)gy.at<short>(i, j); // read x, y derivatives MagG = sqrt((float)(fdx*fdx) + (float)(fdy*fdy)); //Magnitude = Sqrt(gx^2 +gy^2) direction =cvFastArctan((float)fdy,(float)fdx); //Direction = invtan (Gy / Gx) if(i==0||j==0) { magrows.push_back(0); } else { magrows.push_back(MagG); } if(MagG>MaxGradient) MaxGradient=MagG; // get maximum gradient value for normalizing. // get closest angle from 0, 45, 90, 135 set //可以看出接近水平的都被化为了0,接近45的变为45。 if ( (direction>0 && direction < 22.5) || (direction >157.5 && direction < 202.5) || (direction>337.5 && direction<360) ) direction = 0; else if ( (direction>22.5 && direction < 67.5) || (direction >202.5 && direction <247.5) ) direction = 45; else if ( (direction >67.5 && direction < 112.5)||(direction>247.5 && direction<292.5) ) direction = 90; else if ( (direction >112.5 && direction < 157.5)||(direction>292.5 && direction<337.5) ) direction = 135; else direction = 0; orients.push_back((int)direction); } magMat.push_back(magrows); } int count=0; // init count // non maximum suppression double leftPixel,rightPixel; for(int i = 1; i < Ssize.height-1; i++ ) { for(int j = 1; j < Ssize.width-1; j++ ) { switch (orients[count]) { case 0: //水平情况下的左右像素 leftPixel = magMat[i][j-1]; rightPixel = magMat[i][j+1]; break; case 45: leftPixel = magMat[i-1][j+1]; rightPixel = magMat[i+1][j-1]; break; case 90: leftPixel = magMat[i-1][j]; rightPixel = magMat[i+1][j]; break; case 135: leftPixel = magMat[i-1][j-1]; rightPixel = magMat[i+1][j+1]; break; } // compare current pixels value with adjacent pixels if ((magMat[i][j] < leftPixel) || (magMat[i][j] < rightPixel)) nmsEdges.at<float>(i,j) = 0; else nmsEdges.at<float>(i,j) = (uchar)(magMat[i][j] / MaxGradient * 255); count++; } } int RSum=0,CSum=0; int curX,curY; int flag=1; //Hysterisis threshold for(int i = 1; i < Ssize.height-1; i++ ) { for(int j = 1; j < Ssize.width; j++ ) { fdx = (double)gx.at<short>(i, j); fdy = (double)gy.at<short>(i, j); // read x, y derivatives MagG = sqrt(fdx*fdx + fdy*fdy); //Magnitude = Sqrt(gx^2 +gy^2) DirG =cvFastArctan((float)fdy,(float)fdx); //Direction = tan(y/x) //((uchar*)(imgGDir->imageData + imgGDir->widthStep*i))[j]= MagG; flag=1; //这里的意义在于,大于高阈值的边缘直接保留(因为是真边缘),低于低阈值的删除(认定为假边缘),在 //中间的考虑邻域像素进行判断 if(((double)(nmsEdges.at<float>(i,j)) < maxContrast)) { if(((double)(nmsEdges.at<float>(i,j))< minContrast)) { (nmsEdges.at<float>(i,j)) = 0; flag=0; // remove from edge //((uchar*)(imgGDir->imageData + imgGDir->widthStep*i))[j]=0; } else { // if any of 8 neighboring pixel is not greater than max contraxt remove from edge if ((double)nmsEdges.at<float>(i - 1, j - 1) <maxContrast && (double)nmsEdges.at<float>(i, j - 1) <maxContrast && (double)nmsEdges.at<float>(i + 1, j - 1) <maxContrast && (double)nmsEdges.at<float>(i - 1, j) <maxContrast && (double)nmsEdges.at<float>(i + 1, j) <maxContrast && (double)nmsEdges.at<float>(i - 1, j + 1) <maxContrast && (double)nmsEdges.at<float>(i, i + 1) <maxContrast && (double)nmsEdges.at<float>(i + 1, j - 1) <maxContrast) { nmsEdges.at<float>(i,j) = 0; flag=0; //((uchar*)(imgGDir->imageData + imgGDir->widthStep*i))[j]=0; } } } // save selected edge information curX = i; curY = j; if (flag != 0) { if (fdx != 0 || fdy != 0) { RSum = RSum + curX; CSum = CSum + curY; // Row sum and column sum for center of gravity cordinates[noOfCordinates].x = curX; cordinates[noOfCordinates].y = curY; edgeDerivativeX[noOfCordinates] = fdx; edgeDerivativeY[noOfCordinates] = fdy; //handle divide by zero if (MagG != 0) edgeMagnitude[noOfCordinates] = 1 / MagG; // gradient magnitude else edgeMagnitude[noOfCordinates] = 0; noOfCordinates++; } } } } centerOfGravity.x = RSum /noOfCordinates; // center of gravity centerOfGravity.y = CSum /noOfCordinates ; // center of gravity // change coordinates to reflect center of gravity for(int m=0;m<noOfCordinates ;m++) { int temp; temp=cordinates[m].x; cordinates[m].x=temp-centerOfGravity.x; temp=cordinates[m].y; cordinates[m].y =temp-centerOfGravity.y; } modelDefined=true; return 1; } double geomatch::FindGeoMatchModel(Mat srcarr,double minScore,double greediness,Point *resultPoint) { double resultScore=0; double partialSum=0; double sumOfCoords=0; double partialScore; int i,j,m ; // count variables double iTx,iTy,iSx,iSy; double gradMag1; int curX,curY; Mat src; srcarr.copyTo(src); // source image size Size Ssize; Ssize.width = src.size().width; Ssize.height= src.size().height; vector<vector<double>> matGradMag; // create image to save gradient magnitude values Mat Sdx(Ssize.height, Ssize.width, CV_16SC1); // X derivatives Mat Sdy(Ssize.height, Ssize.width, CV_16SC1); // y derivatives Sobel( src, Sdx, CV_16S,1, 0, 3); // find X derivatives Sobel( src, Sdy, CV_16S,0, 1, 3); // find Y derivatives namedWindow("Sdx",WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); imshow("Sdx",Sdx); // stoping criterias to search for model double normMinScore = minScore / noOfCordinates; // precompute minumum score double normGreediness = ((1- greediness * minScore)/(1-greediness)) /noOfCordinates; // precompute greedniness for( i = 0; i < Ssize.height; i++ ) { vector<double> gradMag; gradMag.clear(); for( j = 0; j < Ssize.width; j++ ) { iSx = (double)Sdx.at<short>(i,j); // X derivative of Source image iSy = (double)Sdy.at<short>(i,j); // Y derivative of Source image gradMag1=sqrt((iSx*iSx)+(iSy*iSy)); //Magnitude = Sqrt(dx^2 +dy^2) if(gradMag1!=0) // hande divide by zero gradMag.push_back(1/gradMag1); // 1/Sqrt(dx^2 +dy^2) else gradMag.push_back(0); } matGradMag.push_back(gradMag); } for( i = 0; i < Ssize.height; i++ ) { for( j = 0; j < Ssize.width; j++ ) { partialSum = 0; // initilize partialSum measure for(m=0;m<noOfCordinates;m++) { curX = i + cordinates[m].x ; // template X coordinate curY = j + cordinates[m].y ; // template Y coordinate iTx = edgeDerivativeX[m]; // template X derivative iTy = edgeDerivativeY[m]; // template Y derivative if(curX<0 ||curY<0||curX>Ssize.height-1 ||curY>Ssize.width-1) continue; short* _Sdx = Sdx.ptr<short>(curX); short* _Sdy = Sdy.ptr<short>(curX); iSx=_Sdx[curY]; // get curresponding X derivative from source image iSy=_Sdy[curY]; // get curresponding Y derivative from source image if((iSx!=0 || iSy!=0) && (iTx!=0 || iTy!=0)) { //partial Sum = Sum of(((Source X derivative* Template X drivative) + Source Y derivative * Template Y derivative)) / Edge magnitude of(Template)* edge magnitude of(Source)) partialSum = partialSum + ((iSx*iTx)+(iSy*iTy))*(edgeMagnitude[m] * matGradMag[curX][curY]); } sumOfCoords = m + 1; partialScore = partialSum /sumOfCoords ; // check termination criteria // if partial score score is less than the score than needed to make the required score at that position // break serching at that coordinate. if( partialScore < (MIN((minScore -1) + normGreediness*sumOfCoords,normMinScore* sumOfCoords))) break; } if(partialScore > resultScore) { resultScore = partialScore; // Match score resultPoint->x = i; // result coordinate X resultPoint->y = j; // result coordinate Y } } } // free used resources and return score return resultScore; } // destructor geomatch::~geomatch(void) { delete[] cordinates; delete[] edgeMagnitude; delete[] edgeDerivativeX; delete[] edgeDerivativeY; } // draw contours around result image void geomatch::DrawContours(Mat source,Point COG,Scalar color,int lineWidth) { Point point; point.y=COG.x; point.x=COG.y; for(int i=0; i<noOfCordinates; i++) { point.y=cordinates[i].x + COG.x; point.x=cordinates[i].y + COG.y; line(source,point,point,color,lineWidth); } } // draw contour at template image void geomatch::DrawContours(Mat source,Scalar color,int lineWidth) { Point point; for(int i=0; i<noOfCordinates; i++) { point.y=cordinates[i].x + centerOfGravity.x; point.x=cordinates[i].y + centerOfGravity.y; line(source,point,point,color,lineWidth); } }
main.cpp

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> 3 #include "geomatch.h" 4 5 using namespace std; 6 using namespace cv; 7 8 int main() 9 { 10 geomatch GM; // object to implent geometric matching 11 int lowThreshold = 10; //deafult value 12 int highThreashold = 100; //deafult value 13 14 double minScore=0.7; //deafult value 15 double greediness=0.8; //deafult value 16 17 double total_time =0; 18 double score= 0; 19 Point result; 20 21 //Load Template image 22 Mat templateImage =imread("t.jpg",-1); 23 24 //Load Search Image 25 Mat searchImage = imread("s1.jpg",-1); 26 27 lowThreshold = 10; 28 highThreashold = 100; 29 minScore = 0.7; 30 greediness = 0.5; 31 32 Mat grayTemplateImg(templateImage.size(), CV_8UC1); 33 34 // Convert color image to gray image. 35 if(templateImage.channels()==3) 36 { 37 cvtColor(templateImage,grayTemplateImg,CV_BGR2GRAY); 38 } 39 else 40 { 41 templateImage.copyTo(grayTemplateImg); 42 } 43 44 cout << "\n Edge Based Template Matching Program\n"; 45 cout << " ------------------------------------\n"; 46 47 if(!GM.CreateGeoMatchModel(grayTemplateImg,lowThreshold,highThreashold)) 48 { 49 cout<<"ERROR: could not create model..."; 50 return 0; 51 } 52 53 GM.DrawContours(templateImage,CV_RGB(255, 0, 0),1); 54 55 Mat graysearchImg(searchImage.size(), CV_8UC1); 56 57 // Convert color image to gray image. 58 if(searchImage.channels()==3) 59 { 60 cvtColor(searchImage,graysearchImg,CV_BGR2GRAY); 61 } 62 else 63 { 64 searchImage.copyTo(graysearchImg); 65 } 66 67 namedWindow("Template", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); 68 imshow("Template", grayTemplateImg); 69 namedWindow("Search Image", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); 70 imshow("Search Image", graysearchImg); 71 72 cout << " Finding Shape Model.." << " Minumum Score = " << minScore << " Greediness = " << greediness << "\n\n"; 73 cout << " ------------------------------------\n"; 74 75 double time0 = static_cast<double>(getTickCount()); 76 score = GM.FindGeoMatchModel(graysearchImg, minScore, greediness, &result); 77 time0 = ((double)getTickCount()-time0)/getTickFrequency(); 78 cout<<"time is"<<time0<<"s"<<endl; 79 80 if(score>minScore) // if score is atleast 0.4 81 { 82 cout<<" Found at ["<<result.x<<", "<<result.y<<"]\n Score = "<<score<<"\n Searching Time = "<<total_time*1000<<"ms"; 83 GM.DrawContours(searchImage,result,CV_RGB( 0, 255, 0 ),1); 84 } 85 else 86 cout<<" Object Not found"; 87 88 cout<< "\n ------------------------------------\n\n"; 89 cout<<"\n Press any key to exit!"; 90 91 // Display result 92 namedWindow("Template", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); 93 imshow("Template", templateImage); 94 namedWindow("Search Image", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); 95 imshow("Search Image", searchImage); 96 97 waitKey(50000); 98 99 }
关于非极大值抑制和滞后阈值参考:Canny边缘检测详解及编程实现




