练习_使用递归计算1-n之间的和与练习_使用递归计算阶乘
练习_使用递归计算1-n之间的和
package Demo_Recurison; public class DiGuiDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //计算1~num的和,使用递归完成 int num = 5; // 调用求和的方法 int sum = getSum(num); // 输出结果 System.out.println(sum); } /* 通过递归算法实现 */ public static int getSum(int num) { // 方法出口 if(num == 1){ return 1; } /* num不为1时,方法返回 num +(num-1)的累和 递归调用getSum方法 */ return num + getSum(num-1); } }
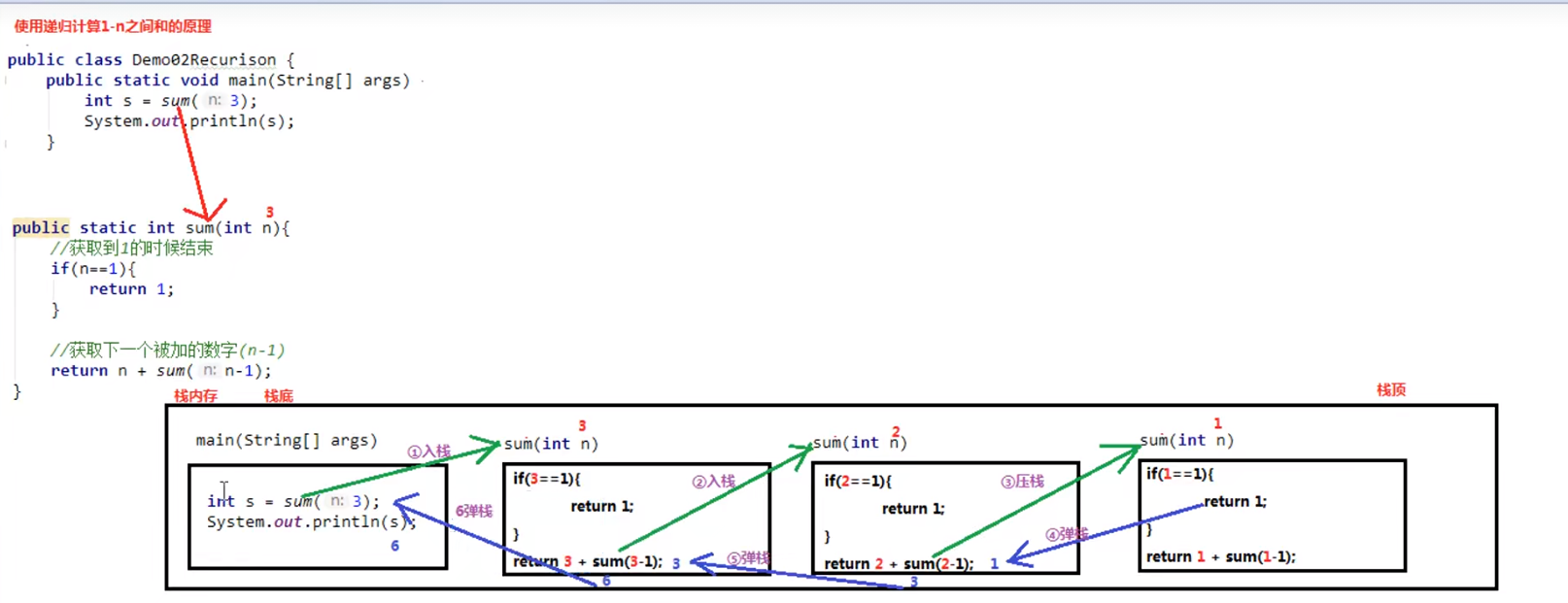
注意:
使用递归求和,main方法调用sum方法,sum方法会一直调用sum方法
导致在内存中有多个sum方法(频繁的创建方法,调用方法,销毁方法)效率低下
所以如果仅仅计算1-n之间的和,不推荐使用递归,使用for循环集合即可
递归求阶乘
package Demo_Recurison; import java.util.Scanner; public class DiGuiDemo { //计算n的阶乘,使用递归完成 public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); int n = scanner.nextInt(); // 调用求阶乘的方法 int value = getValue(n); // 输出结果 System.out.println("阶乘为:"+ value); } // 通过递归算法实现 public static int getValue(int n) { // 方法出口 if (n == 1) { return 1; } /* n不为1时,方法返回 n! = n*(n-1)! 递归调用getValue方法 */ return n * getValue(n - 1); } }
package Demo_Recurison; import java.util.Scanner; public class DiGuiDemo { //计算n的阶乘,使用递归完成 public static void main(String[] args) { int n =5 // 调用求阶乘的方法 int value = getValue(n); // 输出结果 System.out.println("阶乘为:"+ value); } // 通过递归算法实现 public static int getValue(int n) { // 方法出口 if (n == 1) { return 1; } /* n不为1时,方法返回 n! = n*(n-1)! 递归调用getValue方法 */ return n * getValue(n - 1); } }






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享4款.NET开源、免费、实用的商城系统
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· 白话解读 Dapr 1.15:你的「微服务管家」又秀新绝活了
· 上周热点回顾(2.24-3.2)