python:常用模块
一,time & datetime模块
1 #_*_coding:utf-8_*_ 2 3 4 import time 5 6 7 # print(time.clock()) #返回处理器时间,3.3开始已废弃 , 改成了time.process_time()测量处理器运算时间,不包括sleep时间,不稳定,mac上测不出来 8 # print(time.altzone) #返回与utc时间的时间差,以秒计算\ 9 # print(time.asctime()) #返回时间格式"Fri Aug 19 11:14:16 2016", 10 # print(time.localtime()) #返回本地时间 的struct time对象格式 11 # print(time.gmtime(time.time()-800000)) #返回utc时间的struc时间对象格式 12 13 # print(time.asctime(time.localtime())) #返回时间格式"Fri Aug 19 11:14:16 2016", 14 #print(time.ctime()) #返回Fri Aug 19 12:38:29 2016 格式, 同上
#print(time.strftime("%Y%m%d"))
15 16 17 18 # 日期字符串 转成 时间戳 19 # string_2_struct = time.strptime("2019/06/22","%Y/%m/%d") #将 日期字符串 转成 struct时间对象格式 20 # print(string_2_struct) 21 # # 22 # struct_2_stamp = time.mktime(string_2_struct) #将struct时间对象转成时间戳 23 # print(struct_2_stamp) 24 25 26 27 #将时间戳转为字符串格式 28 # print(time.gmtime(time.time()-86640)) #将utc时间戳转换成struct_time格式 29 # print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",time.gmtime()) ) #将utc struct_time格式转成指定的字符串格式 30 31 32 33 34 35 #时间加减 36 import datetime 37 38 # print(datetime.datetime.now()) #返回 2019-06-22 12:47:03.941925 39 #print(datetime.date.fromtimestamp(time.time()) ) # 时间戳直接转成日期格式 2019-06-22 40 # print(datetime.datetime.now() ) 41 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(3)) #当前时间+3天 42 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(-3)) #当前时间-3天 43 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(hours=3)) #当前时间+3小时 44 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(minutes=30)) #当前时间+30分 45 46 47 # 48 # c_time = datetime.datetime.now() 49 # print(c_time.replace(minute=3,hour=2)) #时间替换
二,random
import random print(random.random())#返回0.6549224731884532
print(random.randint(1,3)) #左开右开
print(random.randrange(1,3)) #左开右闭
生成四位验证码
import random checkcode = '' for i in range(4): current = random.randrange(0,4) if current != i: temp = chr(random.randint(65,90)) else: temp = random.randint(0,9) checkcode += str(temp) print(checkcode)
三,os模块
提供对操作系统进行调用的接口
os.getcwd() 获取当前工作目录,即当前python脚本工作的目录路径 os.chdir("dirname") 改变当前脚本工作目录;相当于shell下cd os.curdir 返回当前目录: ('.') os.pardir 获取当前目录的父目录字符串名:('..') os.makedirs('dirname1/dirname2') 可生成多层递归目录 os.removedirs('dirname1') 若目录为空,则删除,并递归到上一级目录,如若也为空,则删除,依此类推 os.mkdir('dirname') 生成单级目录;相当于shell中mkdir dirname os.rmdir('dirname') 删除单级空目录,若目录不为空则无法删除,报错;相当于shell中rmdir dirname os.listdir('dirname') 列出指定目录下的所有文件和子目录,包括隐藏文件,并以列表方式打印 os.remove() 删除一个文件 os.rename("oldname","newname") 重命名文件/目录 os.stat('path/filename') 获取文件/目录信息 os.sep 输出操作系统特定的路径分隔符,win下为"\\",Linux下为"/" os.linesep 输出当前平台使用的行终止符,win下为"\t\n",Linux下为"\n" os.pathsep 输出用于分割文件路径的字符串 os.name 输出字符串指示当前使用平台。win->'nt'; Linux->'posix' os.system("bash command") 运行shell命令,直接显示 os.environ 获取系统环境变量 os.path.abspath(path) 返回path规范化的绝对路径 os.path.split(path) 将path分割成目录和文件名二元组返回 os.path.dirname(path) 返回path的目录。其实就是os.path.split(path)的第一个元素 os.path.basename(path) 返回path最后的文件名。如何path以/或\结尾,那么就会返回空值。即os.path.split(path)的第二个元素 os.path.exists(path) 如果path存在,返回True;如果path不存在,返回False os.path.isabs(path) 如果path是绝对路径,返回True os.path.isfile(path) 如果path是一个存在的文件,返回True。否则返回False os.path.isdir(path) 如果path是一个存在的目录,则返回True。否则返回False os.path.join(path1[, path2[, ...]]) 将多个路径组合后返回,第一个绝对路径之前的参数将被忽略 os.path.getatime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后存取时间 os.path.getmtime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后修改时间
os.system() 在当前进程中打开一个子shell(子进程)来执行系统命令。
os.popen() 这个方法会打开一个管道,返回结果是一个连接管道的文件对象,该文件对象的操作方法同open(),可以从该文件对象中读取返回结果。如果执行成功,不会返回状态码,如果执行失败,则会将错误信息输出到stdout,并返回一个空字符串
四,sys模块
sys.argv 命令行参数List,第一个元素是程序本身路径 sys.exit(n) 退出程序,正常退出时exit(0) sys.version 获取Python解释程序的版本信息 sys.path 返回模块的搜索路径,初始化时使用PYTHONPATH环境变量的值 sys.platform 返回操作系统平台名称 sys.stdout.write('please:')
五,shutil
https://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/4963027.html
高级的 文件、文件夹、压缩包 处理模块
shutil.copyfileobj(fsrc, fdst[, length])
将文件内容拷贝到另一个文件中,可以部分内容
import shutil
f1 = open("os_test.py",encoding='utf-8')
f2 = open("os_test123.py","w")
shutil.copyfileobj(f1,f2)
shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
shutil.copyfile("os_test.py","os_test1234")
shutil.copymode(src, dst)
仅拷贝权限。内容、组、用户均不变
shutil.copystat(src, dst)
拷贝状态的信息,包括:mode bits, atime, mtime, flags
shutil.copy(src, dst)
拷贝文件和权限
shutil.copy2(src, dst)
拷贝文件和状态信息
shutil.ignore_patterns(*patterns)
shutil.copytree(src, dst, symlinks=False, ignore=None)
递归的去拷贝文件
shutil.copytree("test","test1") #test test1为目录
shutil.rmtree(path[, ignore_errors[, onerror]])
递归的去删除文件
shutil.move(src, dst)
递归的去移动文件
shutil.make_archive(base_name, format,...) 创建压缩包并返回文件路径,例如:zip、tar base_name: 压缩包的文件名,也可以是压缩包的路径。只是文件名时,则保存至当前目录,否则保存至指定路径, 如:www =>保存至当前路径 如:/Users/wupeiqi/www =>保存至/Users/wupeiqi/ format: 压缩包种类,“zip”, “tar”, “bztar”,“gztar” root_dir: 要压缩的文件夹路径(默认当前目录) owner: 用户,默认当前用户 group: 组,默认当前组 logger: 用于记录日志,通常是logging.Logger对象 #将 /Users/wupeiqi/Downloads/test 下的文件打包放置当前程序目录 import shutil ret = shutil.make_archive("wwwwwwwwww", 'gztar', root_dir='/Users/wupeiqi/Downloads/test') #将 /Users/wupeiqi/Downloads/test 下的文件打包放置 /Users/wupeiqi/目录 import shutil ret = shutil.make_archive("/Users/wupeiqi/wwwwwwwwww", 'gztar', root_dir='/Users/wupeiqi/Downloads/test')
shutil 对压缩包的处理是调用 ZipFile 和 TarFile 两个模块来进行的,详细:
import zipfile # 压缩 z = zipfile.ZipFile('laxi.zip', 'w') z.write('a.log') z.write('data.data') z.close() # 解压 z = zipfile.ZipFile('laxi.zip', 'r') z.extractall() z.close() zipfile 压缩解压
import tarfile # 压缩 tar = tarfile.open('your.tar','w') tar.add('/Users/wupeiqi/PycharmProjects/bbs2.zip', arcname='bbs2.zip') tar.add('/Users/wupeiqi/PycharmProjects/cmdb.zip', arcname='cmdb.zip') tar.close() # 解压 tar = tarfile.open('your.tar','r') tar.extractall() # 可设置解压地址 tar.close()
六, ConfigParser
用于生成和修改常见配置文档,当前模块的名称在 python 3.x 版本中变更为 configparser。 来看一个好多软件的常见文档格式如下 [DEFAULT] ServerAliveInterval = 45 Compression = yes CompressionLevel = 9 ForwardX11 = yes [bitbucket.org] User = hg [topsecret.server.com] Port = 50022 ForwardX11 = no
用python生成这样一个文档
import configparser config = configparser.ConfigParser() config["DEFAULT"] = {'ServerAliveInterval': '45', 'Compression': 'yes', 'CompressionLevel': '9'} config['bitbucket.org'] = {} config['bitbucket.org']['User'] = 'hg' config['topsecret.server.com'] = {} topsecret = config['topsecret.server.com'] topsecret['Host Port'] = '50022' # mutates the parser topsecret['ForwardX11'] = 'no' # same here config['DEFAULT']['ForwardX11'] = 'yes' with open('example.ini', 'w') as configfile: config.write(configfile)
读文件
>>> import configparser >>> config = configparser.ConfigParser() >>> config.sections() [] >>> config.read('example.ini') ['example.ini'] >>> config.sections() ['bitbucket.org', 'topsecret.server.com'] >>> 'bitbucket.org' in config True >>> 'bytebong.com' in config False >>> config['bitbucket.org']['User'] 'hg' >>> config['DEFAULT']['Compression'] 'yes' >>> topsecret = config['topsecret.server.com'] >>> topsecret['ForwardX11'] 'no' >>> topsecret['Port'] '50022' >>> for key in config['bitbucket.org']: print(key) ... user compressionlevel serveraliveinterval compression forwardx11 >>> config['bitbucket.org']['ForwardX11'] 'yes'
增删改查
[section1] k1 = v1 k2:v2 [section2] k1 = v1 import ConfigParser config = ConfigParser.ConfigParser() config.read('i.cfg') # ########## 读 ########## #secs = config.sections() #print secs #options = config.options('group2') #print options #item_list = config.items('group2') #print item_list #val = config.get('group1','key') #val = config.getint('group1','key') # ########## 改写 ########## #sec = config.remove_section('group1') #config.write(open('i.cfg', "w")) #sec = config.has_section('wupeiqi') #sec = config.add_section('wupeiqi') #config.write(open('i.cfg', "w")) #config.set('group2','k1',11111) #config.write(open('i.cfg', "w")) #config.remove_option('group2','age') #config.write(open('i.cfg', "w"))
七,hashlib
用于加密相关的操作,3.x里代替了md5模块和sha模块,主要提供 SHA1, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512 ,MD5 算法
import hashlib m = hashlib.md5() m.update(b"Hello") m.update(b"It's me") print(m.digest()) m.update(b"It's been a long time since last time we ...") print(m.digest()) #2进制格式hash print(len(m.hexdigest())) #16进制格式hash ''' def digest(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the digest value as a string of binary data. """ pass def hexdigest(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the digest value as a string of hexadecimal digits. """ pass ''' import hashlib # ######## md5 ######## hash = hashlib.md5() hash.update('admin') print(hash.hexdigest()) # ######## sha1 ######## hash = hashlib.sha1() hash.update('admin') print(hash.hexdigest()) # ######## sha256 ######## hash = hashlib.sha256() hash.update('admin') print(hash.hexdigest()) # ######## sha384 ######## hash = hashlib.sha384() hash.update('admin') print(hash.hexdigest()) # ######## sha512 ######## hash = hashlib.sha512() hash.update('admin') print(hash.hexdigest())
八,xml模块
xml格式
<?xml version="1.0"?> <data> <country name="Liechtenstein"> <rank updated="yes">2</rank> <year>2008</year> <gdppc>141100</gdppc> <neighbor name="Austria" direction="E"/> <neighbor name="Switzerland" direction="W"/> </country> <country name="Singapore"> <rank updated="yes">5</rank> <year>2011</year> <gdppc>59900</gdppc> <neighbor name="Malaysia" direction="N"/> </country> <country name="Panama"> <rank updated="yes">69</rank> <year>2011</year> <gdppc>13600</gdppc> <neighbor name="Costa Rica" direction="W"/> <neighbor name="Colombia" direction="E"/> </country> </data>
遍历XML
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET tree = ET.parse("xmltest.xml") root = tree.getroot() print(root.tag) #遍历xml文档 for child in root: print(child.tag, child.attrib) for i in child: print(i.tag,i.text) #只遍历year 节点 for node in root.iter('year'): print(node.tag,node.text)
修改和删除xml文档内容
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET tree = ET.parse("xmltest.xml") root = tree.getroot() #修改 for node in root.iter('year'): new_year = int(node.text) + 1 node.text = str(new_year) node.set("updated","yes") tree.write("xmltest.xml") #删除node for country in root.findall('country'): rank = int(country.find('rank').text) if rank > 50: root.remove(country) tree.write('output.xml')
自己创建xml
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET new_xml = ET.Element("namelist") name = ET.SubElement(new_xml,"name",attrib={"enrolled":"yes"}) age = ET.SubElement(name,"age",attrib={"checked":"no"}) sex = ET.SubElement(name,"sex") sex.text = '33' name2 = ET.SubElement(new_xml,"name",attrib={"enrolled":"no"}) age = ET.SubElement(name2,"age") age.text = '19' et = ET.ElementTree(new_xml) #生成文档对象 et.write("test.xml", encoding="utf-8",xml_declaration=True) ET.dump(new_xml) #打印生成的格式
九,shelve
shelve模块是一个简单的k,v将内存数据通过文件持久化的模块,可以持久化任何pickle可支持的python数据格式
import shelve d = shelve.open('shelve_test') #打开一个文件 class Test(object): def __init__(self,n): self.n = n t = Test(123) t2 = Test(123334) name = ["alex","rain","test"] d["test"] = name #持久化列表 d["t1"] = t #持久化类 d["t2"] = t2 d.close()
十,正则表达式
常用正则表达式符号
'.' 默认匹配除\n之外的任意一个字符,若指定flag DOTALL,则匹配任意字符,包括换行 '^' 匹配字符开头,若指定flags MULTILINE,这种也可以匹配上(r"^a","\nabc\neee",flags=re.MULTILINE) '$' 匹配字符结尾,或e.search("foo$","bfoo\nsdfsf",flags=re.MULTILINE).group()也可以 '*' 匹配*号前的字符0次或多次,re.findall("ab*","cabb3abcbbac") 结果为['abb', 'ab', 'a'] '+' 匹配前一个字符1次或多次,re.findall("ab+","ab+cd+abb+bba") 结果['ab', 'abb'] '?' 匹配前一个字符1次或0次 '{m}' 匹配前一个字符m次 '{n,m}' 匹配前一个字符n到m次,re.findall("ab{1,3}","abb abc abbcbbb") 结果'abb', 'ab', 'abb'] '|' 匹配|左或|右的字符,re.search("abc|ABC","ABCBabcCD").group() 结果'ABC' '(...)' 分组匹配,re.search("(abc){2}a(123|456)c", "abcabca456c").group() 结果 abcabca456c '\A' 只从字符开头匹配,re.search("\Aabc","alexabc") 是匹配不到的 '\Z' 匹配字符结尾,同$ '\d' 匹配数字0-9 '\D' 匹配非数字 '\w' 匹配[A-Za-z0-9] '\W' 匹配非[A-Za-z0-9] 's' 匹配空白字符、\t、\n、\r , re.search("\s+","ab\tc1\n3").group() 结果 '\t' '(?P<name>...)' 分组匹配 re.search("(?P<province>[0-9]{4})(?P<city>[0-9]{2})(?P<birthday>[0-9]{4})","371481199306143242").groupdict("city") 结果{'province': '3714', 'city': '81', 'birthday': '1993'}
最常用的匹配语法
re.match 从头开始匹配
re.search 匹配包含
re.findall 把所有匹配到的字符放到以列表中的元素返回
re.splitall 以匹配到的字符当做列表分隔符
re.sub 匹配字符并替换
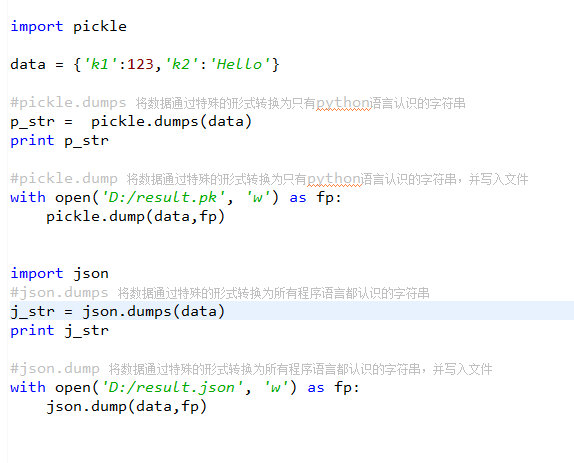
十一,json和pickle
用于序列化的两个模块
- json,用于字符串 和 python数据类型间进行转换(不能序列化函数)
- pickle,用于python特有的类型 和 python的数据类型间进行转换
Json模块提供了四个功能:dumps、dump、loads、load
pickle模块提供了四个功能:dumps、dump、loads、load
序列化
import json data = {"k1":123,"k2":234} f= open("test.text","w") f.write(json.dumps(data))
反序列化
import json f = open("test.text",'r') data = json.loads(f.read()) print(type(data))